A forward genetic screen in Drosophila looking for Notch signaling regulators identifies Tempura, a new and non-redundant protein prenyltransferase of Rab proteins.
Abstract
Vesicular trafficking plays a key role in tuning the activity of Notch signaling. Here, we describe a novel and conserved Rab geranylgeranyltransferase (RabGGT)-α–like subunit that is required for Notch signaling-mediated lateral inhibition and cell fate determination of external sensory organs. This protein is encoded by tempura, and its loss affects the secretion of Scabrous and Delta, two proteins required for proper Notch signaling. We show that Tempura forms a heretofore uncharacterized RabGGT complex that geranylgeranylates Rab1 and Rab11. This geranylgeranylation is required for their proper subcellular localization. A partial dysfunction of Rab1 affects Scabrous and Delta in the secretory pathway. In addition, a partial loss Rab11 affects trafficking of Delta. In summary, Tempura functions as a new geranylgeranyltransferase that regulates the subcellular localization of Rab1 and Rab11, which in turn regulate trafficking of Scabrous and Delta, thereby affecting Notch signaling.
Author Summary
Notch signaling is an evolutionarily conserved signaling pathway that regulates many developmental processes. Abnormal Notch signaling activity can lead to numerous diseases and developmental defects. To better understand the regulation of this pathway, we performed a forward genetic screen for Notch signaling components that have not been previously identified in Drosophila. Here, we report the identification of an evolutionarily conserved protein, Tempura, which is required for Notch signaling-mediated lateral inhibition and cell fate determination of external sensory organs. We show that loss of tempura leads to mistrafficking of Delta and Scabrous, two important Notch signaling components. In addition, Rab1 and Rab11, two major coordinators of vesicular trafficking, are mislocalizaed in tempura mutants. We further show that Tempura functions as a subunit of a previously uncharacterized lipid modification complex to geranylgeranylate (a type of prenylation) Rab1 and Rab11. This post-translational modification is shown to be required for the proper subcellular localization and function of these Rabs. We find that dysfunction of Rab1 causes an accumulation of Delta and Scabrous in the secretory pathway and dysfunction of Rab11 further interferes with the trafficking of Delta. In addition to the known Rab geranylgeranyltransferse, our data indicate the presence of another functionally nonredundant Rab geranylgeranyltransferse, Tempura.
Introduction
Notch signaling is an evolutionarily conserved pathway that plays a pivotal role in many developmental processes, including lateral inhibition, binary cell fate determination, and boundary formation [1],[2]. Aberrant Notch signaling is implicated in diseases such as Alagille syndrome, spondylocostal dysostosis (SCD), cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL), and numerous types of cancer [3],[4]. Notch signaling depends on the direct contact between cells: the membrane-bound ligand, Delta (Dl) or Serrate, activates Notch on neighboring cells, resulting in proteolytic cleavages of Notch to generate a Notch intracellular domain (NICD) that activates the transcription of target genes [5].
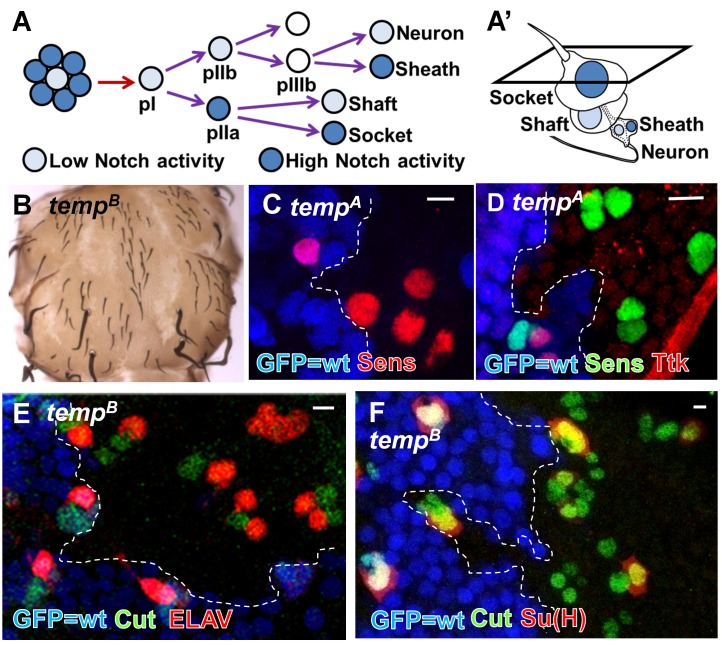
The developing adult external sensory organs (ESOs) on the Drosophila notum serves as a model system to study lateral inhibition and cell fate determination [6] and have led to the isolation of some Notch signaling components in forward genetic screens [7]–[10]. An ESO consists of four cells—shaft, socket, sheath, and neuron—which are derived from a single mother cell, the sensory organ precursor (SOP or pI) (Figure 1A and 1A′). Lateral inhibition ensures that only one SOP is selected from a proneural cluster. SOPs undergo several rounds of asymmetric cell division to generate four different cells and Notch signaling activity determines cell fates in each division (Figure 1A and 1A′). Loss of Notch signaling during lateral inhibition results in a higher density of ESOs, whereas its loss during cell fate determination causes ESO cells to take on neuronal fates, resulting in adult notum balding [11].
Figure 1. temp is essential for proper Notch signaling activity during ESO development.
(A–A′) An ESO of Drosophila consists of four cells: shaft, socket, sheath, and neuron. During lateral inhibition, Notch ensures that only one SOP is selected from a proneural cluster. Subsequently, asymmetric Notch signaling activity also determines cell fates of the four descendants of the SOP. (B) temp mutant clones exhibit balding on an adult notum, a typical loss-of-Notch signaling phenotype. (C) At 12 h APF, the density of SOP (marked by Sens) is higher in temp mutant clones (GFP-negative), indicating a lateral inhibition defect. (D) At 19 h APF, Ttk, a Notch signaling effector strongly up-regulated in the pIIa cell, is lost in temp mutant sensory organs, indicating a loss of Notch signaling activity at this stage. (E) At 27 h APF, the presence of multiple neurons (marked by ELAV staining) per sensory cluster (marked by Cut staining) indicates that cell fate specification is impaired. (F) Su(H)-positive socket cells are lost in many mutant sensory organs, further indicating defects in cell fate decisions. Scale bars, 5 µm.
Notch signaling activity can be altered by defects in vesicular trafficking [12], coordinated by specific Rabs and their effectors. Rabs are small GTPases belonging to the Ras superfamily of small G proteins, which can switch between GDP-bound inactive and GTP-bound active forms [13]–[15]. Newly synthesized Rabs are prenylated with geranylgeranyl groups on C-terminal cysteines by a protein prenyltransferase (PPT) complex, a process required for their proper membrane localization and hence function [16]–[20]. PPTs are composed of αβ heterodimers and they add prenyl lipids (15-carbon farnesyl or 20-carbon geranylgeranyl groups) to cysteine residues located close to the C-termini of their substrates. Three PPTs have been identified so far: farnesyltransferase (FT), geranylgeranyltransferase I (GGTI), and the Rab geranylgeranyl-transferase [RabGGT, also known as geranylgeranyltransferase II (GGTII)] (Figure S1) [21],[22].
Here, we describe the isolation of mutations in a novel PPT α subunit repeat (PPTA) motif containing protein from an unbiased forward mosaic genetic screen for essential genes that affect Notch signaling. Due to its role in adding lipids to its substrates, we name this gene “tempura” (temp), based on a Japanese deep-fried dish. Our data show that Temp forms a new PPT to modify a small subset of Rabs, including Rab1, which has not previously been implicated in Notch signaling, and Rab11. Loss of temp leads to aberrant subcellular distribution of Rab1 and Rab11, which in turn leads to Notch signaling defects. In summary, we describe the function of a previously unidentified PPT, provide the first link between Rab1 and Notch signaling, and show that some Rabs are modified by two nonredundant PPTs. These data imply a complex regulation of Rabs by different PPTs that was not previously appreciated.
Results
temp Is Required for Notch Signaling Activity During ESO Development
To identify novel modulators of Notch signaling, we performed a forward genetic screen on the Drosophila X chromosome using ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) [23]. We induced homozygous mutant clones of essential genes in the notum of otherwise heterozygous mutant animals with the FLP/FRT system [24], and screened for adult notum balding. We identified a novel complementation group named temp, consisting of seven alleles that exhibit a strong balding phenotype (Figure 1B).
To characterize the ESO development defects in temp mutant clones, we examined lateral inhibition and cell fate determination at different pupal stages. At 12 h after puparium formation (APF), the density of SOPs [marked by Senseless (Sens)] [25] is higher in temp mutant clones than in neighboring wild-type (wt) tissue, indicating a lateral inhibition defect (Figure 1C). To determine if cell fate specification is impaired, we assessed the expression of Tramtrack (Ttk), a downstream effector of Notch that is up-regulated in the signal-receiving pIIa cell but not in the signal-sending pIIb cell at 19 h AFP [26],[27]. We observed a loss of Ttk in temp mutant pIIa, indicating a loss of Notch signaling during cell fate determination at the two-cell stage (Figure 1D). At 27 h APF, when the four cells comprising an ESO are specified, many temp mutant ESOs contain multiple neurons (marked by the neuronal marker Embryonic Lethal Abnormal Vision, ELAV, [28] and lack socket cells, marked by Suppressor of Hairless, Su(H)) [29], indicating an alteration in cell fate (Figure 1A and 1E–F). This phenotype is not fully penetrant as 63% of the tempB mutant ESO cells are ELAV-positive, similar to what we observed previously for dEHBP1 and sec15 [8],[9], two players that affect vesicle trafficking and Notch signaling during ESO development. Although we observe some minor apoptosis in some tempA mutant clones (a strong allele; Figure S2A), there is no obvious apoptosis in tempB mutant clones (a less strong allele; Figure S2B). Overexpression of the antiapoptotic protein p35 in tempA mutant clones (Figure S2C) does not alter the phenotype (Figure S2D) when compared to temp mutant clones without p35 expression. In addition, there is no decrease in the number of sensory progenitor cells (marked by either Sens or Cut) (Figure 1C–F). These data indicate that lateral inhibition and cell fate transformation are due to loss-of-Notch signaling. Hence, temp is necessary for proper Notch signaling during the development of ESO lineage.
temp Encodes a Protein with a PPTA Motif
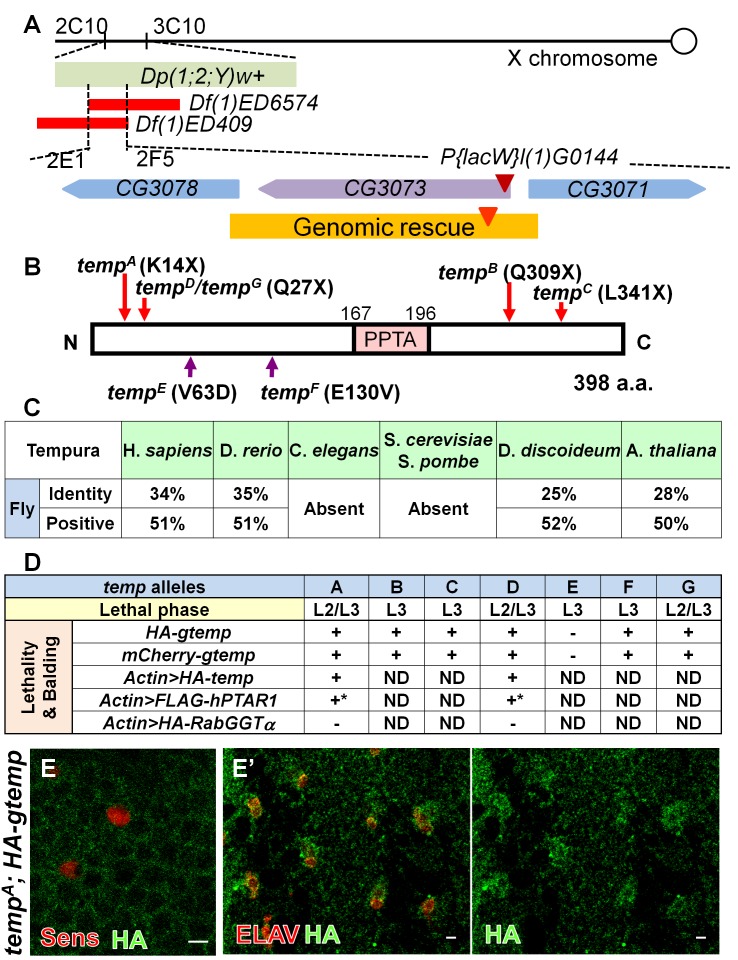
Through duplication mapping [30], deficiency mapping [31], and complementation tests with existing lethal P element insertion lines [32], we mapped temp to CG3073 (Figure 2A). This gene encodes a 398 amino acid (a.a.) protein containing a single small 29 a.a. PPTA motif which has only been found to be present in the α subunit of PPTs (Figure 2B). temp is evolutionarily conserved in most but not all species queried (Figure 2C), implicating that the function of the temp homolog might be assumed by another protein in species lacking this gene. The vertebrate homolog of temp is named PPTA containing protein 1 (PTAR1), but its biochemical or in vivo function has not yet been characterized.
