Abstract
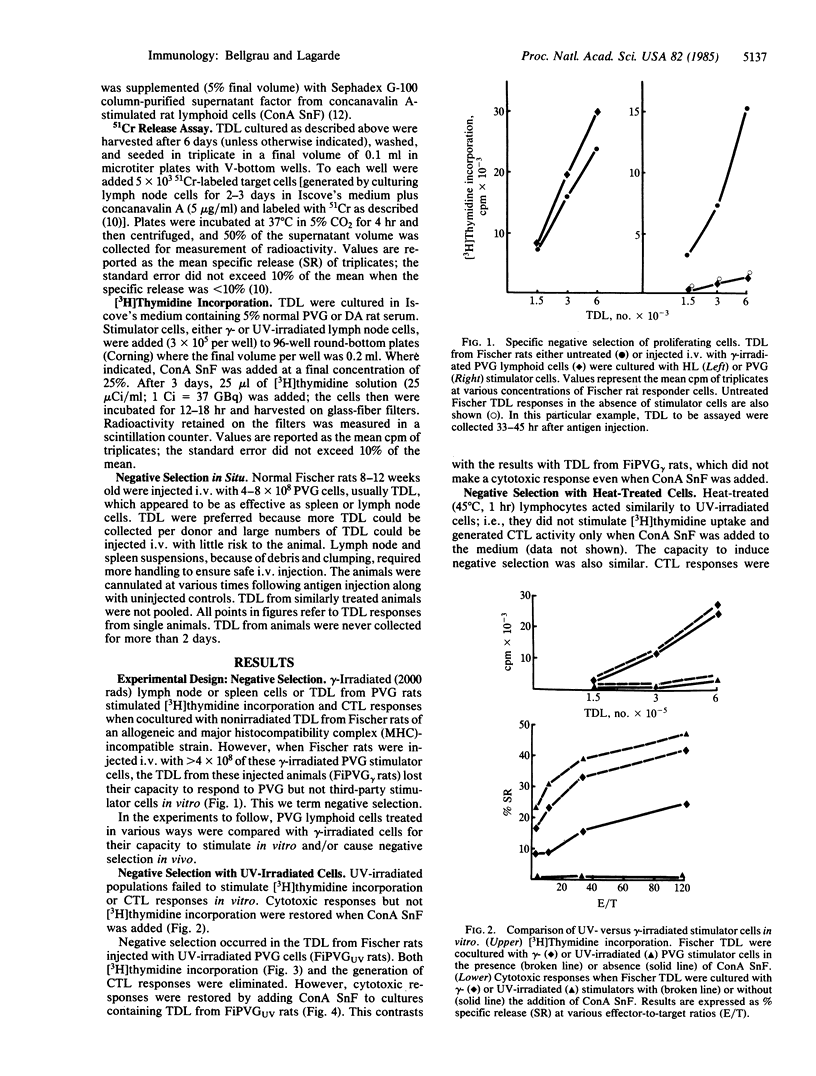
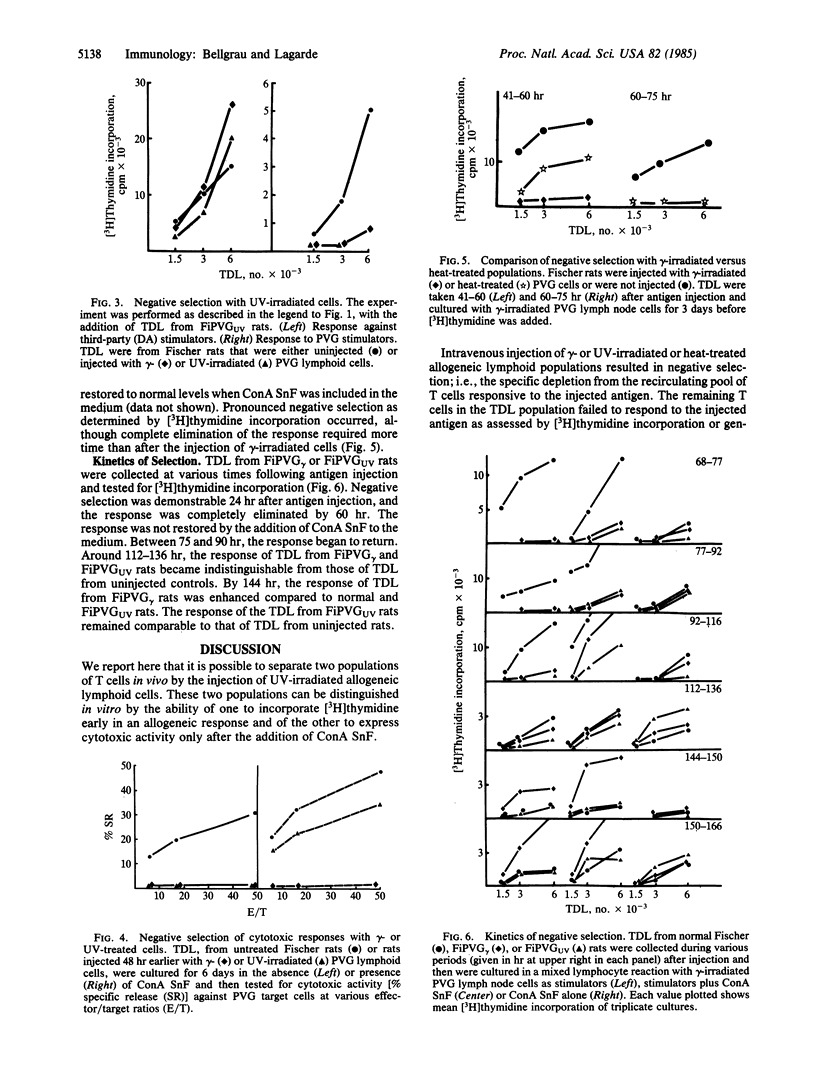
Negative selection occurred when gamma-irradiated lymphoid cells of rat strain PVG were injected intravenously into strain Fischer rats, which differ from PVG rats at the major histocompatibility complex. By 48 hr after injection, thoracic duct lymphocytes (TDL) from these animals failed to proliferate or generate cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) in vitro in response to gamma-irradiated PVG lymphoid cells. Responses to cells of a third rat strain were unaffected. By about 6 days after antigen injection, positive selection had occurred, as shown by enhanced responses to gamma-irradiated PVG cells in the same assays. Ultraviolet-irradiated strain PVG populations were tested in the same way. They differed from gamma-irradiated PVG cells in that they failed to induce proliferation or stimulate CTL in vitro. TDL from Fischer rats injected with UV-irradiated PVG cells failed to proliferate or generate CTL in response to gamma-irradiated PVG cells in vitro. The CTL response of TDL from rats injected with UV-irradiated cells was restored by the addition of supernatant factor(s) from concanavalin A-stimulated lymphoid cells (ConA SnF). Therefore, CTL precursors did not undergo negative selection after injection of UV-treated cells. There was also no detectable positive selection 6 days after injection of UV-treated cells. These experiments show that it is possible to separate two populations of T cells in vivo by the injection of UV-irradiated allogeneic lymphoid cells. One population incorporates [3H]thymidine early in an allogeneic response in vitro, the other expresses cytotoxic activity only after the addition of ConA SnF in vitro. The first population can replace the requirement for ConA SnF by the CTL population.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansel J., Luger T. A., Kock A., Hochstein D., Green I. The effect of in vitro UV irradiation on the production of IL 1 by murine macrophages and P388D1 cells. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1350–1355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach F. H., Bach M. L., Sondel P. M. Differential function of major histocompatibility complex antigens in T-lymphocyte activation. Nature. 1976 Jan 29;259(5541):273–281. doi: 10.1038/259273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellgrau D. Induction of cytotoxic T cell precursors in vivo. Role of T helper cells. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1505–1515. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Johnson H. M., Farrar J. J. Regulation of the production of immune interferon and cytotoxic T lymphocytes by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1120–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford W. L., Simmonds S. J., Atkins R. C. Early cellular events in a systemic graft-vs.