Abstract
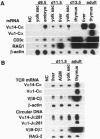
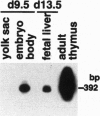
The majority of T lymphocytes start to develop at around day 15 of gestation (d15)-d17 in the thymus and comprise the peripheral repertoire characterized by the expression of polymorphic T-cell antigen receptors (TCRs). Contrary to these conventional T cells, a subset of T cells, called natural killer (NK) T cells (most of them expressing an invariant TCR encoded by the Valpha14Jalpha281 gene with a 1-nt N-region), preferentially differentiates extrathymically and dominates the peripheral T-cell population at a high frequency (5% in splenic T cells and 40% in bone marrow T cells). Here, we investigated the development of NK T cells and found that the invariant Valpha14+ TCR transcripts and the circular DNA created by Valpha14 and Jalpha281 gene rearrangements can be detected in the embryo body at d9.5 of gestation and in the yolk sac and the fetal liver at d11.5-d13.5 of gestation, but not in the thymus, whereas T cells with Valpha1+ TCR expression, a major population in the thymus, were not observed at these early stages of gestation. Fluorescence-activated cell sorter analysis also demonstrated that there exist CD3+ alpha beta+ T cells, almost all of which are Valpha14/Vbeta8+ NK+ T cells, during early embryogenesis. To our knowledge, this demonstrates for the first time that a T lymphocyte subset develops in extrathymic tissues during the early stages of embryogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi Y., Koseki H., Zijlstra M., Taniguchi M. Positive selection of invariant V alpha 14+ T cells by non-major histocompatibility complex-encoded class I-like molecules expressed on bone marrow-derived cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 14;92(4):1200–1204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.4.1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Baltimore D. Joining of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene segments: implications from a chromosome with evidence of three D-JH fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4118–4122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballas Z. K., Rasmussen W. NK1.1+ thymocytes. Adult murine CD4-, CD8- thymocytes contain an NK1.1+, CD3+, CD5hi, CD44hi, TCR-V beta 8+ subset. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1039–1045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendelac A., Killeen N., Littman D. R., Schwartz R. H. A subset of CD4+ thymocytes selected by MHC class I molecules. Science. 1994 Mar 25;263(5154):1774–1778. doi: 10.1126/science.7907820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bix M., Coles M., Raulet D. Positive selection of V beta 8+ CD4-8- thymocytes by class I molecules expressed by hematopoietic cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):901–908. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clevers H., Alarcon B., Wileman T., Terhorst C. The T cell receptor/CD3 complex: a dynamic protein ensemble. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:629–662. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.003213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Bjorkman P. J. T-cell antigen receptor genes and T-cell recognition. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):395–402. doi: 10.1038/334395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes B. J., Kruisbeek A. M., Ton-That H., Weston M. A., Coligan J. E., Schwartz R. H., Pardoll D. M. A novel population of T-cell receptor alpha beta-bearing thymocytes which predominantly expresses a single V beta gene family. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):251–254. doi: 10.1038/329251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilfillan S., Dierich A., Lemeur M., Benoist C., Mathis D. Mice lacking TdT: mature animals with an immature lymphocyte repertoire. Science. 1993 Aug 27;261(5125):1175–1178. doi: 10.1126/science.8356452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godin I. E., Garcia-Porrero J. A., Coutinho A., Dieterlen-Lièvre F., Marcos M. A. Para-aortic splanchnopleura from early mouse embryos contains B1a cell progenitors. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):67–70. doi: 10.1038/364067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Carmack C. E., Li Y. S., Hayakawa K. Distinctive developmental origins and specificities of murine CD5+ B cells. Immunol Rev. 1994 Feb;137:91–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1994.tb00660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto W., Takeda K., Anzai R., Ogasawara K., Sakihara H., Sugiura K., Seki S., Kumagai K. Cytotoxic NK1.1 Ag+ alpha beta T cells with intermediate TCR induced in the liver of mice by IL-12. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4333–4340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta K., Uchida N., Friedman J., Weissman I. L. Lymphocyte development from stem cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:759–783. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.003551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai K., Kanno M., Kimoto H., Shigemoto K., Yamamoto S., Taniguchi M. Sequence and expression of transcripts of the T-cell antigen receptor alpha-chain gene in a functional, antigen-specific suppressor-T-cell hybridoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8708–8712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Ishibashi K., Imai K., Koseki H., Ra C. S., Fernandez E., Kantake M., Saito T., Taniguchi M. Monoclonal antibody against murine T cell receptor V alpha 14 cross-reacts with human CD3 epsilon and detects disulfide-linked dimeric form. Int Immunol. 