Figure 2. temp encodes a conserved PPTA motif-containing protein.
(A) The lethality and phenotype of temp mutant is rescued by Dp(1;2;Y)w+ (cytological regions 2C10–3C10) and fails to be complemented by Df(1)ED6574 and Df(1)ED409 narrowing the candidate region to 2E1 and 2F5. P{lacW}l(1)G0144 [72], a P-element insertion (maroon triangle) in CG3073, fails to complement all temp alleles. The orange region indicates the extent of the genomic rescue constructs tagged with mCherry- or HA-tag (red triangle). (B) After sequencing the genomic region to which the temp alleles are mapped, we identified both nonsense mutations (tempA, tempB, tempC, tempD, and tempG) and missense mutations (tempE and tempF) within CG3073. This gene encodes a 398 a.a. protein containing a conserved PPTA subunit repeat motif (shown in pink). (C) temp homologs are conserved in many species queried. The percentage in the table is obtained via bl2seq. (D) Both lethality and balding phenotypes in all temp alleles (except for tempE) can be rescued by genomic and cDNA rescue constructs of CG3073. Because the lethality and balding of tempE can be rescued by the duplication, Dp(1;2;Y)w+ (cytological regions 2C10–3C10) but not gtemp, this indicates that tempE carries a second lethal mutation in the 2C10–3C10 interval. Based on lethal phase analysis, the tempA, tempD, and tempG with early nonsense mutations are the most severe alleles. +, rescued; −, not rescued; ND, not determined. *Overexpression of human homolog of temp, hPTAR1, can rescue the balding phenotype in temp mutant clones on the notum, but its ubiquitous overexpression is toxic in flies even in the wt background. (E–E′) HA-tagged genomic temp (HA-gtemp) is expressed very weakly in the cytoplasm on the pupal notum during early ESO development (12 h APF) (E) and becomes slightly enriched in the sensory organs at the later stage (27 h APF) (E′). Scale bars, 5 µm.
The lethality and loss-of-Notch signaling phenotypes of temp are rescued by both genomic and cDNA rescue constructs (Figure 2A and 2D). Moreover, the human PTAR1 cDNA can also rescue the ESO developmental defects in temp mutant clones (Figure 2D). These data indicate that the lethality and balding phenotypes in temp mutants are caused by mutations in CG3073 and that the molecular function of temp is evolutionarily conserved between fly and human. To investigate the endogenous expression pattern of Temp, we attempted to generate several antibodies against Temp, but these were unsuccessful. We therefore examined the expression pattern of Hemagglutinin (HA)-tagged genomic constructs (HA–gtemp) in a tempA homozygous mutant background. We find that Temp is expressed weakly during early ESO development (Figure 2E) and that it is somewhat enriched in the cytoplasm of ESOs at the four-cell stage (Figure 2E′). HA–gtemp is expressed weakly and dispersed throughout the cytoplasm. Similarly, when we overexpress HA–temp cDNA using dpp–Gal4 in the wing disc, HA–Temp is also diffuse in the cytoplasm (Figure S3).
temp Is Required for Scabrous Secretion
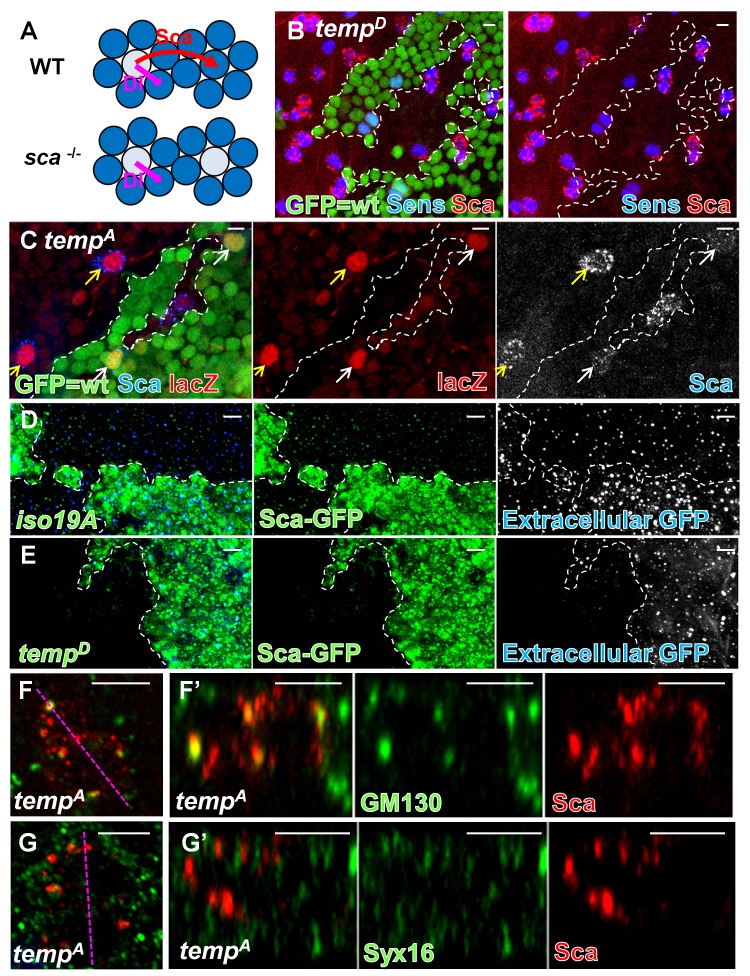
The elevated SOP density in temp mutant clones (Figure 1C) is similar to what has been observed in scabrous (sca) mutants (Figure 3A) [33]. Sca is secreted by the SOP to facilitate Notch signaling in nearby cells to promote lateral inhibition [33]–[36]. It is rapidly secreted and degraded upon synthesis [37] and therefore is very difficult to detect in wt tissue on the notum (Figure 3B; GFP-positive cells). Interestingly, Sca is strongly up-regulated in temp mutant ESOs (Figure 3B; GFP-negative cells). A similar elevation of Sca in sensory organs is also observed in developing wing and eye imaginal discs (Figure S4A–B′), indicating that this elevation is not limited to the notum. Given that the lateral inhibition defect in temp mutant clones is similar to that of loss-of-function of sca, we hypothesized that Sca is produced, but that it fails to be secreted, and hence accumulates in temp mutant ESOs. To test this idea, we first determined whether the up-regulation of Sca in temp mutant is transcriptional or posttranscriptional. The expression of the sca–lacZ reporter [36],[38], a readout for sca transcription, is similar between temp mutant and wt ESO (Figures 3C and S4C–D), indicating that the level of Sca in temp mutant ESOs is posttranscriptionally up-regulated. To determine if Sca secretion is impaired, we developed a secretion assay by overexpressing a Sca–GFP fusion protein [39] in wt and temp mutant clones using the mosaic analysis with a repressible cell marker (MARCM) [40]. Sca–GFP can be secreted from wt clones into the neighboring area that does not produce Sca–GFP (Figure 3D). However, Sca–GFP produced in temp mutant clones fails to be secreted into the neighboring area (Figure 3E), indicating defective Sca secretion.
Figure 3. temp is required for Sca secretion in ESO in early secretory pathway.
(A) Sca is secreted by SOPs to facilitate Notch signaling in nearby cells, preventing them from adopting SOP fates. sca mutants exhibit mild lateral inhibition defects similar to that of temp mutants. (B) The expression level of Sca is elevated in temp mutant ESOs (marked by Sens). (C) The expression level of sca–lacZ, as a readout for the transcription level of Sca, is similar between mutant (yellow arrows) and wt (white arrows) SOPs, indicating that an elevated level of Sca in temp mutant clones results from posttranscriptional up-regulation (the mutant SOPs in the middle small clone are out-of-plane). (D–E) Sca secretion assay: Sca–GFP fusion protein is expressed in either control or temp mutant clones (marked by strong GFP staining) using the MARCM strategy. The extracellular dots shown in the images are the extracellular staining for Sca–GFP, as they are secreted by the expressing cells and diffuses into the neighboring nonexpressing region. (D) Sca–GFP expressed in the wt (y w FRT19Aiso) clone can be secreted to the neighboring region. (E) Sca–GFP expressed in temp mutant clones is absent in the neighboring wt region, indicating a secretion defect in temp mutant clones. (F–G′) Colocalization of Sca and Golgi markers. Each image is a projection of three optical slices. (F) Intracellular Sca puncta largely colocalize with GM130, a marker predominantly localized to the cis-Golgi, in temp mutant ESO. (F′) z axis view of (F). (G) Sca puncta do not colocalize with Syx16, a trans-Golgi marker, in temp mutant ESO. (G′) z axis view of (G). Scale bars, 5 µm.
