Abstract
The pathogenic protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica, the cause of amebic dysentery and amebic liver abscess, is an obligate anaerobe, and derives energy from the fermentation of glucose to ethanol with pyruvate and acetyl coenzyme A as intermediates. We have isolated EhADH2, a key enzyme in this pathway, that is a NAD+- and Fe2+-dependent bifunctional enzyme with acetaldehyde dehydrogenase and alcohol dehydrogenase activities. EhADH2 is the only known eukaryotic member of a newly defined family of prokaryotic multifunctional enzymes, which includes the Escherichia coli AdhE enzyme, an enzyme required for anaerobic growth of E. coli. Because of the critical role of EhADH2 in the amebic fermentation pathway and the lack of known eukaryotic homologues of the EhADH2 enzyme, EhADH2 represents a potential target for antiamebic chemotherapy. However, screening of compounds for antiamebic activity is hampered by the cost of large scale growth of Ent. histolytica, and difficulties in quantitating drug efficacy in vitro. To approach this problem, we expressed the EhADH2 gene in a mutant strain of E. coli carrying a deletion of the adhE gene. Expression of EhADH2 restored the ability of the mutant E. coli strain to grow under anaerobic conditions. By screening compounds for the ability to inhibit the anaerobic growth of the E. coli/EhADH2 strain, we have developed a rapid assay for identifying compounds with anti-EhADH2 activity. Using bacteria to bypass the need for parasite culture in the initial screening process for anti-parasitic agents could greatly simplify and reduce the cost of identifying new therapeutic agents effective against parasitic diseases.
Full text
PDF


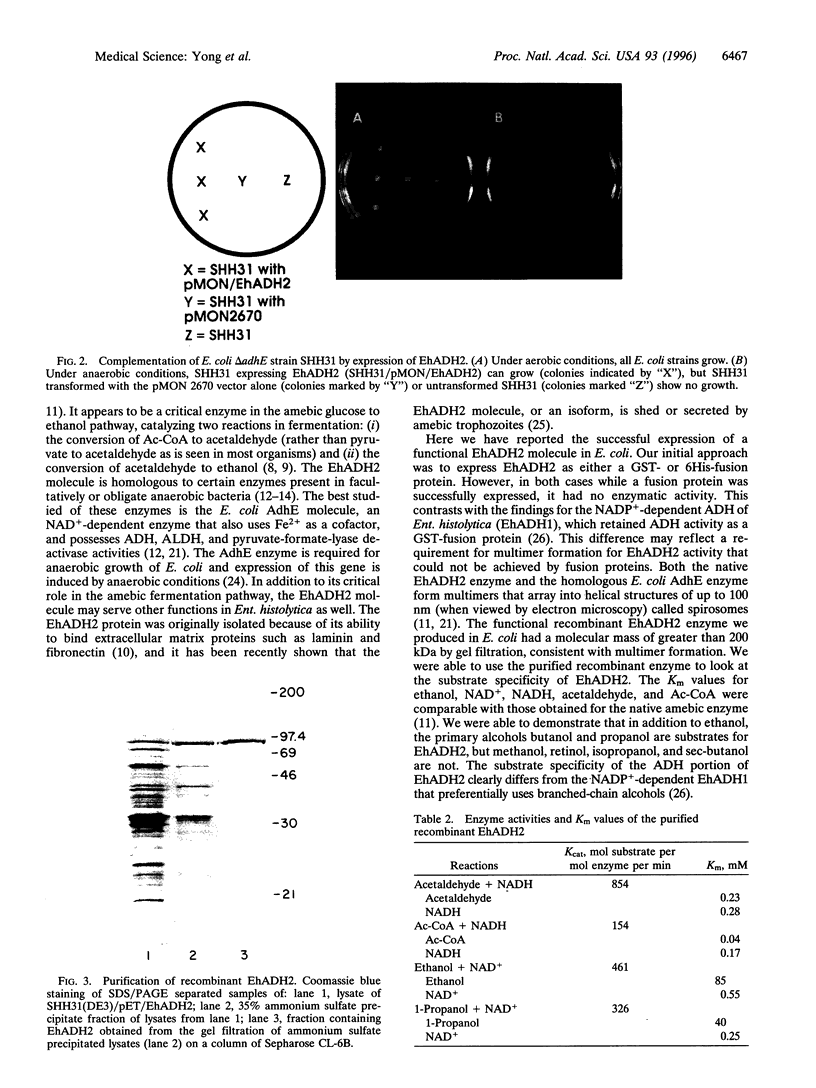
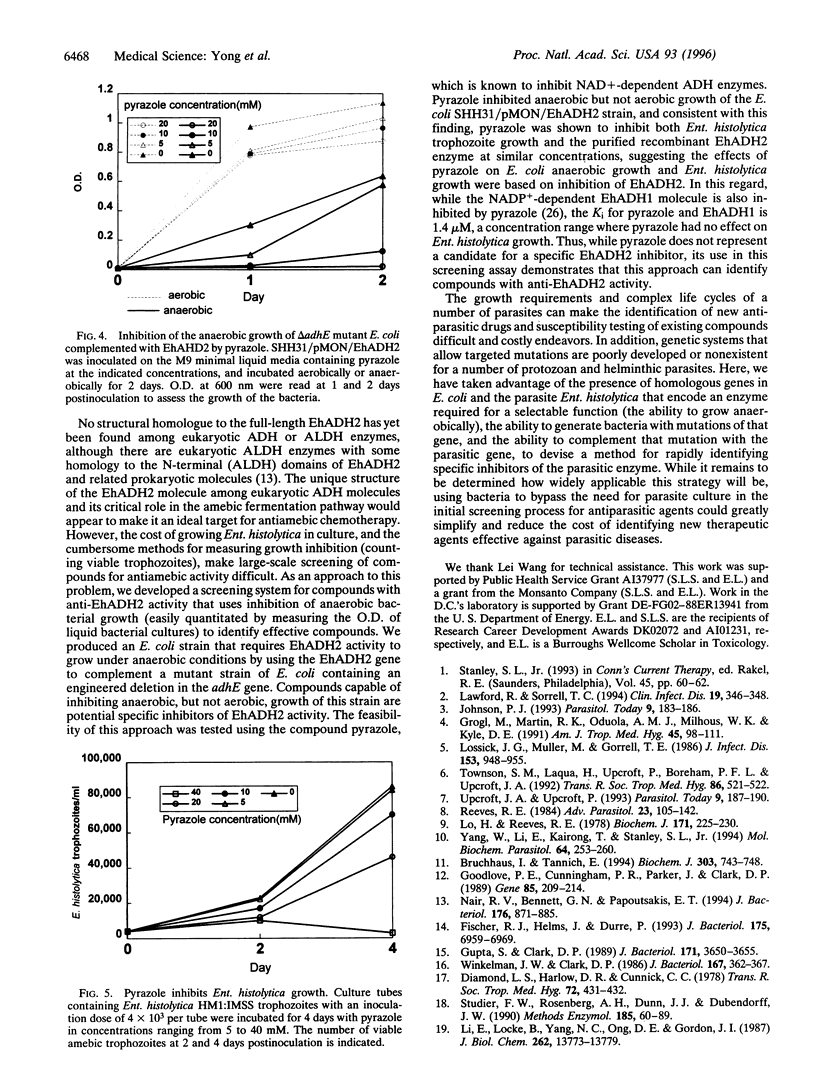

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bruchhaus I., Tannich E. Purification and molecular characterization of the NAD(+)-dependent acetaldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase from Entamoeba histolytica. Biochem J. 1994 Nov 1;303(Pt 3):743–748. doi: 10.1042/bj3030743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer R. J., Helms J., Dürre P. Cloning, sequencing, and molecular analysis of the sol operon of Clostridium acetobutylicum, a chromosomal locus involved in solventogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1993 Nov;175(21):6959–6969. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.21.6959-6969.