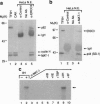
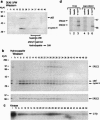
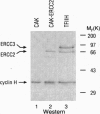
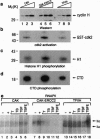
Abstract
Transcription factor IIH (TFIIH) is a multisubunit complex required for transcription and for DNA nucleotide excision repair. TFIIH possesses three enzymatic activities: (i) an ATP-dependent DNA helicase, (ii) a DNA-dependent ATPase, and (iii) a kinase with specificity for the carboxyl-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. The kinase activity was recently identified as the cdk (cyclin-dependent kinase) activating kinase, CAK, composed of cdk7, cyclin H, and MAT-1. Here we report the isolation and characterization of three distinct CAK-containing complexes from HeLa nuclear extracts: CAK, a novel CAK-ERCC2 complex, and TFIIH. CAK-ERCC2 can efficiently associate with core-TFIIH to reconstitute holo-TFIIH transcription activity. We present evidence proposing a critical role for ERCC2 in mediating the association of CAK with core TFIIH subunits.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akoulitchev S., Mäkelä T. P., Weinberg R. A., Reinberg D. Requirement for TFIIH kinase activity in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1995 Oct 12;377(6549):557–560. doi: 10.1038/377557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell L., Bardwell A. J., Feaver W. J., Svejstrup J. Q., Kornberg R. D., Friedberg E. C. Yeast RAD3 protein binds directly to both SSL2 and SSL1 proteins: implications for the structure and function of transcription/repair factor b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3926–3930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck V., Russell P., Millar J. B. Identification of a cdk-activating kinase in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1995 Dec 15;14(24):6173–6183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00308.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadena D. L., Dahmus M. E. Messenger RNA synthesis in mammalian cells is catalyzed by the phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12468–12474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cismowski M. J., Laff G. M., Solomon M. J., Reed S. I. KIN28 encodes a C-terminal domain kinase that controls mRNA transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae but lacks cyclin-dependent kinase-activating kinase (CAK) activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;15(6):2983–2992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.6.2983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahmus M. E. The role of multisite phosphorylation in the regulation of RNA polymerase II activity. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1994;48:143–179. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60855-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damagnez V., Mäkelä T. P., Cottarel G. Schizosaccharomyces pombe Mop1-Mcs2 is related to mammalian CAK. EMBO J. 1995 Dec 15;14(24):6164–6172. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00307.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault A., Martinez A. M., Fesquet D., Labbé J. C., Morin N., Tassan J. P., Nigg E. A., Cavadore J. C., Dorée M. MAT1 ('menage à trois') a new RING finger protein subunit stabilizing cyclin H-cdk7 complexes in starfish and Xenopus CAK. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 16;14(20):5027–5036. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapkin R., Reardon J. T., Ansari A., Huang J. C., Zawel L., Ahn K., Sancar A., Reinberg D. Dual role of TFIIH in DNA excision repair and in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1994 Apr 21;368(6473):769–772. doi: 10.1038/368769a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapkin R., Reinberg D. The multifunctional TFIIH complex and transcriptional control. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Nov;19(11):504–508. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaver W. J., Svejstrup J. Q., Henry N. L., Kornberg R. D. Relationship of CDK-activating kinase and RNA polymerase II CTD kinase TFIIH/TFIIK. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1103–1109. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90040-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. P., Jin P., Chamberlin H. M., Morgan D. O. Alternative mechanisms of CAK assembly require an assembly factor or an activating kinase. Cell. 1995 Oct 6;83(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Lu H., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Identification and characterization of factor IIH. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2786–2793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzder S. N., Qiu H., Sommers C. H., Sung P., Prakash L., Prakash S. DNA repair gene RAD3 of S. cerevisiae is essential for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1994 Jan 6;367(6458):91–94. doi: 10.1038/367091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inostroza J. A., Mermelstein F. H., Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Dr1, a TATA-binding protein-associated phosphoprotein and inhibitor of class II gene transcription. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):477–489. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90172-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Kornberg R. D. Interplay of positive and negative effectors in function of the C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2362–2366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Flores O., Weinmann R., Reinberg D. The nonphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II preferentially associates with the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10004–10008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Zawel L., Fisher L., Egly J. M., Reinberg D. Human general transcription factor IIH phosphorylates the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):641–645. doi: 10.1038/358641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O. Principles of CDK regulation. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):131–134. doi: 10.1038/374131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mu D., Hsu D. S., Sancar A. Reaction mechanism of human DNA repair excision nuclease. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 5;271(14):8285–8294. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.14.8285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mäkelä T. P., Parvin J. D., Kim J., Huber L. J., Sharp P. A., Weinberg R. A. A kinase-deficient transcription factor TFIIH is functional in basal and activated transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 23;92(11):5174–5178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.11.5174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma Y., Hashimoto S., Wang C. K., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Analysis of the role of TFIIE in basal transcription and TFIIH-mediated carboxy-terminal domain phosphorylation through structure-function studies of TFIIE-alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;15(9):4856–4866. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.9.4856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy R., Adamczewski J. P., Seroz T., Vermeulen W., Tassan J. P., Schaeffer L., Nigg E. A., Hoeijmakers J. H., Egly J. M. The MO15 cell cycle kinase is associated with the TFIIH transcription-DNA repair factor. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1093–1101. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A. DNA excision repair. Annu Rev Biochem. 1996;65:43–81. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.65.070196.000355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer L., Moncollin V., Roy R., Staub A., Mezzina M., Sarasin A., Weeda G., Hoeijmakers J. H., Egly J. M. The ERCC2/DNA repair protein is associated with the class II BTF2/TFIIH transcription factor. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2388–2392. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06522.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa H., Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. Phosphorylation of C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II is not required in basal transcription. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):371–374. doi: 10.1038/363371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa H., Mäkelä T. P., Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C., Weinberg R. A., Young R. A. Association of Cdk-activating kinase subunits with transcription factor TFIIH. Nature. 1995 Mar 16;374(6519):280–282. doi: 10.1038/374280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiekhattar R., Mermelstein F., Fisher R. P., Drapkin R., Dynlacht B., Wessling H. C., Morgan D. O., Reinberg D. Cdk-activating kinase complex is a component of human transcription factor TFIIH. Nature. 1995 Mar 16;374(6519):283–287. doi: 10.1038/374283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejstrup J. Q., Wang Z., Feaver W. J., Wu X., Bushnell D. A., Donahue T. F., Friedberg E. C., Kornberg R. D. Different forms of TFIIH for transcription and DNA repair: holo-TFIIH and a nucleotide excision repairosome. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):21–28. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90447-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassan J. P., Jaquenoud M., Fry A. M., Frutiger S., Hughes G. J., Nigg E. A. In vitro assembly of a functional human CDK7-cyclin H complex requires MAT1, a novel 36 kDa RING finger protein. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 15;14(22):5608–5617. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00248.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valay J. G., Simon M., Dubois M. F., Bensaude O., Facca C., Faye G. The KIN28 gene is required both for RNA polymerase II mediated transcription and phosphorylation of the Rpb1p CTD. J Mol Biol. 1995 Jun 9;249(3):535–544. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee A., Nichols M. A., Wu L., Hall F. L., Kobayashi R., Xiong Y. Molecular cloning of CDK7-associated human MAT1, a cyclin-dependent kinase-activating kinase (CAK) assembly factor. Cancer Res. 1995 Dec 15;55(24):6058–6062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A. RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:689–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Common themes in assembly and function of eukaryotic transcription complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:533–561. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawel L., Reinberg D. Initiation of transcription by RNA polymerase II: a multi-step process. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1993;44:67–108. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60217-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]