To determine where Sca accumulates intracellularly, we performed coimmunostaining of Sca and an array of subcellular organelle markers (Table S1). The Sca-positive puncta mainly colocalize with GM130 [41], a cis-Golgi marker, but not with Syntaxin 16 (Syx16) [42], a trans-Golgi marker (Figure 3F–G′). Therefore, in temp mutant cells, Sca accumulates in a GM130-positive compartment and cannot be secreted, which in turn contributes to the defect in Notch-signaling–mediated lateral inhibition.
temp Is Required for Proper Localization of dEHBP1 and Dl
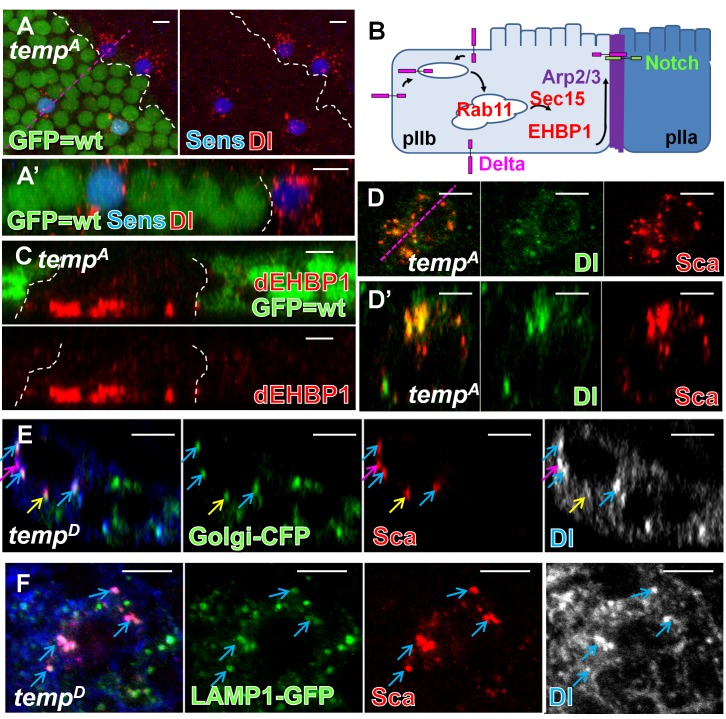
Since Sca is primarily involved in the lateral inhibition process, other proteins are likely to contribute to the cell fate specification defect in temp mutant clones (Figure 1E and 1F). Cell fate determinants, including the adaptor protein Numb [26],[43] and the E3 ligase Neuralized [44]–[46], are asymmetrically segregated during the division of the pI cell to bias Notch signaling between the pIIa and pIIb. We did not observe obvious defects in the localization of either protein, suggesting that asymmetric segregation of cell fate determinants is not affected (not shown). Although the expression and localization of Notch is not affected (Figure S5A–C), the number of Dl-positive puncta is increased in temp mutant sensory organs (Figure 4A and 4A′). We previously proposed that recycled Dl travels to the apical actin-rich structure (ARS) localized between the pIIa and pIIb at the two-cell stage (Figure 4B) [10]. This process is necessary for proper Notch signaling activation and requires the Arp2/3 complex as well as the vesicle trafficking regulators Sec15 and dEHBP1, two binding partners of Rab11 [8],[9],[47],[48]. Mutations in these genes have been shown to exhibit cell fate defects and notum balding, similar to the loss of temp. While the ARS is properly formed (not shown) and apical-basal polarity is not affected in temp mutant clones (Figure S5E), we found that dEHBP1 accumulates basally (Figure 4C), similar to what is observed in sec15 mutants [8]. In dEHBP1 mutant ESOs, the level of Dl is reduced at the cell surface [8], a feature that we also observe in about half (yellow arrows) of the ESOs in temp mutant clones (Figure S5D). These data indicate that Dl accumulates intracellularly and that the mislocalization of EHBP1 may at least partially contribute to the Dl trafficking defect in temp mutant ESOs. Additionally, we found that many of the Dl and Sca puncta colocalize in temp mutant ESO, indicating that some of them are trapped in the same intracellular compartments (Figure 4D and 4D′). The majority of colocalized proteins are in the Golgi complex (Figure 4E, blue arrows). However, some of the Dl- and Sca-positive puncta colocalize with a late endosomal and lysosomal marker LAMP1–GFP (Figure 4F), suggesting that defects in the secretory pathway may cause some Sca and Dl to be sorted to the endo-lysosomal pathway for degradation. Therefore, mistrafficking of Dl is also likely to contribute to both lateral inhibition and cell fate defects in temp mutants.
Figure 4. temp is required for proper localization of dEHBP1 and Dl during ESO development.
(A) At 16 h APF, more Dl puncta are present in the temp mutant SOPs (marked by Sens) compared to the wt ones. (A′) z axis view of (A). (B) Dl recycling model at two-cell stage: Recycling of Dl in the pIIb is required for proper Notch signaling activity in the pIIa. After endocytosis, Dl is recycled through Rab11–Sec15–dEHBP1-dependent recycling route along the ARS to the apical interface between pIIb and pIIa, where Dl is thought to activate Notch receptor on the pIIa. (C) dEHBP1 accumulates basally in temp mutant clones. (D–D′) Many Dl puncta colocalize with Sca in temp mutant ESO. (D) Single x–y section. (D′) Single z section. (E) Dl and Sca puncta largely colocalize with Golgi–CFP in temp mutant clones with some distribution dynamics (single z section). Blue arrow, colocalized proteins locate to the Golgi–CFP-positive compartments; pink arrow, colocalized proteins not associated with the Golgi complex; yellow arrow, Sca, but not Dl, colocalizes with Golgi–CFP-positive compartments. (F) Some Dl and Sca puncta colocalize with LAMP-1–GFP in temp mutant clones (single z section). Scale bars, 5 µm.
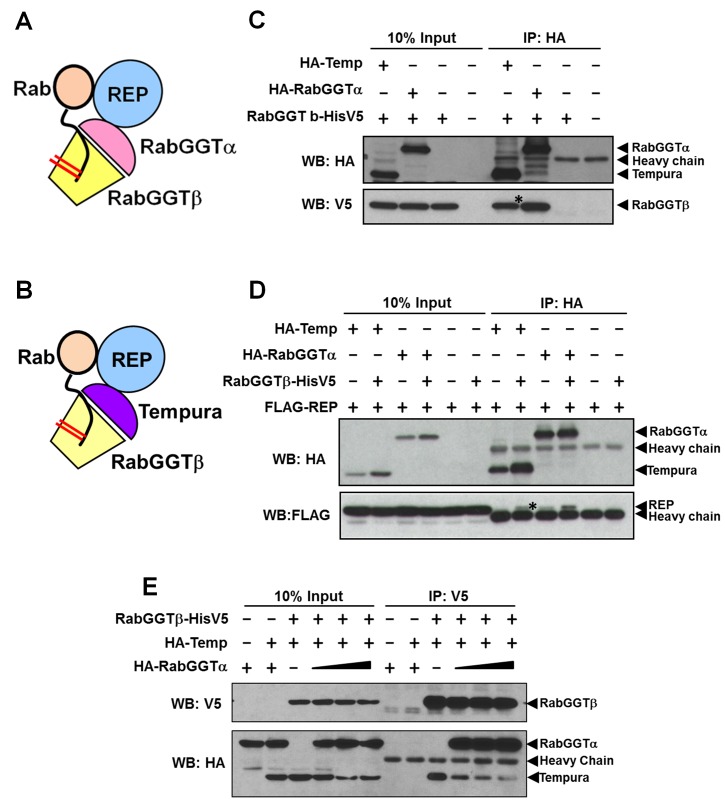
Temp Is a New α Subunit of RabGGT Complex
Protein prenylation regulates protein targeting and activity of numerous proteins [21],[22]. Given that Temp contains a PPTA motif and that temp mutants affect protein trafficking, Temp may regulate the prenylation of proteins involved in vesicular trafficking. Indeed, RabGGTβ was identified as a potential interactor for Drosophila Temp in a high-throughput yeast-2 hybrid screen [49]. RabGGTβ forms a complex with RabGGTα [also called PPTA containing protein 3 (PTAR3)] and Rab escort protein (REP) to geranylgeranylate Rabs (Figure 5A) [16],[50]–[54], which are major coordinators of vesicle trafficking [13],[14]. We therefore tested if Temp may act as an alternative α subunit of the RabGGT complex (Figure 5B). Indeed, we found that Temp can interact with RabGGTβ and REP in coimmunoprecipitation (coIP) experiments in Drosophila S2 cells (Figure 5C and 5D). In the presence of RabGGTβ, the expression level of Temp is increased, suggesting that Temp is stabilized by RabGGTβ. To assess whether Temp is an additional subunit of the original RabGGT complex or an alternative α subunit in a new RabGGT complex, we performed a RabGGTβ competition assay (Figure 5E). We pulled down the same amount of RabGGTβ and found that its binding to Temp is reduced when the amount of RabGGTα increases, indicating that Temp and RabGGTα compete for RabGGTβ. Note that the total level of Temp is also decreased when it cannot bind to RabGGTβ. These data suggest that RabGGTβ can form two RabGGT complexes: a canonical complex with RabGGTα and a novel complex with Temp.
Figure 5. Temp is a novel α subunit of RabGGT complex.
(A) The canonical RabGGT complex is composed of α and β subunits. After REP recruits Rabs, RabGGT adds geranylgeranyl groups to cysteine residues located close to the C-terminal of Rabs. (B) Proposed model of Temp function: Temp functions as an alternative α subunit in RabGGT complex to prenylate specific Rabs with geranylgeranyl groups. (C–D) CoIP experiments in Drosophila S2 cells reveal interactions between Temp, RabGGTβ, and REP. Drosophila RabGGTα (PTAR3) also interacts with RabGGTβ and REP, shown as a positive control. Note that the expression level of Temp is increased in the presence of RabGGTβ, suggesting that Temp is stabilized through binding to RabGGTβ. (C) Temp interacts with RabGGTβ. (D) Temp interacts with REP. (E) Temp and RabGGTα compete for RabGGTβ: The amount of RabGGTβ is kept at a low level to serve as a limiting factor in complex formation. The transfection levels of both RabGGTβ and Temp are kept the same, whereas the amount of RabGGTα is increased gradually. The same amount of RabGGTβ is pulled down by α-V5 beads. The interaction between RabGGTβ and Temp (pulled down by RabGGTβ) is reduced when the amount of RabGGTα is increased. To show all the bands using the same exposure time, the signal for RabGGTα is saturated. Note that the expression level of Temp is also reduced when it lost its binding to RabGGTβ.
Impairing Rab1 and Rab11 Functions Phenocopies Loss of temp
Rabs are the only known substrates of the canonical RabGGT complex (RabGGTα–RabGGTβ) [16],[21],[55]. Hence, the targets of the Temp–RabGGTβ complex may also be Rabs. To identify the substrate Rabs responsible for the loss-of-Notch signaling phenotypes in temp mutants, we performed a genetic screen and overexpressed a subset of UAS–YFP dominant-negative Rab (DN-Rab) lines [56] in wing imaginal discs and pupal notum to screen for Sca accumulation and balding phenotypes similar to temp mutant clones, respectively (Table S2). Because Sca secretion defects in temp mutants are not restricted to the notum, we tested Rabs that are broadly expressed [57] and those involved in protein secretion [14].
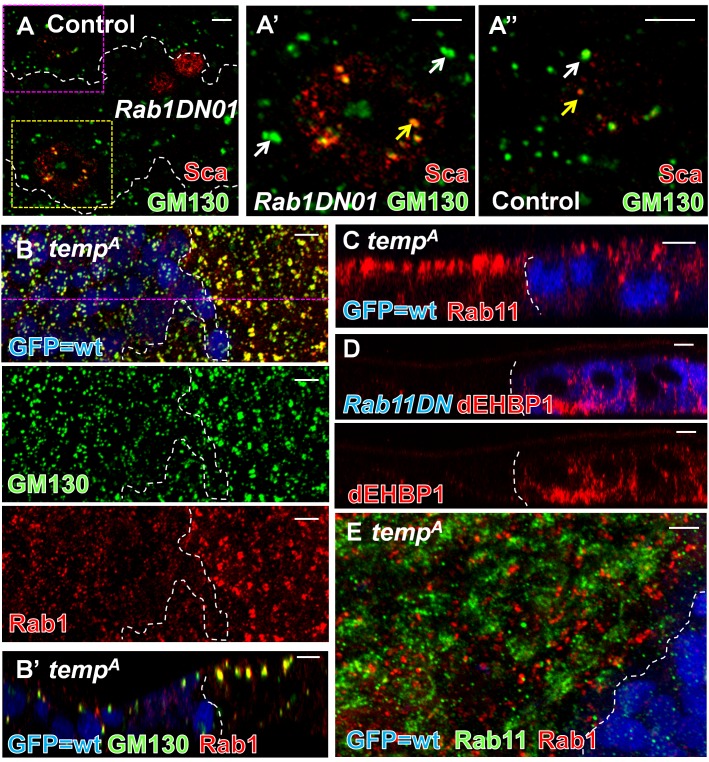
Among the 15 Rabs tested for Sca accumulation, only overexpression of DN-Rab1 reproduces key features of temp mutant cells. It causes a strong Sca accumulation in ESO in third instar wing discs (Table S2), consistent with what we observed in rab1 homozygous mutant clones (Figure S6A) [58]. We also observe a co-accumulation of both Dl and Sca in DN-Rab1-expressing ESOs on the pupal notum (Figure S6B). Similar to temp mutants, large Sca puncta colocalize with enlarged GM130 compartments [59] when we overexpress DN-Rab1 (Figure 6A–A″). Most importantly, Rab1 accumulates in enlarged GM130-positive compartments in temp mutant clones (Figure 6B and 6B′), suggesting that Temp regulates the subcellular distribution of Rab1. Together, these data suggest that Rab1 may be a substrate for Temp. Therefore, loss of temp leads to aberrant localization of Rab1 and its effector GM130, which in turn causes an accumulation of Sca and Dl.
