Abstract
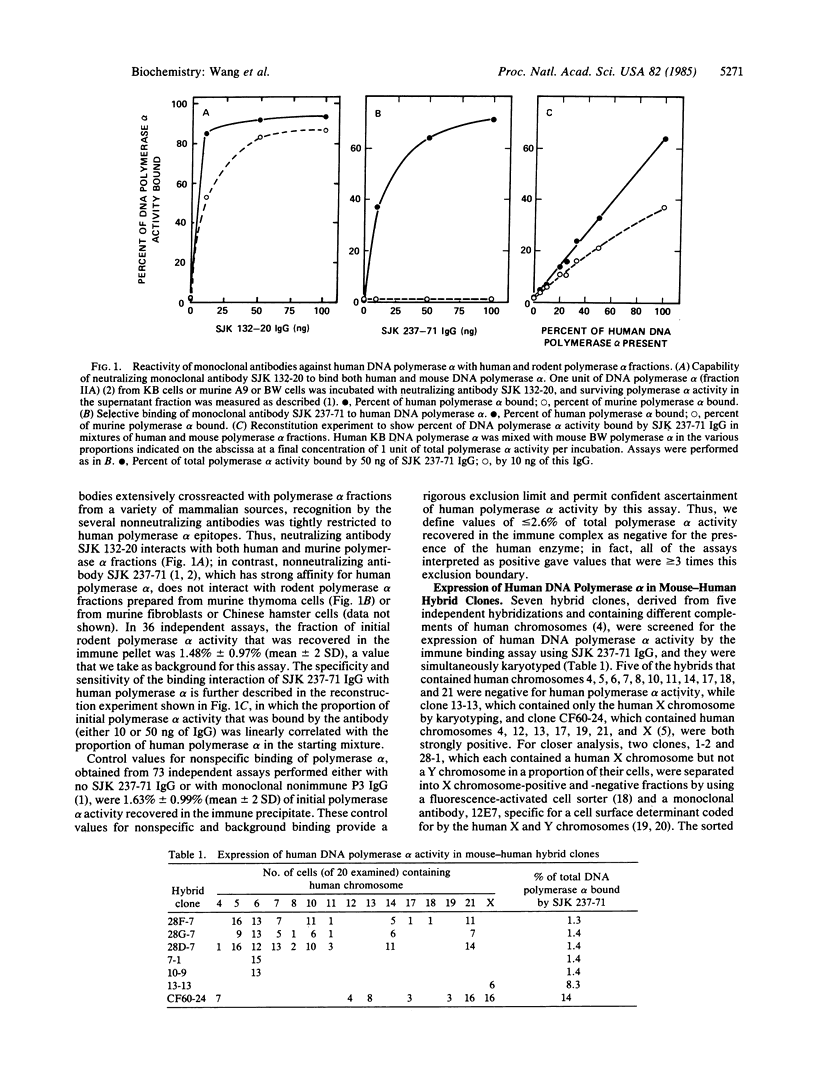
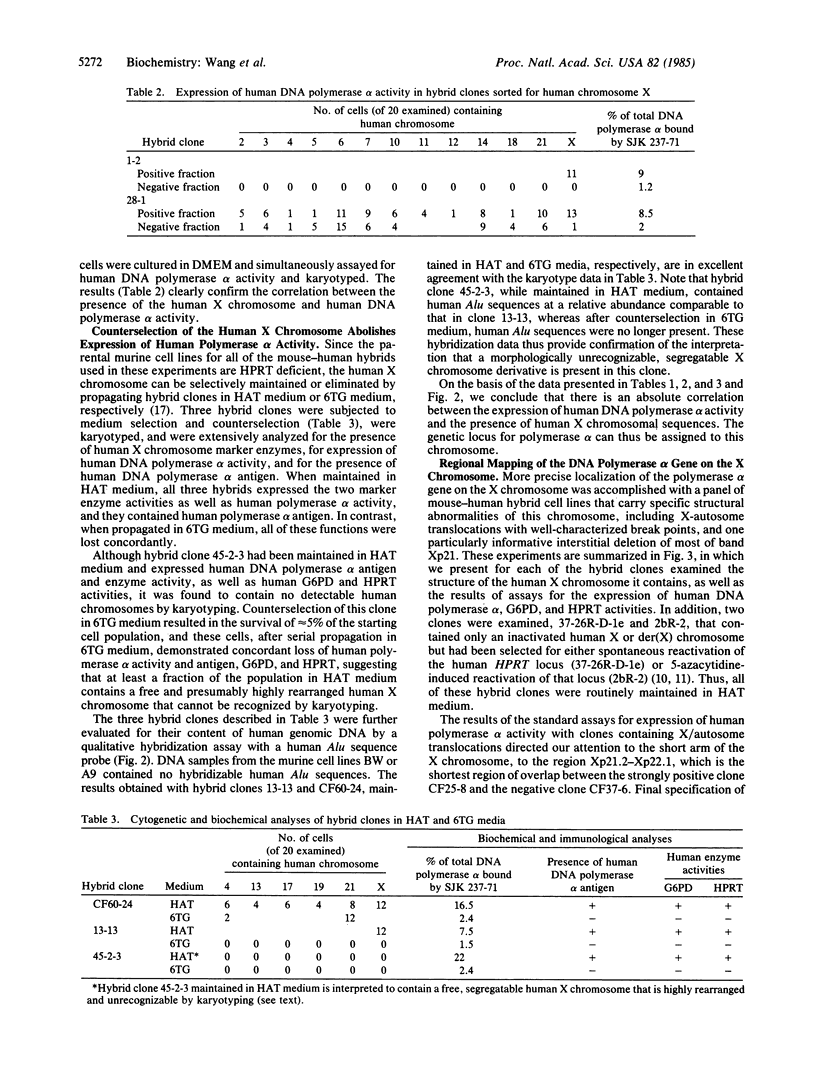
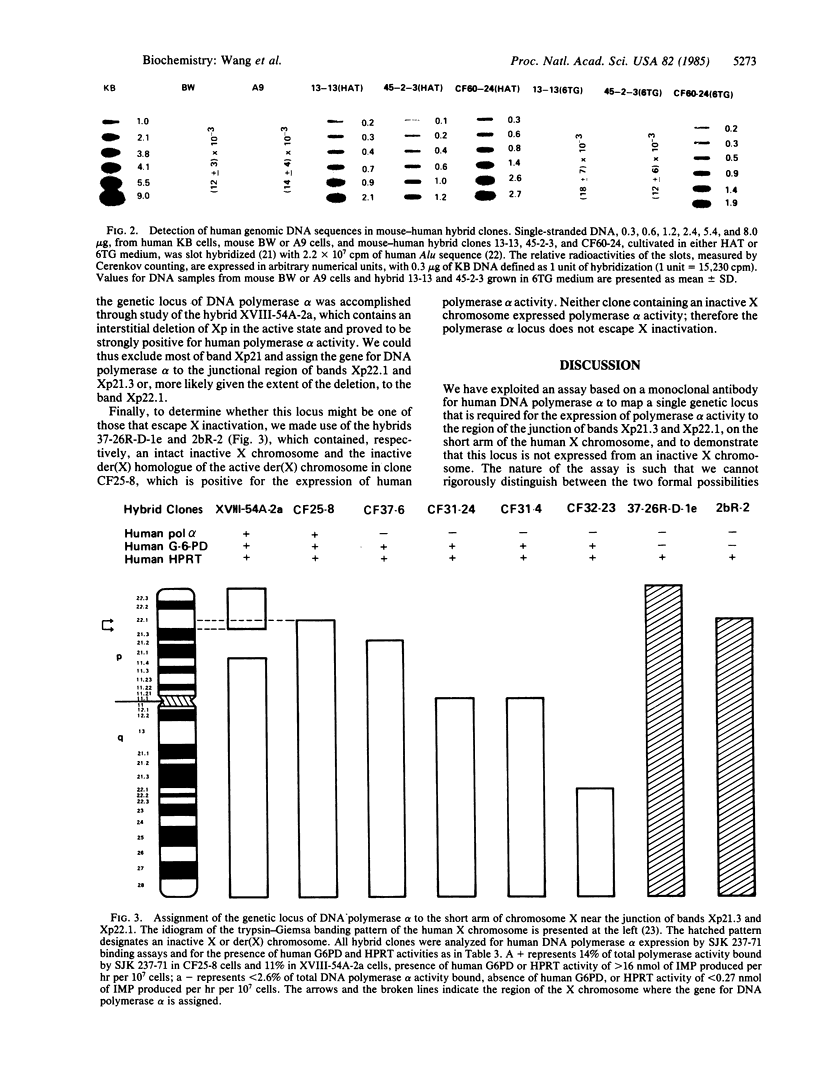
We have applied an assay based on a monoclonal antibody that discriminates the activity of human DNA polymerase alpha in rodent-human somatic cell hybrid clones to identify a single genetic locus that is both necessary and sufficient for the expression of DNA polymerase alpha. We have mapped this locus to the short arm of the human X chromosome, near the junction of bands Xp21.3 and Xp22.1, and demonstrated that it is not expressed from an inactive X chromosome.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold W. J., Kelley W. N. Human hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Purification and subunit structure. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7398–7404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. H., Jagadeeswaran P., Wang R. R., Weissman S. M. Structural analysis of templates and RNA polymerase III transcripts of Alu family sequences interspersed among the human beta-like globin genes. Gene. 1981 Mar;13(2):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U. Random X inactivation resulting in mosaic nullisomy of region Xp21.1----p21.3 associated with heterozygosity for ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency and for chronic granulomatous disease. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(4):298–307. doi: 10.1159/000132078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P., Banting G., Levy R., Povey S., McMichael A. A human X-linked antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Nov;6(6):777–787. doi: 10.1007/BF01538976. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P., Pym B., Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J. The cell surface antigen locus, MIC2X, escapes X-inactivation. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jul;36(4):777–782. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenstein R. M., Reardon M. P., Chan T. S., Middleton A. B., Mulivor R. A., Greene A. E., Coriell L. L. An (X;11) translocation in a girl with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Repository identification No. GM1695. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(4):268–268. doi: 10.1159/000131496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. Z., Wang T. S., Korn D. DNA primase from KB cells. Evidence for a novel model of primase catalysis by a highly purified primase/polymerase-alpha complex. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2602–2609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeeswaran P., Lavelle D. E., Kaul R., Mohandas T., Warren S. T. Isolation and characterization of human factor IX cDNA: identification of Taq I polymorphism and regional assignment. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1984 Sep;10(5):465–473. doi: 10.1007/BF01534851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren V., de Martinville B., Horwich A. L., Rosenberg L. E., Francke U. Human ornithine transcarbamylase locus mapped to band Xp21.1 near the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Science. 1984 Nov 9;226(4675):698–700. doi: 10.1126/science.6494904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P. Enzyme electrophoresis on cellulose acetate gel: zymogram patterns in mgh-mouse and man--Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Aug;145(2):470–483. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(71)80007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller O. J., Drayna D., Goodfellow P. Report of the Committee on the Genetic Constitution of the X and Y Chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;37(1-4):176–204. doi: 10.1159/000132009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Shapiro L. J., Sparkes R. S., Sparkes M. C. Regional assignment of the steroid sulfatase-X-linked ichthyosis locus: implications for a noninactivated region on the short arm of human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5779–5783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Hellkuhl B., Grzeschik K. H., Shapiro L. J. Expression of an X-linked gene from an inactive human X chromosome in mouse-human hybrid cells: further evidence for the noninactivation of the steroid sulfatase locus in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6759–6763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Shapiro L. J. Genetic evidence for the inactivation of a human autosomal locus attached to an inactive X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1982 Sep;34(5):811–817. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Shapiro L. J. Reactivation of an inactive human X chromosome: evidence for X inactivation by DNA methylation. Science. 1981 Jan 23;211(4480):393–396. doi: 10.1126/science.6164095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai G. S., Sprenkle J. A., Do T. T., Mareni C. E., Migeon B. R. Localization of loci for hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and biochemical evidence of nonrandom X chromosome expression from studies of a human X-autosome translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2810–2813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J., Nikinmaa B., Kavathas P., Herzenberg L. A. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting of mouse-human hybrid cells aids in locating the gene for the Leu 7 (HNK-1) antigen to human chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3421–3424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seabright M. A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1971 Oct 30;2(7731):971–972. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen H. A., Goldsby R. A., Osborne B. A., Schröder J. Mouse/human T-cell hybrids rosetting with sheep erythrocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1980;11(2):163–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Hu S. Z., Wang T. S., Korn D. Preparation and preliminary characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human DNA polymerase alpha. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8386–8390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Hu S. Z., Korn D. DNA primase from KB cells. Characterization of a primase activity tightly associated with immunoaffinity-purified DNA polymerase-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1854–1865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyandt H. E., Wysham D. G., Minden S. K., Anderson R. S., Hecht F. Mechanisms of giemsa banding of chromosomes. I. Giemsa-11 banding with azure and eosin. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Oct 1;102(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90302-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]