1991 Oct;3(10):991–995. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.10.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori T., Okada A., Stewart V., Alt F. W. Lack of N regions in antigen receptor variable region genes of TdT-deficient lymphocytes. Science. 1993 Aug 27;261(5125):1171–1175. doi: 10.1126/science.8356451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koseki H., Asano H., Inaba T., Miyashita N., Moriwaki K., Lindahl K. F., Mizutani Y., Imai K., Taniguchi M. Dominant expression of a distinctive V14+ T-cell antigen receptor alpha chain in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7518–7522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koseki H., Imai K., Nakayama F., Sado T., Moriwaki K., Taniguchi M. Homogenous junctional sequence of the V14+ T-cell antigen receptor alpha chain expanded in unprimed mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5248–5252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafaille J. J., DeCloux A., Bonneville M., Takagaki Y., Tonegawa S. Junctional sequences of T cell receptor gamma delta genes: implications for gamma delta T cell lineages and for a novel intermediate of V-(D)-J joining. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):859–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90609-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lantz O., Bendelac A. An invariant T cell receptor alpha chain is used by a unique subset of major histocompatibility complex class I-specific CD4+ and CD4-8- T cells in mice and humans. J Exp Med. 1994 Sep 1;180(3):1097–1106. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.3.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitsky H. I., Golumbek P. T., Pardoll D. M. The fate of CD4-8- T cell receptor-alpha beta+ thymocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1113–1117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino Y., Kanno R., Ito T., Higashino K., Taniguchi M. Predominant expression of invariant V alpha 14+ TCR alpha chain in NK1.1+ T cell populations. Int Immunol. 1995 Jul;7(7):1157–1161. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.7.1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino Y., Yamagata N., Sasho T., Adachi Y., Kanno R., Koseki H., Kanno M., Taniguchi M. Extrathymic development of V alpha 14-positive T cells. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1399–1408. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcos M. A., Godin I., Cumano A., Morales S., Garcia-Porrero J. A., Dieterlen-Lievre F., Gaspar M. L. Developmental events from hemopoietic stem cells to B-cell populations and Ig repertoires. Immunol Rev. 1994 Feb;137:155–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1994.tb00663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medvinsky A. L., Samoylina N. L., Müller A. M., Dzierzak E. A. An early pre-liver intraembryonic source of CFU-S in the developing mouse. Nature. 1993 Jul 1;364(6432):64–67. doi: 10.1038/364064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombaerts P., Iacomini J., Johnson R. S., Herrup K., Tonegawa S., Papaioannou V. E. RAG-1-deficient mice have no mature B and T lymphocytes. Cell. 1992 Mar 6;68(5):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90030-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki-Hamazaki H., Makino Y., Kanno M., Koseki H., Akasaka T., Taniguchi M. TCR repertoire in early fetal mouse thymus. Int Immunol. 1995 Mar;7(3):493–499. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.3.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Imhof B. A. At day 8-8.5 of mouse development the yolk sac, not the embryo proper, has lymphoid precursor potential in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6581–6585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz D. G., Oettinger M. A., Baltimore D. The V(D)J recombination activating gene, RAG-1. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1035–1048. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90760-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L. Developmental biology of T cell receptors. Science. 1989 May 26;244(4907):943–950. doi: 10.1126/science.2658058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sykes M. Unusual T cell populations in adult murine bone marrow. Prevalence of CD3+CD4-CD8- and alpha beta TCR+NK1.1+ cells. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3209–3215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahama Y., Kosugi A., Singer A. Phenotype, ontogeny, and repertoire of CD4-CD8- T cell receptor alpha beta + thymocytes. Variable influence of self-antigens on T cell receptor V beta usage. J Immunol. 1991 Feb 15;146(4):1134–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Dennert G. The development of autoimmunity in C57BL/6 lpr mice correlates with the disappearance of natural killer type 1-positive cells: evidence for their suppressive action on bone marrow stem cell proliferation, B cell immunoglobulin secretion, and autoimmune symptoms. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):155–164. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankelevich B., Knobloch C., Nowicki M., Dennert G. A novel cell type responsible for marrow graft rejection in mice. T cells with NK phenotype cause acute rejection of marrow grafts. J Immunol. 1989 May 15;142(10):3423–3430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]