Figure 6. Dysfunction of Rab1 and Rab11 each phenocopies some features of loss of function of temp.
(A) Sca colocalizes with expanded GM130-positive compartment in Rab1DN-expressing cells (single section). (A′) Enlargement of the yellow boxed Rab1DN-expressing region in (A). (A″) Enlargement of the pink boxed control region in (A). (B–B′) Rab1 and its effector GM130 exhibit an altered distribution in temp mutant clones. (B) Projection. (B′) Single z section of (B). (C) Rab11 mislocalizes apically in temp mutant clones. (D) dEHBP1, a Rab11 interactor, accumulates basally in DN-Rab11-expressing cells, similar to what has been observed in sec15 mutant and temp mutant clones. (E) Rab1 and Rab11 are present in distinct compartments and do not colocalize with each other in temp mutant clones. Scale bars, 5 µm.
Because dysfunction of Rab1 only leads to minor adult balding (Table S2 and Figure S6C), the cell fate transformations observed in temp mutant cells may be contributed by the dysfunction of other Rab(s). Among the 10 broadly expressed Rabs [57], we found that expression of DN-Rab5 and DN-Rab11 lead to strong balding (Table S2). Because we observed aberrant subcellular localization of Rab11 (Figure 6C), but not Rab5 (not shown), in temp mutant clones, we focused on Rab11, which functions in Dl recycling during ESO development [9],[47]. In temp mutant cells, Rab11 is enriched apically (Figure 6C). This apical clustering is likely due to mislocalization of Rab11 because the protein level of Rab11 is not changed in temp mutant animals (Figure S6D).. Cells that express DN-Rab11 exhibit an accumulation of Dl but not of Sca (Figure S6E and S6F), indicating that Rab11 regulates trafficking of Dl but not of Sca. In addition, dEHBP1, a Rab11 binding partner [8], aberrantly accumulates basally in DN-Rab11-expressing notum (Figure 6D), similar to temp mutants (Figure 4C). Therefore, loss of temp causes an aberrant localization of Rab11, which leads to a mislocalization of dEHBP1 and mistrafficking of Dl. These data indicate that Rab11 may also be a substrate of Temp.
Because temp mutant clones exhibit an altered distribution of both Rab1 and Rab11, we tested whether they are misdistributed to the same intracellular compartment. Coimmunostaining of Rab1 and Rab11 reveals that they mostly do not overlap in temp mutant clones (Figure 6E), suggesting that additional factors regulate their aberrant subcellular distribution in the absence of temp.
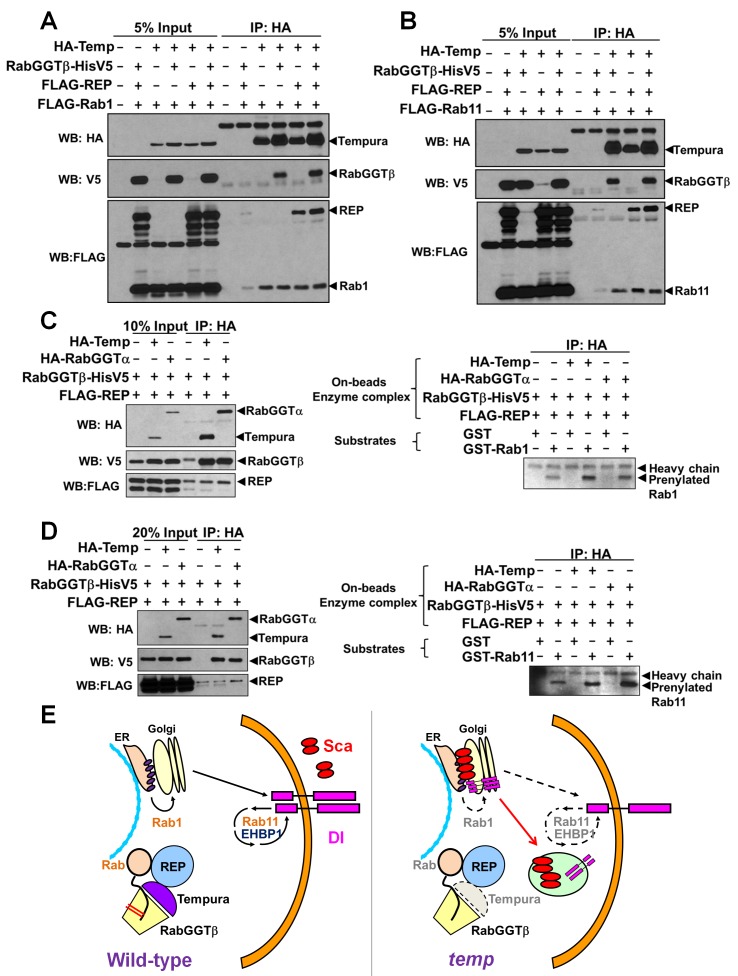
Rab1 and Rab11 Are Substrates of the Temp–RabGGTβ Prenyltransferase Complex
As shown previously, Temp can form a new RabGGT complex with RabGGTβ and interact with REP (Figure 5B–D). If Rab1 and Rab11 are substrates of this complex, they should physically interact with Temp. Indeed, Temp binds to Rab1 and Rab11 in coIP experiments in S2 cells (Figure 7A and 7B, last lanes). Temp and these Rabs can also be pulled down without cotransfecting RabGGTβ or REP, possibly because of the presence of these proteins in S2 cells. We knocked down the REP and RabGGTα proteins in S2 cells using RNAis that we designed. Unfortunately, these cells grow very slowly and most die, suggesting that REP and RabGGTα are required for the viability of S2 cells. These data are in agreement with our observation that RabGGTα mutant cells are lethal in vivo (unpublished data). To determine whether Temp can prenylate Rab1 and Rab11 with geranylgeranyl groups, we performed an in vitro prenylation assay [60]. We cotransfected REP, RabGGTβ, and HA–Temp or HA–RabGGTα into S2 cells and pulled down the enzyme complex with anti-HA beads (Figure 7C and 7D, left panels). We also purified GST–Rab1 and GST–Rab11 as unmodified substrates from bacteria. The prenylation assays were performed by adding GST–Rab1 or GST–Rab11 to biotin-labeled geranylgeranyl groups and the anti-HA beads loaded with the enzymatic complex (HA–Temp–RabGGTβ–REP or HA–RabGGTα–RabGGTβ–REP). In the absence of Temp and RabGGTα, we observe weakly prenylated bands, likely due to nonspecific pull-down of endogenous RabGGT complexes (Figure 7C and 7D). However, in the presence of Temp or RabGGTα (positive control) the prenylated band is obviously enhanced (Figure 7C and 7D, right panels). These data indicate that the complexes containing Temp can prenylate Rab1 and Rab11. Temp seems to be more efficient in prenylating Rab1, whereas RabGGTα seems to be more efficient in prenylating Rab11, indicating that they may have different substrate preferences. In conclusion, our data show that Temp can form a novel PPT complex to prenylate Rab1 and Rab11.
Figure 7. Rab1 and Rab11 are substrates of the Temp–RabGGTβ–REP complex.
(A–B) Co-IP assay in S2 cells: Temp interacts with Rab1 (A) and Rab11 (B). The interaction can occur without the transfection of RabGGTβ and REP. This is possibly due to the endogenous expression of these two proteins in S2. The very weak pulled down band of Rab1/Rab11 in the absence of Temp is due to nonspecific binding to α-HA beads. (C–D) In vitro prenylation assays: (C, Left) Western blot result of input and IP for the prenylation assay. Because the whole pull-down process is performed in the prenylation buffer, which is not an optimal condition for IP, some nonspecific binding is present in the control. (C, Right) GST–Rab1 can be prenylated with geranylgeranyl groups in the presence of Temp and RabGGTα. The prenylation efficiency for Rab1 is much higher with Temp than with RabGGTα. The weak band in the control condition might be due to endogenous activity. (D, Left) Western blot result of input and IP for the prenylation assay. (D, Right) GST–Rab11 can be prenylated with geranylgeranyl groups in the presence of Temp and RabGGTα. The prenylation efficiency for Rab11 is higher with RabGGTα than with Temp under this substrate concentration. The weak band in the control condition might be due to endogenous activity. (E) Model of the role of Temp in Notch signaling: Temp functions in a new RabGGT complex. Rab1 and Rab11 are two substrates of this new RabGGT complex. The trafficking and localization of Notch signaling components are regulated by Rab1 and Rab11. Thus, in the absence of Temp, Rab1 and Rab11 are mislocalized, which in turn causes mistrafficking of Sca and Dl, resulting in the Notch signaling defects.
Discussion
We isolated a novel Notch signaling player, temp, whose loss causes defects in lateral inhibition and cell fate determination of ESO from an unbiased genetic screen. temp encodes an unstudied protein with a 29 a.a. PPTA motif implicated in protein prenylation. Here, we show that Temp forms a complex with RabGGTβ and REP to prenylate Rab1 and Rab11. Loss of temp leads to an aberrant subcellular distribution of Rab1 and Rab11. Loss-of-function of Rab1 causes an accumulation of Sca and Dl, whereas loss-of-function of Rab11 further contributes to the Dl trafficking defect. Together, our data indicate that Temp functions as the α subunit of a new RabGGT complex that modulates Notch signaling via Rab1 and Rab11.
Although the role of Rab11 in Notch signaling pathway has been previously documented [47], our data indicate that Rab1 is required for proper trafficking of Sca and Dl. To our knowledge, this is the first time that Rab1 has been linked to Notch signaling. Sca trafficking is mainly affected by Rab1, whereas Dl trafficking is affected by both Rab1 and Rab11. Because null alleles of both Rabs are cell lethal (not shown), but temp mutant clones are not, the loss of Rab1 and Rab11 function can only be partial in the temp mutant clones. This suggests that the other α subunit, RabGGTα, still prenylates a portion of Rab1 and Rab11 that play a role in other cellular processes in the absence of temp, consistent with the prenylation assay results (Figure 7C and 7D). In addition, overexpression of constitutively active (CA) forms of Rab1 and Rab11 (Rab1CA and Rab11CA) in temp mutant clones does not alter Sca accumulation (Figure S7A and S7B) nor does it alter cell fate transformation (Figure S7C and S7D). This suggests that loss of temp is epistatic to the constitutively active forms of Rabs. These genetic interaction data are consistent with our model as constitutively active forms of Rab must be properly prenylated [18].