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores B. M., Stanley S. L., Jr, Yong T. S., Ali M., Yang W., Diedrich D. L., Torian B. E. Surface localization, regulation, and biologic properties of the 96-kDa alcohol/aldehyde dehydrogenase (EhADH2) of pathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. J Infect Dis. 1996 Jan;173(1):226–231. doi: 10.1093/infdis/173.1.226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodlove P. E., Cunningham P. R., Parker J., Clark D. P. Cloning and sequence analysis of the fermentative alcohol-dehydrogenase-encoding gene of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90483-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogl M., Martin R. K., Oduola A. M., Milhous W. K., Kyle D. E. Characteristics of multidrug resistance in Plasmodium and Leishmania: detection of P-glycoprotein-like components. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Jul;45(1):98–111. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1991.45.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90534-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Clark D. P. Escherichia coli derivatives lacking both alcohol dehydrogenase and phosphotransacetylase grow anaerobically by lactate fermentation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):3650–3655. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.3650-3655.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. J. Metronidazole and drug resistance. Parasitol Today. 1993 May;9(5):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(93)90143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler D., Leibrecht I., Knappe J. Pyruvate-formate-lyase-deactivase and acetyl-CoA reductase activities of Escherichia coli reside on a polymeric protein particle encoded by adhE. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):59–63. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80358-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Shen P. S., Descoteaux S., Pohl J., Bailey G., Samuelson J. Cloning and expression of an NADP(+)-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase gene of Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10188–10192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawford R., Sorrell T. C. Amebic abscess of the spleen complicated by metronidazole-induced neurotoxicity: case report. Clin Infect Dis. 1994 Aug;19(2):346–348. doi: 10.1093/clinids/19.2.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonardo M. R., Cunningham P. R., Clark D. P. Anaerobic regulation of the adhE gene, encoding the fermentative alcohol dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):870–878. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.870-878.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li E., Locke B., Yang N. C., Ong D. E., Gordon J. I. Characterization of rat cellular retinol-binding protein II expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 5;262(28):13773–13779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li T. K., Theorell H. Human liver alcohol dehydrogenase: inhibition by pyrazole and pyrazole analogs. Acta Chem Scand. 