Abstract
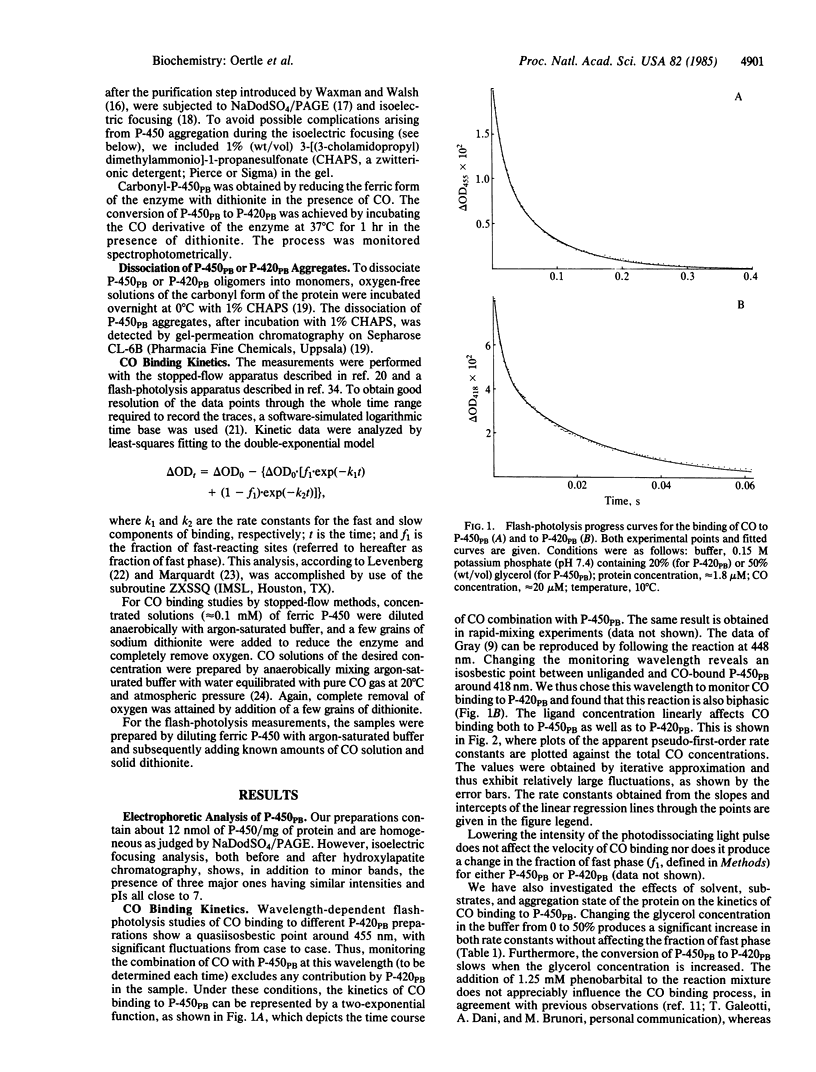
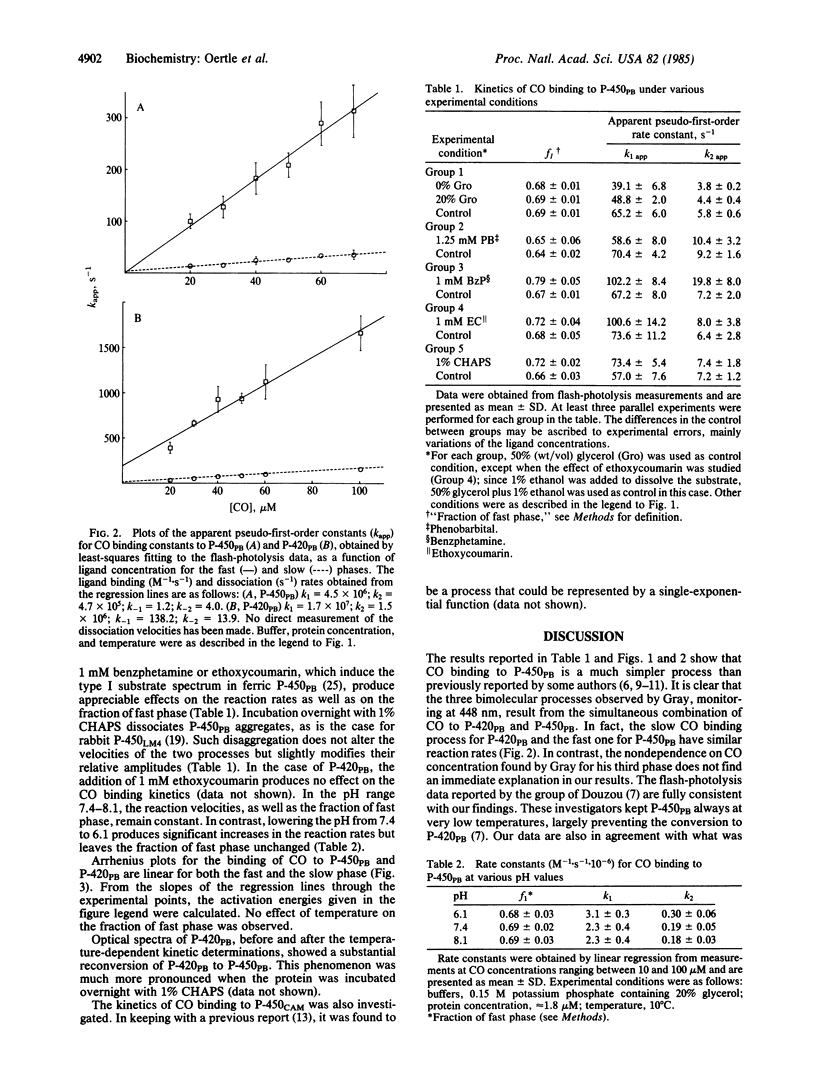
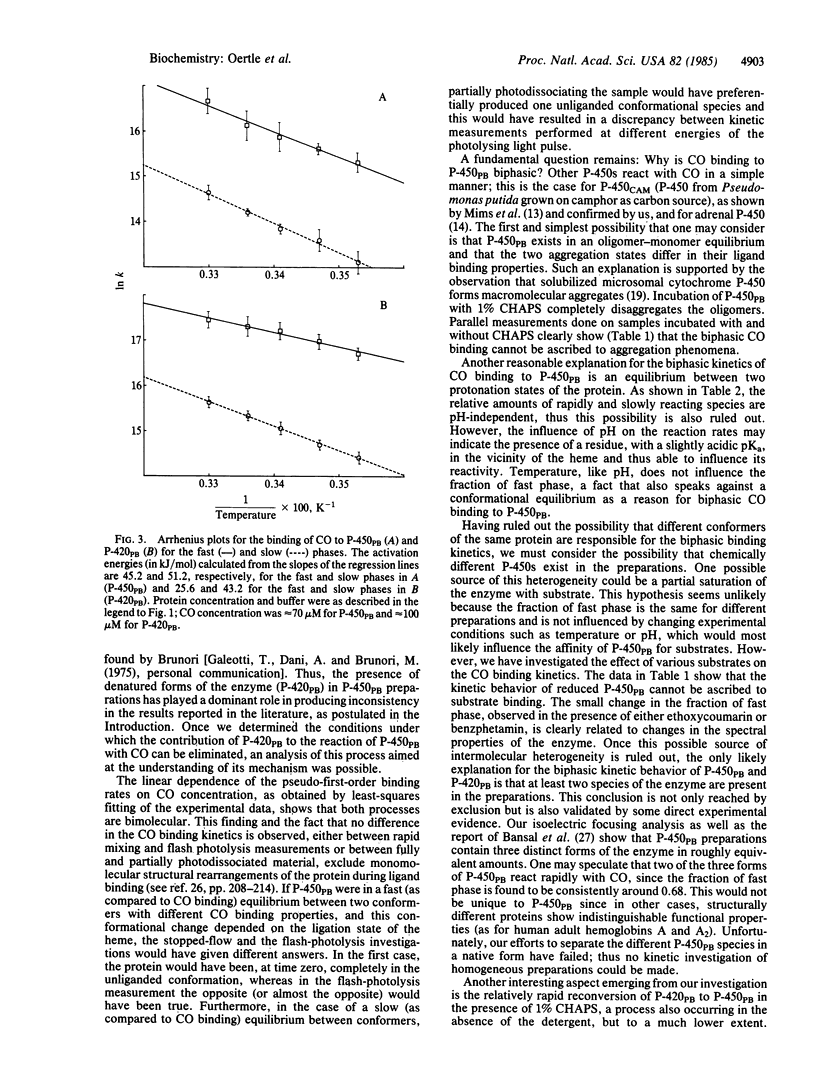
The kinetics of carbon monoxide binding to phenobarbital-induced cytochrome P-450 (P-450PB) and to its enzymatically inactive form P-420PB have been investigated by both stopped-flow and flash-photolysis spectrophotometry. When the simultaneous presence of both forms of the enzyme is taken into account, the binding of CO to these two proteins can be described in terms of two bimolecular processes with rate constants of 4.5 X 10(6) M-1.S-1 and 4.7 X 10(5) M-1.S-1 for P-450PB and 1.7 X 10(7) M-1.S-1 and 1.5 X 10(6) M-1.S-1 for P-420PB. From kinetic studies of the binding of CO to P-450PB under different experimental conditions, investigations of the homogeneity of our P-450PB preparations, and comparative kinetic investigations of P-450s from different sources, we conclude that CO binding to reduced P-450PB is a simple bimolecular process and that the observed biphasic traces are due to heterogeneity of the proteins. This conclusion is in contrast with previous reports of complex reaction mechanisms for the binding of CO to P-450PB. Optical spectroscopy studies indicate the existence of an equilibrium between P-450PB and P-420PB, at least for the reduced carbonyl derivatives of the enzymes. The interconversion is strongly influenced by the aggregation state of the protein. Large differences between the CO binding properties of P-450PB and those of P-420PB are found. These are discussed in terms of possible effects of the proximal ligation state of the iron on heme reactivity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bansal S. K., Love J., Gurtoo H. L. High pressure liquid chromatographic separation of multiple forms of cytochrome P-450. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 30;117(1):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91570-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. K., Dolphin D. Carbon monoxide binding to pentacoordinate mercaptide-heme complexes: kinetic study on models for cytochrome P-450. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3338–3342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davydov D. R., Kurganov B. I. Sravnitel'noe issledovanie kinetiki reaktsii vosstanovleniia tsitokhroma P-450 NADPH-tsitokhrom-P-450-reduktazoi i ditionitom. Biokhimiia. 1982 Sep;47(9):1476–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debey P., Balny C., Douzou P. Low temperature studies of microsomal cytochrome P450 flash photolysis experiments. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 1;35(1):86–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debey P., Douzou P. Photodissociation of Fe2+-CO by continuous irradiation. FEBS Lett. 1974 Mar 1;39(3):271–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debey P., Hui-Bon-Hoa G., Douzou P. Low temperature studies of microsomal cytochrome P450. I. Stopped-flow experiments. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 1;32(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80838-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desideri A., Meier U. T., Winterhalter K. H., Di Iorio E. E. Electron paramagnetic resonance properties of liver fluke (Dicrocoelium dendriticum) nitrosyl hemoglobin. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 30;166(2):378–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80116-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Iorio E. E., Meier U. T., Smit J. D., Winterhalter K. H. Kinetics of oxygen and carbon monoxide binding to liver fluke (Dicrocoelium dendriticum) hemoglobin. An extreme case? J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2160–2164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Iorio E. E. Preparation of derivatives of ferrous and ferric hemoglobin. Methods Enzymol. 1981;76:57–72. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)76114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dlott D. D., Frauenfelder H., Langer P., Roder H., DiIorio E. E. Nanosecond flash photolysis study of carbon monoxide binding to the beta chain of hemoglobin Zürich [beta 63(E7)His leads to Arg]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6239–6243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doster W., Beece D., Bowne S. F., DiIorio E. E., Eisenstein L., Frauenfelder H., Reinisch L., Shyamsunder E., Winterhalter K. H., Yue K. T. Control and pH dependence of ligand binding to heme proteins. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):4831–4839. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R. D. Kinetics and mechanism of CO binding to cytochromes P-450LM2 and P-450LM4. Effect of phospholipid, nonionic detergent, and substrate binding. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3764–3768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R. D. Kinetics and mechanism of carbon monoxide binding to purified liver microsomal cytochrome P-450 isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):1086–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R. D. Kinetics of CO binding to and dissociation from microsomal cytochrome P-450 induced by phenobarbital in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4364–4369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gut J., Richter C., Cherry R. J., Winterhalter K. H., Kawato S. Rotation of cytochrome P-450. II. Specific interactions of cytochrome P-450 with NADPH-cytochrome P-450 reductase in phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7030–7036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz B. C., Richter C. Chemical modification of microsomal cytochrome P450: role of lysyl residues in hydroxylation activity. FEBS Lett. 1983 Sep 19;161(2):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims M. P., Porras A. G., Olson J. S., Noble R. W., Peterson J. A. Ligand binding to heme proteins. An evaluation of distal effects. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14219–14232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oertle M., Winterhalter K. H., Di Iorio E. E. Kinetic properties of cobalt--iron hybrid hemoglobins. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 7;153(1):213–216. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oprian D. D., Gorsky L. D., Coon M. J. Properties of the oxygenated form of liver microsomal cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8684–8691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rösen P., Stier A. Kinetics of CO and O 2 complexes of rabbit liver microsomal cytochrome P 450 . Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 2;51(3):603–611. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuckey R. C., Kamin H. Kinetics of O2 and CO Binding to adrenal cytochrome P-450scc. Effect of cholesterol, intermediates, and phosphatidylcholine vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4232–4237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlasuk G. P., Walz F. G., Jr Liver endoplasmic reticulum polypeptides resolved by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jun;105(1):112–120. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90431-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman D. J., Walsh C. Phenobarbital-induced rat liver cytochrome P-450. Purification and characterization of two closely related isozymic forms. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10446–10457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. E., Coon M. J. Oxygen activation by cytochrome P-450. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:315–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