In temp mutant clones and notum cells expressing DN-Rab1, Sca mostly accumulates in GM130-positive compartments, traditionally considered as cis-Golgi. However, because Rab1 functions in ER-to-Golgi trafficking [13],[14], loss of Rab1 is expected to prevent cargo from entering the Golgi apparatus. This may be because the cis-Golgi is closely associated with the ER exit sites (tER) to form the “tER–Golgi unit” [61], which is optically difficult to distinguish from the cis-Golgi compartment. Indeed, a number of Golgi proteins including GM130, GRASP, and p115 localize at tER sites in S2 cells [61]–[63]. For example, GRASP also colocalizes with Sca in temp mutants (Figure S4E). Therefore, loss of temp or its target, Rab1, causes Sca to accumulate in GM130-positive compartments corresponding to the cis-Golgi, the tER, or an intermediate compartment between the two.
In yeast and cultured mammalian cells, Rabs that lack proper geranylgeranylation diffuse in the cytoplasm [17],[18]. Surprisingly, we find that the distribution of Rab1 and Rab11 in temp mutants is restricted to specific subcellular compartments: Rab1 colocalizes with enlarged GM130 compartments (Figure 6B) whereas the majority of Rab11 is apically enriched (Figure 6C). Given that Rab1 and Rab11 do not diffuse in the cytoplasm and that they do not redistribute to the same microdomains (Figure 6E), we propose that the subcellular localization of Rab1 and Rab11 is in part determined by different/other Rab binding partners upon reduction of proper prenylation in temp mutants.
The fly and human genomes both contain three genes that encode proteins containing the PPTA motif: PTAR1/Temp, PTAR2/FTα, and PTAR3/RabGGTα. PTAR2 forms PPTs with two different β subunits, whereas PTAR3 forms a RabGGT with RabGGTβ (Figure S1) [21],[22],[52]–[54],[64]. We show that PTAR1 and RabGGTβ form an alternative RabGGT complex to prenylate Rab1 and Rab11. This raises an interesting question: what is the labor distribution of RabGGTα–RabGGTβ and Temp–RabGGTβ complexes? Because the PTAR1 (temp) homolog is absent in some species like S. cerevisiae and C. elegans, but is present in Dictyostelium and Arabidopsis (Figure 2C), it is likely that it was lost in some evolutionary branches and that its function is covered by PTAR3 in these species. While we can obtain large homozygous mutant clones with temp null alleles, we find that homozygous RabGGTα mutant clones in the thorax and eyes are cell lethal (not shown). Hence, we speculate that Temp has evolved to play a more specific role to prenylate a subset of Rabs, whereas RabGGTα is able to modify most, if not all, Rabs [16],[21],[55] yet is not sufficient for proper trafficking of Scabrous and Delta. Indeed, although both Temp and RabGGTα can prenylate Rab1 and Rab11 in vitro with different efficiency (Figure 7C and 7D), expression of fly RabGGTα fails to rescue the ESO phenotypes in temp mutant clones (Figure 2D). Moreover, expression of fly temp does not alleviate the cell lethality in RabGGTα mutant clones (data not shown). These data indicate that the functions of the two RabGGT complexes are nonredundant in vivo and that the functions of the two RabGGT complexes towards different Rabs may also be regulated in a tissue-specific manner through unknown interaction partners and/or posttranslational modifications in vivo. This tissue-specific regulation is supported by the gene expression data from FlyAtlas (Figure S8) [65],[66]. RabGGTα mRNA is transcribed ubiquitously at moderate levels and the expression pattern of temp mRNA is much more restricted to the nervous system with high levels in thoracic-abdominal ganglion cells. This suggests that Temp plays a role in the nervous system, including ESO development.
As major coordinators of vesicular trafficking, Rabs are crucial for maintaining normal cellular function and misregulation of some Rabs results in cellular dysfunction. Indeed, dysfunction of some Rabs and their prenylation factors are implicated in several diseases [13],[55],[67]. For example, Choroideremia, an inherited retinal degenerative disease, is caused by mutations in REP1. On the other hand, Rab1 is hijacked by the pathogen Legionella pneumophila during infection to support the bacterium with the ER-to-Golgi secretory system [68]. In various cancers, the expression level of numerous Rabs, including Rab1 and Rab11, is up-regulated. Up-regulation of Rab11 family members (Rab11A/11B/25) is associated with more aggressive prostate, ovarian, and breast cancers [13],[55]. Finally, toxins produced by Bacillus anthracis inhibit Rab11 and Sec15, which in turn reduce Notch signaling activity in both flies and mammalian endothelial cells [69], suggesting a possible role for Temp in aberrant Notch signaling induced by bacterial infection.
Materials and Methods
Fly Strains, Transgenesis, and Crossing Schemes
The following stocks were used in this study: (1) isogenized y w FRT19A (y w FRT19Aiso or iso19A), (2) Df(1)JA27/FM7c Kr-GFP, (3) w sn FRT19A; Ubx-FLP(2), (4) cl(1) Ubi-GFP FRT19A/FM6; Ubx-FLP(2), (5) Ubx-FLP tub-GAL80 FRT19A; Actin-GAL4 UAS-CD8::GFP (MARCM line), (6) hs-FLP Ubi-GFP FRT19A (D. Bilder), (7) y w; P{lacW}scaA2–6(sca-lacZ reporter) [36],[38], (8) y w; UAS-Sca-GFP/Cyo (Sca-GFP used in secretion assay) [39], (9) w; UAS-CFP-Golgi(2) [70], (10) w; UAS-Lamp1-GFP; M3–12/S-T (C-K Yao) [71], (11) y w; T(2;3)ap[Xa]/SM5; TM3, Sb, ER-YFP [19], (12) C96-Gal4/(TM3, Sb), (13) Dp(1;2;Y)w+, (14) w Df(1)ED6574/FM7h, (15) w Df(1)ED409/FM7h, (16) P{lacW}l(1)G0144 w/FM7c [72], (17) FRT82B dar6[12-3-73]/TM3, Sb [58] (a severe loss-of-function allele for Rab1), (18) y w Ubx-FLP; FRT82B M [19] Ubi-GFP, (19) y w; P{w[+mW.hs] = FRT(w[hs])}2A P{ry[+t7.2] = neoFRT} 82B PBac{SAstopDsRed}LL03248 P{y[+t7.7] ry[+t7.2] = Car20y}96E/TM6B, Tb [73], and (20) UAS-p35 (a kind gift from Andreas Bergmann).
The forward genetic screen that identified alleles of temp was performed as previously described [23]. A total of 577 stocks have wing notching or notum balding phenotypes and were mapped through X chromosome duplication mapping, deficiency mapping, and complementation tests.
Genomic and cDNA rescue transgenic flies were generated by phiC31-mediated transgenesis at vk33 or vk37 docking sites [74]. Phenotypic rescue was assessed in temp mutant background either in whole animal or by overexpression in temp MARCM clones. UAS–YFP–DN-Rab flies [56] were crossed to C96–Gal4 [75], which can drive ectopic expression of UAS transgenes around the wing margin, and used for immunostaining against Sca in the third instar larval wing disc. We overexpressed UAS–GFPnls as a negative control.
We used the MARCM strategy in the balding screen and to assess Sca secretion and mark subcellular compartments. Because these transgenes encode GFP/YFP/CFP fusion proteins, we crossed out Actin–Gal4, UAS CD8::GFP in MARCM line, which was then combined with the transgene of interest and subsequently crossed to either y w FRT19Aiso; Actin–Gal4/Cyo or y w temp FRT19A; Actin–Gal4/Cyo (tempA and tempD) for performing experiments in control and mutant genetic backgrounds, respectively. Stocks were maintained at RT and crosses were performed at 25°C.
Genomic and cDNA Constructs
A genomic rescue construct was constructed by PCR amplification of a 4.5 kb amplicon spanning CG3073 locus and cloned into pattB [76]. We added N-terminal HA or mCherry tags to the genomic rescue construct via conventional cloning methods. cDNA of RabGGTβ was constructed in the pMT vector, while human PTAR1(hPTAR1), temp, RabGGTα, REP, rab1, and rab11 were cloned into pUASTattB [76] with N-terminal HA and FLAG tags. In addition, rab1 and rab11 were cloned to pGEX vectors (GE Healthcare). Cloning and DNA purification were performed based on standard protocols. Enzymes are from NEB, and DNA purification kits are from Invitrogen and Qiagen. All constructs were sequenced before injection or transfection.
Dissection, Immunostaining, and Imaging
For notum immunostaining, fly pupae were aged until the indicated time points at 25°C. For the wing disc staining, we dissected third instar larvae. Dissection and immunostaining were performed as previously described [8]. Primary antibodies were used at the following dilutions: mouse α-Rab11 1∶100 (BD Biosciences), rabbit α-Rab11 1∶1,000 [69], mouse α-Rab1 1∶500 [77], guinea pig α-Boca 1∶1,000 [78], guinea pig α-Hrs 1∶600 [79], mouse α-Dl 1∶200 (DSHB) [80], guinea pig α-Dl 1∶1,000 [81], mouse α-NICD 1∶200 (DSHB) [82], mouse α-NECD 1∶100 (DSHB), chicken α-GFP 1∶1,000 (Abcam), rabbit α-GFP 1∶500 (Invitrogen), rabbit α-GM130 1∶500 (Abcam), rabbit α-Syx16 1∶500 (Abcam), rabbit α-Neur 1∶600 [83], rabbit α-beta-Galactosidase 1∶500 (Cappel), rabbit α-Numb 1∶1,000 [43], rabbit α-GRASP55 1∶500 [84], guinea pig α-Sens 1∶1,000 [25], rat α-ELAV 1∶500 (DSHB) [85], mouse α-Cut 1∶500 (DSHB) [86], rat α-Su(H) 1∶500 [29], rat α-DE-cadherin 1∶50 (DSHB) [87], and rat α-Ttk69 1∶500 [88]. Alexa 488–conjugated (Invitrogen) and Cy2-, Cy3-, Cy5-, or DyLight649-conjugated secondary antibodies (Jackson ImmunoResearch) were used at 1∶200. Samples were mounted in Slowfade reagent (Invitrogen). All confocal figures were acquired with confocal microscope (LSM510; Carl Zeiss) using Plan Apochromat 40× NA 1.4 and Plan Apochromat 63× NA 1.4 objectives (Carl Zeiss), followed by processing in LSM software, ImageJ, and Photoshop (Adobe).
For Sca secretion assays, we assess extracellular Sca–GFP by staining for rabbit α-GFP without any detergents. Then, we permeabilize the notum tissue with 0.1% Triton-PBS and perform a staining for the total GFP using chicken α-GFP antibody. To costain both extracellular and total Dl in temp mosaic notums, we first stain extracellular Dl using mouse α-Dl antibody without detergents. Then we permeabilize the noum with 0.1% Triton-PBS and stain for the total Dl with the guinea pig α-Dl antibody. For Notch extracellular staining, the notum tissue is first stained with mouse α-NECD antibody without any detergents. Then, we permeabilize the notum tissue with 0.1% Triton-PBS and perform the later steps of immunostaining similarly.
Cell Culture, CoIP, and Western Blot
S2 cell line was cultured in Schneider's media (Gibco) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Sigma-Aldrich) and antibiotics mix (penicillin and streptomycin, Invitrogen) at RT. The transfection was performed using Effectene (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Proteins were expressed using Actin–GAL4/UAS system or pMT inducible system (Invitrogen). In co-IP experiments, cells were harvested 48 h after transfection and lysed on ice in lysis buffer [50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 5% glycerol, 0.5% TritonX-100, and EDTA-free cocktail complete protease inhibitor (Roche)]. Lysate supernatant was incubated with EZ red α-HA beads (Sigma-Aldrich) overnight, and beads were washed with lysis buffer and boiled in 2× Laemmli buffer. PAGE, transfer, and Western blot were performed according to standard protocols. In the RabGGTβ competition assay, we performed coIP using α-V5 beads (Sigma-Aldrich) instead. Primary antibodies were used at the following dilution: rabbit α-HA 1∶2,000 (Abcam), rabbit α-FLAG antibody 1∶2,000 (Abcam), mouse α-FLAG (M2, Sigma-Aldrich) 1∶1,000, mouse α-V5 1∶5,000 (Invitrogen), mouse α-Actin 1∶1,000 (MP Biomedicals), and mouse α-Rab11 1∶500 (BD Biosciences). Goat HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies were used at 1∶2,000 dilution (Jackson ImmunoResearch). Membranes were developed using Western Lightning Plus-ECL (PerkinElmer) followed by X-ray film (Thermo Scientific) detection.