1969;23(3):892–902. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.23-0892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo H. S., Reeves R. E. Pyruvate-to-ethanol pathway in Entamoeba histolytica. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 1;171(1):225–230. doi: 10.1042/bj1710225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lossick J. G., Müller M., Gorrell T. E. In vitro drug susceptibility and doses of metronidazole required for cure in cases of refractory vaginal trichomoniasis. J Infect Dis. 1986 May;153(5):948–955. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.5.948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair R. V., Bennett G. N., Papoutsakis E. T. Molecular characterization of an aldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase gene from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. J Bacteriol. 1994 Feb;176(3):871–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.3.871-885.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. E. Metabolism of Entamoeba histolytica Schaudinn, 1903. Adv Parasitol. 1984;23:105–142. doi: 10.1016/s0065-308x(08)60286-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley S. L., Jr, Becker A., Kunz-Jenkins C., Foster L., Li E. Cloning and expression of a membrane antigen of Entamoeba histolytica possessing multiple tandem repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):4976–4980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.4976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townson S. M., Laqua H., Upcroft P., Boreham P. F., Upcroft J. A. Induction of metronidazole and furazolidone resistance in Giardia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Sep-Oct;86(5):521–522. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(92)90095-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upcroft J. A., Upcroft P. Drug resistance and Giardia. Parasitol Today. 1993 May;9(5):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(93)90144-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelman J. W., Clark D. P. Anaerobically induced genes of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):362–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.362-367.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W., Li E., Kairong T., Stanley S. L., Jr Entamoeba histolytica has an alcohol dehydrogenase homologous to the multifunctional adhE gene product of Escherichia coli. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1994 Apr;64(2):253–260. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(93)00020-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]