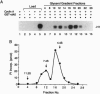
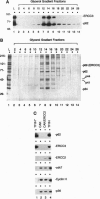
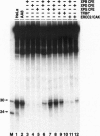
Abstract
Transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) is a multisubunit protein complex essential for both the initiation of RNA polymerase class II (pol II)-catalyzed transcription and nucleotide excision repair of DNA. Recent studies have shown that TFIIH copurifies with the cyclin-dependent kinase (cdk)-activating kinase complex (CAK) that includes cdk7, cyclin H, and p36/MAT1. Here we report the isolation of two TFIIH-related complexes: TFIIH* and ERCC2/CAK. TFIIH* consists of a subset of the TFIIH complex proteins including ERCC3 (XPB), p62, p44, p41, and p34 but is devoid of detectable levels of ERCC2 (XPD) and CAK. ERCC2/CAK was isolated as a complex that exhibits CAK activity that cosediments with the three CAK components (cdk7, cyclin H, and p36/MAT1) as well as the ERCC2 (XPD) protein. TFIIH* can support pol II-catalyzed transcription in vitro with lower efficiency compared with TFIIH. This TFIIH*-dependent transcription reaction was stimulated by ERCC2/CAK. The ERCC2/CAK and TFIIH* complexes are each active in DNA repair as shown by their ability to complement extracts prepared from ERCC2 (XPD)- and ERCC3 (XPB)-deficient cells, respectively, in supporting the excision of DNA containing a cholesterol lesion. These data suggest that TFIIH* and ERCC2/CAK interact to form the TFIIH holoenzyme capable of efficiently assembling the pol II transcription initiation complex and directly participating in excision repair reactions.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardwell L., Bardwell A. J., Feaver W. J., Svejstrup J. Q., Kornberg R. D., Friedberg E. C. Yeast RAD3 protein binds directly to both SSL2 and SSL1 proteins: implications for the structure and function of transcription/repair factor b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3926–3930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell-Crowley L., Solomon M. J., Wei N., Harper J. W. Phosphorylation independent activation of human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 by cyclin A in vitro. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Jan;4(1):79–92. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault A., Martinez A. M., Fesquet D., Labbé J. C., Morin N., Tassan J. P., Nigg E. A., Cavadore J. C., Dorée M. MAT1 ('menage à trois') a new RING finger protein subunit stabilizing cyclin H-cdk7 complexes in starfish and Xenopus CAK. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 16;14(20):5027–5036. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapkin R., Reardon J. T., Ansari A., Huang J. C., Zawel L., Ahn K., Sancar A., Reinberg D. Dual role of TFIIH in DNA excision repair and in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1994 Apr 21;368(6473):769–772. doi: 10.1038/368769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapkin R., Reinberg D. The multifunctional TFIIH complex and transcriptional control. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Nov;19(11):504–508. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Jin P., Chamberlin H. M., Morgan D. O. Alternative mechanisms of CAK assembly require an assembly factor or an activating kinase. Cell. 1995 Oct 6;83(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Morgan D. O. A novel cyclin associates with MO15/CDK7 to form the CDK-activating kinase. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90535-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Roeder R. G. Purification, cloning, and characterization of a human coactivator, PC4, that mediates transcriptional activation of class II genes. Cell. 1994 Aug 12;78(3):513–523. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich J. A., Tjian R. Transcription factors IIE and IIH and ATP hydrolysis direct promoter clearance by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90242-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzder S. N., Habraken Y., Sung P., Prakash L., Prakash S. Reconstitution of yeast nucleotide excision repair with purified Rad proteins, replication protein A, and transcription factor TFIIH. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 2;270(22):12973–12976. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.22.12973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzder S. N., Sung P., Bailly V., Prakash L., Prakash S. RAD25 is a DNA helicase required for DNA repair and RNA polymerase II transcription. Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):578–581. doi: 10.1038/369578a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Svoboda D. L., Reardon J. T., Sancar A. Human nucleotide excision nuclease removes thymine dimers from DNA by incising the 22nd phosphodiester bond 5' and the 6th phosphodiester bond 3' to the photodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humbert S., van Vuuren H., Lutz Y., Hoeijmakers J. H., Egly J. M., Moncollin V. p44 and p34 subunits of the BTF2/TFIIH transcription factor have homologies with SSL1, a yeast protein involved in DNA repair. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2393–2398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Ishimi Y., Kenny M. K., Bullock P., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. An inhibitor of the in vitro elongation reaction of simian virus 40 DNA replication is overcome by proliferating-cell nuclear antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9469–9473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma D., Watanabe H., Mermelstein F., Admon A., Oguri K., Sun X., Wada T., Imai T., Shiroya T., Reinberg D. Isolation of a cDNA encoding the largest subunit of TFIIA reveals functions important for activated transcription. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2246–2257. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., De Bondt H. L. Protein kinase regulation: insights from crystal structure analysis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;6(2):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mu D., Park C. H., Matsunaga T., Hsu D. S., Reardon J. T., Sancar A. Reconstitution of human DNA repair excision nuclease in a highly defined system. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 10;270(6):2415–2418. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.6.2415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan Z. Q., Reardon J. T., Li L., Flores-Rozas H., Legerski R., Sancar A., Hurwitz J. Inhibition of nucleotide excision repair by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):22008–22016. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.22008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. T., Thompson L. H., Sancar A. Excision repair in man and the molecular basis of xeroderma pigmentosum syndrome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:605–617. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy R., Adamczewski J. P., Seroz T., Vermeulen W., Tassan J. P., Schaeffer L., Nigg E. A., Hoeijmakers J. H., Egly J. M. The MO15 cell cycle kinase is associated with the TFIIH transcription-DNA repair factor. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1093–1101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A. Mechanisms of DNA excision repair. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):1954–1956. doi: 10.1126/science.7801120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L., Moncollin V., Roy R., Staub A., Mezzina M., Sarasin A., Weeda G., Hoeijmakers J. H., Egly J. M. The ERCC2/DNA repair protein is associated with the class II BTF2/TFIIH transcription factor. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2388–2392. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L., Roy R., Humbert S., Moncollin V., Vermeulen W., Hoeijmakers J. H., Chambon P., Egly J. M. DNA repair helicase: a component of BTF2 (TFIIH) basic transcription factor. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):58–63. doi: 10.1126/science.8465201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa H., Mäkelä T. P., Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C., Weinberg R. A., Young R. A. Association of Cdk-activating kinase subunits with transcription factor TFIIH. Nature. 1995 Mar 16;374(6519):280–282. doi: 10.1038/374280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiekhattar R., Mermelstein F., Fisher R. P., Drapkin R., Dynlacht B., Wessling H. C., Morgan D. O., Reinberg D. Cdk-activating kinase complex is a component of human transcription factor TFIIH. Nature. 1995 Mar 16;374(6519):283–287. doi: 10.1038/374283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon M. J., Lee T., Kirschner M. W. Role of phosphorylation in p34cdc2 activation: identification of an activating kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jan;3(1):13–27. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejstrup J. Q., Wang Z., Feaver W. J., Wu X., Bushnell D. A., Donahue T. F., Friedberg E. C., Kornberg R. D. Different forms of TFIIH for transcription and DNA repair: holo-TFIIH and a nucleotide excision repairosome. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90447-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Wood R. D. Xeroderma pigmentosum and nucleotide excision repair of DNA. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90040-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassan J. P., Jaquenoud M., Fry A. M., Frutiger S., Hughes G. J., Nigg E. A. In vitro assembly of a functional human CDK7-cyclin H complex requires MAT1, a novel 36 kDa RING finger protein. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 15;14(22):5608–5617. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Buratowski S., Svejstrup J. Q., Feaver W. J., Wu X., Kornberg R. D., Donahue T. F., Friedberg E. C. The yeast TFB1 and SSL1 genes, which encode subunits of transcription factor IIH, are required for nucleotide excision repair and RNA polymerase II transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;15(4):2288–2293. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.4.2288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Common themes in assembly and function of eukaryotic transcription complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:533–561. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]