Rab Protein Purification and In Vitro Rab Prenylation Assay
GST, GST–Rab1, and GST–Rab11 were purified from BL21 pLys (Invitrogen): 25 ml overnight cultures were diluted to 250 ml with LB medium and kept growing at 37°C until OD600 reached 0.5∼0.7. GST, GST–Rab1, and GST–Rab11 proteins were induced at 37°C for 3 h by adding IPTG at a final concentration of 0.1 mM. Bacteria were then lysed using CelLytic express (Sigma-Aldrich) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Supernatant was incubated with Glutathione Sepharose 4B (GE healthcare) at 4°C for 2 h and then the beads were washed with 50 mM HEPES pH 8.0 buffer by inversion for three times. GST fusion proteins were eluted with 10 mM glutathione in 50 mM HEPES pH 8.0 buffer. Protein concentration was measured using Bradford method (BioRad). We used 0.3 µM GST–Rab1 and 3 µM GST–Rab11 as substrates in the prenylation assays with 0.3 µM and 3 µM GST as negative controls, respectively. On the other hand, all components of the RabGGT complex (His–RabGGTβ–V5, FLAG–REP, and HA, HA–Temp, or HA–RabGGTα) were transfected to S2 cells as described in the previous section. Cells were lysed on ice in prenylation buffer [50 mM HEPES, pH 7.2, 50 mM MaCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 0.01% Triton X-100, and EDTA-free cocktail complete protease inhibitor (Roche)] [60] using syringes. Supernatant was then incubated with EZ red α-HA beads (Sigma-Aldrich) for 4 h at 4°C, and beads were washed with prenylation buffer. We added HA, HA–Temp, or HA–RabGGTα binding beads together with GST control or GST–Rab substrates, 5 µM biotin-labeled lipid precursor (B-GPP; Jena Bioscience), 2 mM DTE, and 20 mM GDP. The prenylation assays were carried out on beads at 25°C for 1 h. Reactions were stopped by adding 2× Laemmli buffer. Western blot was performed as described in the previous section with 5% BSA as blocking solution and Streptavidin–HRP 1∶50,000 (Jackson ImmunoResearch) for Biotin detection.
Supporting Information
Schematic diagram and features of the three well-characterized PPTs. PPTs are heterodimers of α and β subunits. They can be subdivided into three types: FT, GGTI, and GGTII (also called RabGGT) based on the lipid length and target motif present on their substrate proteins. All these genes are conserved from yeast to human. Because the α subunits of PPTs contain PPTA subunit repeat motifs, the FTα is also called PTAR2 and RabGGTα is also called PTAR3. PPTs add prenyl lipids (15-carbon farnesyl or 20-carbon geranylgeranyl group) via a thioether linkage (-C-S-C-) to a cysteine residue of soluble proteins. FT and GGTI share the same α subunit for substrate recognition and have a unique β subunit. They recognize the CaaX motif (C for cysteine residue, a for aliphatic residues, X can be a wide range of residues) in the C-terminal region of various substrates, including lamins as well as many small GTPases such as Ras and Rho. On the other hand, GGTII does not require a specific C-terminal motif for recognition. Because all of its substrates identified to date are Rab proteins, it is also called RabGGT. It requires assistance from REP to recruit Rab substrates. The target motif on most of the Rab proteins contains two Cysteine residues, and both are conjugated with geranylgeranyl groups.
(TIF)
The cell fate transformation defect is not related to apoptosis in temp mutant clones. (A–B) At 27 h APF, there are some apoptotic cells (Caspase3-positive cells) in some tempA mutant clones (A). However, there is no obvious apoptosis in tempB mutant clones (B). (C–D) When an anti-apoptotic protein, p35, is overexpressed in tempA mutant clones (24 h APF) to suppress the apoptotic effect (C), we observe no obvious differences in phenotype (D) when we compare these clones with temp mutant clones without p35 expression. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
HA–Temp protein is localized diffusedly throughout the cytoplasm. HA–temp cDNA is expressed using dpp–Gal4 in the wing disc and HA–Temp is dispersed in the cytoplasm and does not seem to localize to any particular subcellular area. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
Accumulation of Sca in temp mutant is not restricted to notum ESOs. (A) Sca accumulates in the temp mutant ESOs at the anterior of wing margin in third instar wing imaginal discs. (B) Single section: Sca accumulates in temp mutant R8 photoreceptor cells in the third instar larval eye discs. (B′) Projection of (B). (C) In the temp mutant clones, the expression level of sca–lacZ does not change, whereas the protein level of Sca is up-regulated in sensory organs at the anterior of wing margin during third instar larval stage. (D) In the temp mutant clones, the expression level of sca–lacZ does not change and the protein level of Sca is up-regulated in R8 cells in the third instar larval eye discs. (E) In temp mutant ESO, Sca puncta largely colocalize with GRASP, which locates at both ER exit site (tER) and cis-Golgi compartments. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
The localization of Dl, but not Notch or D E-cadherin, is altered in temp mutant ESOs. (A) Total level of Notch (stained for NICD) is not changed in temp mutant clones. (B) Total level of Notch (stained for Notch extracellular domain) is not changed in temp mutant clones. (C) Extracellular level of Notch (stained for Notch extracellular domain without permeabilization) is not changed in temp mutant clones. (D) Many temp mutant ESOs exhibit increased total level of Dl puncta (yellow arrows and white arrows) compared to wt ESOs (red arrows). Dl in some temp mutant ESOs still localizes to the plasma membrane (white arrows), whereas Dl in other temp mutant ESOs can only be found intracellularly (yellow arrows). (E) Localization of DE-cadherin, an apically enriched transmembrane protein, is not affected in temp mutant clones. Asterisks (*) indicate folds in the notum where lower levels are artifactual. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
Dysfunction of Rab1 and Rab11 phenocopies loss-of-function of temp . (A) Sca accumulates in rab1 mutant sensory organs in the third instar larval wing disc, similar to the temp mutant phenotype. The rab1 clones are mostly cell lethal even when the neighboring tissue has the competitive disadvantage of having a Minute mutation. (B) Single section: Overexpression of Rab1DN causes accumulation of both Dl and Sca on the notum. White arrow, RablDN expressing ESO; yellow arrow, control ESO. Note that the RablDN-expressing ESO in the upper region exhibits a severe Sca accumulation, which can also occasionally be observed in temp mutant ESOs, whereas RablDN-expressing ESO in the lower region exhibits a less severe Sca accumulation (puncta) similar to what is usually observed in temp mutant ESOs. (C) Adult notum: Overexpression of Rab1DN on the notum causing minor balding occasionally (arrow). (D) Western blot: Endogenous expression level of Rab11 is not altered in tempA and tempD mutant larvae compared to mutant larvae with a genomic rescue transgene (control). (E) Single section: Overexpression of Rab11DN does not affect the expression of Sca in the notum. White arrow, Rab11DN-expressing ESO; yellow arrow, wt ESO. (F) Single section: In Rab11DN-expressing cells, Dl is mislocalized in the middle plane of the cells. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
Overexpression of constitutively active form of Rab1 and Rab11 does not restore the temp mutant phenotypes. (A–B) Overexpression of constitutively active forms of Rab1 (Rab1CA) either in control (iso19A) or temp mutant clones at 16–18 h APF: (A) Rab1CA overexpression in the control clones does not cause any phenotypes. (B) Rab1CA overexpression in the temp mutant clones does not rescue Sca accumulation. (C–D) Overexpression of constitutively active forms of Rab11 (Rab11CA) in either control (iso19A) or temp mutant clones at 27 h APF: (C) Rab11CA overexpression in control clones does not cause phenotypes. (D) Rab11CA overexpression in the temp mutant clones does not rescue the cell fate changes. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
temp mRNA expression is highly enriched in the nervous system. The mRNA expression patterns of temp (CG3073) and RabGGTα (CG12007) are quite different in both larval and adult stages based on FlyAtlas data [65]. RabGGTα mRNA is transcribed at moderate level ubiquitously and temp mRNA is expressed highly in the nervous system, suggesting that Temp plays a role in the nervous system. This figure is adapted and modified from Flybase (http://flybase.org/) [66].
(TIF)
Sca accumulates in GM130-positive compartments in both temp mutant and Rab1DN -expressing notum clones. We used MARCM to express ER–YFP, Golgi–CFP, FYVE–GFP, and LAMP-1–GFP in temp mutant or wt clones. For other markers, we performed coimmunostaining using specific antibodies (see Materials and Methods). ER, endoplasmic reticulum. +, colocalization; +/−, minor colocalization; −, no obvious colocalization; N/A, not tested.
(TIF)
Summary of Rab screen for Sca accumulation and balding. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; EE, early endosome; PM, plasma membrane; LE, late endosome; TGN, trans Golgi network; RE, recycling endosome. +, positive, +/−, minor phenotype; −, no obvious phenotype; ND, not determined.
(TIF)
Acknowledgments
We thank the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center and Drosophila Genetic Resource Center for flies and the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank for antibodies. We are grateful to Dr. Y.-N. Jan (rab1 mutant), Dr. A. Satoh (Rab1 antibody), Dr. P. Badenhorst (Ttk antibody), Dr. M.A. Muskavitch (Delta antibody), Dr. F. Schweisguth (Su(H) antibody), and Dr. A. Bergmann (UAS–p35), for fly stocks and antibodies. We thank Drs. C.-K. Yao, C. Tong, H. Tsuda, G. Lin, and K. Venkatachalam for comments and discussion. We thank K. Schulze, Y. Chen, C. Benitez, X. Shi, A. Jawaid, H. Wang, D. Bei, and L. Wang for help with the screen. We thank H. Pan and Y. He for injections to create transgenic flies.