-host reaction. II. Autoradiographic estimates of the frequency of donor lymphocytes which respond to each Ag-B-determined antigenic complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):681–696. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOWANS J. L. The recirculation of lymphocytes from blood to lymph in the rat. J Physiol. 1959 Apr 23;146(1):54–69. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin W. M., Weissman I. L., Butcher E. C. A cell-surface molecule involved in organ-specific homing of lymphocytes. Nature. 1983 Jul 7;304(5921):30–34. doi: 10.1038/304030a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grönvik K. O., Andersson J. The role of T cell growth stimulating factors in T cell triggering. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:35–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Melchers F. Complete replacement of serum by albumin, transferrin, and soybean lipid in cultures of lipopolysaccharide-reactive B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Mar 1;147(3):923–933. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.3.923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty K. J., Cunningham A. J. A new analysis of allogeneic interactions. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1975 Feb;53(1):27–42. doi: 10.1038/icb.1975.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L., Iscove N. N., Coutinho A. Two distinct factors are required for induction of T-cell growth. Nature. 1980 Feb 14;283(5748):664–666. doi: 10.1038/283664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer A., Kruisbeek A. M., Andrysiak P. M. T cell-accessory cell interactions that initiate allospecific cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses: existence of both Ia-restricted and Ia-unrestricted cellular interaction pathways. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2199–2209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J., Miller J. F. Interaction of thymus lymphocytes with histoincompatible cells. II. Recirculating lymphocytes derived from antigen-activated thymus cells. Cell Immunol. 1972 Mar;3(3):385–404. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90245-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L. Significance of class 1 and class 2 major histocompatibility complex antigens: help to allogeneic K and D antigens does not involve I recognition. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2307–2309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L. T cell subsets and the recognition of MHC class. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:129–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Marshak A., Howard J. C. SPECIFIC positive and negative selection of rat lymphocytes reactive to strong histocompatibility antigens: activation with alloantigens in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 1976 Apr;116(4):1030–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