Abbreviations
- a.a.
amino acid
- APF
after puparium formation
- ARS
apical actin-rich
- CA
constitutively active
- CADASIL
cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy
- co-IP
co-immunoprecipitation
- Dl
Delta
- DN
dominant negative
- ELAV
Embryonic Lethal Abnormal Vision
- EMS
ethyl methanesulfonate
- ESO
external sensory organ
- FBS
fetal bovine serum
- FT
farnesyltransferase
- GGT
geranylgeranyltransferase
- HA
Hemagglutinin
- hPTAR1
human PTAR1
- iso19A
isogenized y w FRT19A
- MARCM
mosaic analysis with a repressible cell marker
- NICD
Notch intracellular domain
- PPT
protein prenyltransferase
- PTAR1
PPTA containing protein 1
- PTAR2
PPTA containing protein 2
- PTAR3
PPTA containing protein 3
- RabGGT
Rab geranylgeranyltransferase
- REP
Rab escort protein
- sca
scabrous
- SCD
spondylocostal dysostosis
- sens
senseless
- SOP
sensory organ precursor
- Su(H)
Suppressor of Hairless
- Syx16
Syntaxin 16
- temp
tempura
- Ttk
Tramtrack
- wt
wild-type
Funding Statement
Confocal microscopy is supported by the Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities Research Center (NIH 5P30HD024064). This research was supported by NIH (1RC4GM096355-01 to H.J.B.). W.-L.C. was supported by Taiwan Merit Scholarships Program sponsored by the National Science Council (NSC-095-SAF-I-564-015-TMS). S.Y. was supported by a fellowship from the Nakajima Foundation and is currently supported by the Jan and Dan Duncan Neurological Research Institute. V.B. was supported by the NIH (5T32-HD055200) and the Edward and Josephine Hudson Scholarship Fund. B.X. was supported by the Houston Laboratory and Population Science Training Program in Gene-Environment Interaction from the Burroughs Wellcome Fund (Grant No. 1008200). H.S. was supported by NIH 5R01GM067858 and the Research Education and Career Horizon Institutional Research and Academic Career Development Award Fellowship 5K12GM084897. H.J.B. is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Bray SJ (2006) Notch signalling: a simple pathway becomes complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7: 678–689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Muskavitch MA (2010) Notch: the past, the present, and the future. Curr Top Dev Biol 92: 1–29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Aster JC, Pear WS, Blacklow SC (2008) Notch signaling in leukemia. Annu Rev Pathol 3: 587–613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Gridley T (2003) Notch signaling and inherited disease syndromes. Hum Mol Genet 12 Spec No 1: R9–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kopan R, Ilagan MX (2009) The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell 137: 216–233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Lai EC, Orgogozo V (2004) A hidden program in Drosophila peripheral neurogenesis revealed: fundamental principles underlying sensory organ diversity. Dev Biol 269: 1–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Acar M, Jafar-Nejad H, Takeuchi H, Rajan A, Ibrani D, et al. (2008) Rumi is a CAP10 domain glycosyltransferase that modifies Notch and is required for Notch signaling. Cell 132: 247–258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Giagtzoglou N, Yamamoto S, Zitserman D, Graves HK, Schulze KL, et al. (2012) dEHBP1 controls exocytosis and recycling of Delta during asymmetric divisions. J Cell Biol 196: 65–83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Jafar-Nejad H, Andrews HK, Acar M, Bayat V, Wirtz-Peitz F, et al. (2005) Sec15, a component of the exocyst, promotes notch signaling during the asymmetric division of Drosophila sensory organ precursors. Dev Cell 9: 351–363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Rajan A, Tien AC, Haueter CM, Schulze KL, Bellen HJ (2009) The Arp2/3 complex and WASp are required for apical trafficking of Delta into microvilli during cell fate specification of sensory organ precursors. Nat Cell Biol 11: 815–824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Hartenstein V, Posakony JW (1990) A dual function of the Notch gene in Drosophila sensillum development. Dev Biol 142: 13–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Yamamoto S, Charng WL, Bellen HJ (2010) Endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of Notch and its ligands. Curr Top Dev Biol 92: 165–200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Hutagalung AH, Novick PJ (2011) Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology. Physiol Rev 91: 119–149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Stenmark H (2009) Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10: 513–525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Zerial M, McBride H (2001) Rab proteins as membrane organizers. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2: 107–117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Leung KF, Baron R, Seabra MC (2006) Thematic review series: lipid posttranslational modifications. geranylgeranylation of Rab GTPases. J Lipid Res 47: 467–475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Calero M, Chen CZ, Zhu W, Winand N, Havas KA, et al. (2003) Dual prenylation is required for Rab protein localization and function. Mol Biol Cell 14: 1852–1867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Gomes AQ, Ali BR, Ramalho JS, Godfrey RF, Barral DC, et al. (2003) Membrane targeting of Rab GTPases is influenced by the prenylation motif. Mol Biol Cell 14: 1882–1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Johnston PA, Archer BT 3rd, Robinson K, Mignery GA, Jahn R, et al. (1991) rab3A attachment to the synaptic vesicle membrane mediated by a conserved polyisoprenylated carboxy-terminal sequence. Neuron 7: 101–109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Seabra MC (1996) Nucleotide dependence of Rab geranylgeranylation. Rab escort protein interacts preferentially with GDP-bound Rab. J Biol Chem 271: 14398–14404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Maurer-Stroh S, Washietl S, Eisenhaber F (2003) Protein prenyltransferases. Genome Biol 4: 212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Roskoski R Jr (2003) Protein prenylation: a pivotal posttranslational process. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303: 1–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Yamamoto S, Charng WL, Rana NA, Kakuda S, Jaiswal M, et al. (2012) A mutation in EGF repeat-8 of Notch discriminates between Serrate/Jagged and Delta family ligands. Science 338: 1229–1232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Xu T, Rubin GM (1993) Analysis of genetic mosaics in developing and adult Drosophila tissues. Development 117: 1223–1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Nolo R, Abbott LA, Bellen HJ (2000) Senseless, a Zn finger transcription factor, is necessary and sufficient for sensory organ development in Drosophila. Cell 102: 349–362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Guo M, Jan LY, Jan YN (1996) Control of daughter cell fates during asymmetric division: interaction of Numb and Notch. Neuron 17: 27–41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Okabe M, Imai T, Kurusu M, Hiromi Y, Okano H (2001) Translational repression determines a neuronal potential in Drosophila asymmetric cell division. Nature 411: 94–98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Robinow S, White K (1991) Characterization and spatial distribution of the ELAV protein during Drosophila melanogaster development. J Neurobiol 22: 443–461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Schweisguth F, Posakony JW (1992) Suppressor of Hairless, the Drosophila homolog of the mouse recombination signal-binding protein gene, controls sensory organ cell fates. Cell 69: 1199–1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Cook RK, Deal ME, Deal JA, Garton RD, Brown CA, et al. (2010) A new resource for characterizing X-linked genes in Drosophila melanogaster: systematic coverage and subdivision of the X chromosome with nested, Y-linked duplications. Genetics 186: 1095–1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Cook KR, Parks AL, Jacobus LM, Kaufman TC, Matthews KA (2010) New research resources at the Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center. Fly (Austin) 4: 88–91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Bellen HJ, Levis RW, He Y, Carlson JW, Evans-Holm M, et al. (2011) The Drosophila gene disruption project: progress using transposons with distinctive site specificities. Genetics 188: 731–743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Renaud O, Simpson P (2001) scabrous modifies epithelial cell adhesion and extends the range of lateral signalling during development of the spaced bristle pattern in Drosophila. Dev Biol 240: 361–376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Baker NE, Mlodzik M, Rubin GM (1990) Spacing differentiation in the developing Drosophila eye: a fibrinogen-related lateral inhibitor encoded by scabrous. Science 250: 1370–1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Lee EC, Hu X, Yu SY, Baker NE (1996) The scabrous gene encodes a secreted glycoprotein dimer and regulates proneural development in Drosophila eyes. Mol Cell Biol 16: 1179–1188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Mlodzik M, Baker NE, Rubin GM (1990) Isolation and expression of scabrous, a gene regulating neurogenesis in Drosophila. Genes Dev 4: 1848–1861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Powell PA, Wesley C, Spencer S, Cagan RL (2001) Scabrous complexes with Notch to mediate boundary formation. Nature 409: 626–630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Ye Y, Lukinova N, Fortini ME (1999) Neurogenic phenotypes and altered Notch processing in Drosophila Presenilin mutants. Nature 398: 525–529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Chou YH, Chien CT (2002) Scabrous controls ommatidial rotation in the Drosophila compound eye. Dev Cell 3: 839–850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Lee T, Luo L (1999) Mosaic analysis with a repressible cell marker for studies of gene function in neuronal morphogenesis. Neuron 22: 451–461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Nakamura N, Rabouille C, Watson R, Nilsson T, Hui N, et al. (1995) Characterization of a cis-Golgi matrix protein, GM130. J Cell Biol 131: 1715–1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Simonsen A, Bremnes B, Ronning E, Aasland R, Stenmark H (1998) Syntaxin-16, a putative Golgi t-SNARE. Eur J Cell Biol 75: 223–231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Rhyu MS, Jan LY, Jan YN (1994) Asymmetric distribution of numb protein during division of the sensory organ precursor cell confers distinct fates to daughter cells. Cell 76: 477–491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Pavlopoulos E, Pitsouli C, Klueg KM, Muskavitch MA, Moschonas NK, et al. (2001) Neuralized encodes a peripheral membrane protein involved in delta signaling and endocytosis. Dev Cell 1: 807–816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Le Borgne R, Schweisguth F (2003) Unequal segregation of Neuralized biases Notch activation during asymmetric cell division. Dev Cell 5: 139–148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Lai EC, Deblandre GA, Kintner C, Rubin GM (2001) Drosophila neuralized is a ubiquitin ligase that promotes the internalization and degradation of delta. Dev Cell 1: 783–794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Emery G, Hutterer A, Berdnik D, Mayer B, Wirtz-Peitz F, et al. (2005) Asymmetric Rab 11 endosomes regulate delta recycling and specify cell fate in the Drosophila nervous system. Cell 122: 763–773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Wu S, Mehta SQ, Pichaud F, Bellen HJ, Quiocho FA (2005) Sec15 interacts with Rab11 via a novel domain and affects Rab11 localization in vivo. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12: 879–885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Giot L, Bader JS, Brouwer C, Chaudhuri A, Kuang B, et al. (2003) A protein interaction map of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 302: 1727–1736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Anant JS, Desnoyers L, Machius M, Demeler B, Hansen JC, et al. (1998) Mechanism of Rab geranylgeranylation: formation of the catalytic ternary complex. Biochemistry 37: 12559–12568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Andres DA, Seabra MC, Brown MS, Armstrong SA, Smeland TE, et al. (1993) cDNA cloning of component A of Rab geranylgeranyl transferase and demonstration of its role as a Rab escort protein. Cell 73: 1091–1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Armstrong SA, Seabra MC, Sudhof TC, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (1993) cDNA cloning and expression of the alpha and beta subunits of rat Rab geranylgeranyl transferase. J Biol Chem 268: 12221–12229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Seabra MC, Brown MS, Slaughter CA, Sudhof TC, Goldstein JL (1992) Purification of component A of Rab geranylgeranyl transferase: possible identity with the choroideremia gene product. Cell 70: 1049–1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Seabra MC, Goldstein JL, Sudhof TC, Brown MS (1992) Rab geranylgeranyl transferase. A multisubunit enzyme that prenylates GTP-binding proteins terminating in Cys-X-Cys or Cys-Cys. J Biol Chem 267: 14497–14503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Mitra S, Cheng KW, Mills GB (2011) Rab GTPases implicated in inherited and acquired disorders. Semin Cell Dev Biol 22: 57–68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Zhang J, Schulze KL, Hiesinger PR, Suyama K, Wang S, et al. (2007) Thirty-one flavors of Drosophila rab proteins. Genetics 176: 1307–1322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Chan CC, Scoggin S, Wang D, Cherry S, Dembo T, et al. (2011) Systematic discovery of Rab GTPases with synaptic functions in Drosophila. Curr Biol 21: 1704–1715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Ye B, Zhang Y, Song W, Younger SH, Jan LY, et al. (2007) Growing dendrites and axons differ in their reliance on the secretory pathway. Cell 130: 717–729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Moyer BD, Allan BB, Balch WE (2001) Rab1 interaction with a GM130 effector complex regulates COPII vesicle cis–Golgi tethering. Traffic 2: 268–276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Nguyen UT, Wu Y, Goodall A, Alexandrov K (2010) Analysis of protein prenylation in vitro and in vivo using functionalized phosphoisoprenoids. Curr Protoc Protein Sci Chapter 14: Unit14 13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Kondylis V, Rabouille C (2009) The Golgi apparatus: lessons from Drosophila. FEBS Lett 583: 3827–3838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Kondylis V, Rabouille C (2003) A novel role for dp115 in the organization of tER sites in Drosophila. J Cell Biol 162: 185–198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Kondylis V, Spoorendonk KM, Rabouille C (2005) dGRASP localization and function in the early exocytic pathway in Drosophila S2 cells. Mol Biol Cell 16: 4061–4072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Seabra MC, Reiss Y, Casey PJ, Brown MS, Goldstein JL (1991) Protein farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase share a common alpha subunit. Cell 65: 429–434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Chintapalli VR, Wang J, Dow JA (2007) Using FlyAtlas to identify better Drosophila melanogaster models of human disease. Nat Genet 39: 715–720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Marygold SJ, Leyland PC, Seal RL, Goodman JL, Thurmond JR, Strelets VB, Wilson RJ (2013) and the FlyBase Consortium (2013) FlyBase: improvements to the bibliography. Nucleic Acids Res 41 D1: D751–D757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Seabra MC, Mules EH, Hume AN (2002) Rab GTPases, intracellular traffic and disease. Trends Mol Med 8: 23–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Neunuebel MR, Machner MP (2012) The taming of a Rab GTPase by Legionella pneumophila. Small GTPases 3: 28–33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Guichard A, McGillivray SM, Cruz-Moreno B, van Sorge NM, Nizet V, et al. (2010) Anthrax toxins cooperatively inhibit endocytic recycling by the Rab11/Sec15 exocyst. Nature 467: 854–858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Satoh AK, O'Tousa JE, Ozaki K, Ready DF (2005) Rab11 mediates post-Golgi trafficking of rhodopsin to the photosensitive apical membrane of Drosophila photoreceptors. Development 132: 1487–1497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Pulipparacharuvil S, Akbar MA, Ray S, Sevrioukov EA, Haberman AS, et al. (2005) Drosophila Vps16A is required for trafficking to lysosomes and biogenesis of pigment granules. J Cell Sci 118: 3663–3673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Peter A, Schottler P, Werner M, Beinert N, Dowe G, et al.. (2002) Supplementary material. PX-lines.txt. EMBO Reports.
- 73. Schuldiner O, Berdnik D, Levy JM, Wu JS, Luginbuhl D, et al. (2008) piggyBac-based mosaic screen identifies a postmitotic function for cohesin in regulating developmental axon pruning. Dev Cell 14: 227–238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Venken KJ, He Y, Hoskins RA, Bellen HJ (2006) P[acman]: a BAC transgenic platform for targeted insertion of large DNA fragments in D. melanogaster. Science 314: 1747–1751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Gustafson K, Boulianne GL (1996) Distinct expression patterns detected within individual tissues by the GAL4 enhancer trap technique. Genome 39: 174–182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Bischof J, Basler K (2008) Recombinases and their use in gene activation, gene inactivation, and transgenesis. Methods Mol Biol 420: 175–195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Satoh A, Tokunaga F, Kawamura S, Ozaki K (1997) In situ inhibition of vesicle transport and protein processing in the dominant negative Rab1 mutant of Drosophila. J Cell Sci 110 Pt 23: 2943–2953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Culi J, Mann RS (2003) Boca, an endoplasmic reticulum protein required for wingless signaling and trafficking of LDL receptor family members in Drosophila. Cell 112: 343–354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Lloyd TE, Atkinson R, Wu MN, Zhou Y, Pennetta G, et al. (2002) Hrs regulates endosome membrane invagination and tyrosine kinase receptor signaling in Drosophila. Cell 108: 261–269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Qi H, Rand MD, Wu X, Sestan N, Wang W, et al. (1999) Processing of the notch ligand delta by the metalloprotease Kuzbanian. Science 283: 91–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Parks AL, Klueg KM, Stout JR, Muskavitch MA (2000) Ligand endocytosis drives receptor dissociation and activation in the Notch pathway. Development 127: 1373–1385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Fehon RG, Kooh PJ, Rebay I, Regan CL, Xu T, et al. (1990) Molecular interactions between the protein products of the neurogenic loci Notch and Delta, two EGF-homologous genes in Drosophila. Cell 61: 523–534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Lai EC, Rubin GM (2001) neuralized functions cell-autonomously to regulate a subset of notch-dependent processes during adult Drosophila development. Dev Biol 231: 217–233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Shorter J, Watson R, Giannakou ME, Clarke M, Warren G, et al. (1999) GRASP55, a second mammalian GRASP protein involved in the stacking of Golgi cisternae in a cell-free system. Embo J 18: 4949–4960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. O'Neill EM, Rebay I, Tjian R, Rubin GM (1994) The activities of two Ets-related transcription factors required for Drosophila eye development are modulated by the Ras/MAPK pathway. Cell 78: 137–147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Blochlinger K, Bodmer R, Jan LY, Jan YN (1990) Patterns of expression of cut, a protein required for external sensory organ development in wild-type and cut mutant Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev 4: 1322–1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Oda H, Uemura T, Harada Y, Iwai Y, Takeichi M (1994) A Drosophila homolog of cadherin associated with armadillo and essential for embryonic cell-cell adhesion. Dev Biol 165: 716–726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Guo M, Bier E, Jan LY, Jan YN (1995) tramtrack acts downstream of numb to specify distinct daughter cell fates during asymmetric cell divisions in the Drosophila PNS. Neuron 14: 913–925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Schematic diagram and features of the three well-characterized PPTs. PPTs are heterodimers of α and β subunits. They can be subdivided into three types: FT, GGTI, and GGTII (also called RabGGT) based on the lipid length and target motif present on their substrate proteins. All these genes are conserved from yeast to human. Because the α subunits of PPTs contain PPTA subunit repeat motifs, the FTα is also called PTAR2 and RabGGTα is also called PTAR3. PPTs add prenyl lipids (15-carbon farnesyl or 20-carbon geranylgeranyl group) via a thioether linkage (-C-S-C-) to a cysteine residue of soluble proteins. FT and GGTI share the same α subunit for substrate recognition and have a unique β subunit. They recognize the CaaX motif (C for cysteine residue, a for aliphatic residues, X can be a wide range of residues) in the C-terminal region of various substrates, including lamins as well as many small GTPases such as Ras and Rho. On the other hand, GGTII does not require a specific C-terminal motif for recognition. Because all of its substrates identified to date are Rab proteins, it is also called RabGGT. It requires assistance from REP to recruit Rab substrates. The target motif on most of the Rab proteins contains two Cysteine residues, and both are conjugated with geranylgeranyl groups.
(TIF)
The cell fate transformation defect is not related to apoptosis in temp mutant clones. (A–B) At 27 h APF, there are some apoptotic cells (Caspase3-positive cells) in some tempA mutant clones (A). However, there is no obvious apoptosis in tempB mutant clones (B). (C–D) When an anti-apoptotic protein, p35, is overexpressed in tempA mutant clones (24 h APF) to suppress the apoptotic effect (C), we observe no obvious differences in phenotype (D) when we compare these clones with temp mutant clones without p35 expression. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
HA–Temp protein is localized diffusedly throughout the cytoplasm. HA–temp cDNA is expressed using dpp–Gal4 in the wing disc and HA–Temp is dispersed in the cytoplasm and does not seem to localize to any particular subcellular area. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
Accumulation of Sca in temp mutant is not restricted to notum ESOs. (A) Sca accumulates in the temp mutant ESOs at the anterior of wing margin in third instar wing imaginal discs. (B) Single section: Sca accumulates in temp mutant R8 photoreceptor cells in the third instar larval eye discs. (B′) Projection of (B). (C) In the temp mutant clones, the expression level of sca–lacZ does not change, whereas the protein level of Sca is up-regulated in sensory organs at the anterior of wing margin during third instar larval stage. (D) In the temp mutant clones, the expression level of sca–lacZ does not change and the protein level of Sca is up-regulated in R8 cells in the third instar larval eye discs. (E) In temp mutant ESO, Sca puncta largely colocalize with GRASP, which locates at both ER exit site (tER) and cis-Golgi compartments. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
The localization of Dl, but not Notch or D E-cadherin, is altered in temp mutant ESOs. (A) Total level of Notch (stained for NICD) is not changed in temp mutant clones. (B) Total level of Notch (stained for Notch extracellular domain) is not changed in temp mutant clones. (C) Extracellular level of Notch (stained for Notch extracellular domain without permeabilization) is not changed in temp mutant clones. (D) Many temp mutant ESOs exhibit increased total level of Dl puncta (yellow arrows and white arrows) compared to wt ESOs (red arrows). Dl in some temp mutant ESOs still localizes to the plasma membrane (white arrows), whereas Dl in other temp mutant ESOs can only be found intracellularly (yellow arrows). (E) Localization of DE-cadherin, an apically enriched transmembrane protein, is not affected in temp mutant clones. Asterisks (*) indicate folds in the notum where lower levels are artifactual. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
Dysfunction of Rab1 and Rab11 phenocopies loss-of-function of temp . (A) Sca accumulates in rab1 mutant sensory organs in the third instar larval wing disc, similar to the temp mutant phenotype. The rab1 clones are mostly cell lethal even when the neighboring tissue has the competitive disadvantage of having a Minute mutation. (B) Single section: Overexpression of Rab1DN causes accumulation of both Dl and Sca on the notum. White arrow, RablDN expressing ESO; yellow arrow, control ESO. Note that the RablDN-expressing ESO in the upper region exhibits a severe Sca accumulation, which can also occasionally be observed in temp mutant ESOs, whereas RablDN-expressing ESO in the lower region exhibits a less severe Sca accumulation (puncta) similar to what is usually observed in temp mutant ESOs. (C) Adult notum: Overexpression of Rab1DN on the notum causing minor balding occasionally (arrow). (D) Western blot: Endogenous expression level of Rab11 is not altered in tempA and tempD mutant larvae compared to mutant larvae with a genomic rescue transgene (control). (E) Single section: Overexpression of Rab11DN does not affect the expression of Sca in the notum. White arrow, Rab11DN-expressing ESO; yellow arrow, wt ESO. (F) Single section: In Rab11DN-expressing cells, Dl is mislocalized in the middle plane of the cells. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
Overexpression of constitutively active form of Rab1 and Rab11 does not restore the temp mutant phenotypes. (A–B) Overexpression of constitutively active forms of Rab1 (Rab1CA) either in control (iso19A) or temp mutant clones at 16–18 h APF: (A) Rab1CA overexpression in the control clones does not cause any phenotypes. (B) Rab1CA overexpression in the temp mutant clones does not rescue Sca accumulation. (C–D) Overexpression of constitutively active forms of Rab11 (Rab11CA) in either control (iso19A) or temp mutant clones at 27 h APF: (C) Rab11CA overexpression in control clones does not cause phenotypes. (D) Rab11CA overexpression in the temp mutant clones does not rescue the cell fate changes. Scale bars, 5 µm.
(TIF)
temp mRNA expression is highly enriched in the nervous system. The mRNA expression patterns of temp (CG3073) and RabGGTα (CG12007) are quite different in both larval and adult stages based on FlyAtlas data [65]. RabGGTα mRNA is transcribed at moderate level ubiquitously and temp mRNA is expressed highly in the nervous system, suggesting that Temp plays a role in the nervous system. This figure is adapted and modified from Flybase (http://flybase.org/) [66].
(TIF)
Sca accumulates in GM130-positive compartments in both temp mutant and Rab1DN -expressing notum clones. We used MARCM to express ER–YFP, Golgi–CFP, FYVE–GFP, and LAMP-1–GFP in temp mutant or wt clones. For other markers, we performed coimmunostaining using specific antibodies (see Materials and Methods). ER, endoplasmic reticulum. +, colocalization; +/−, minor colocalization; −, no obvious colocalization; N/A, not tested.
(TIF)
Summary of Rab screen for Sca accumulation and balding. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; EE, early endosome; PM, plasma membrane; LE, late endosome; TGN, trans Golgi network; RE, recycling endosome. +, positive, +/−, minor phenotype; −, no obvious phenotype; ND, not determined.
(TIF)