Abstract
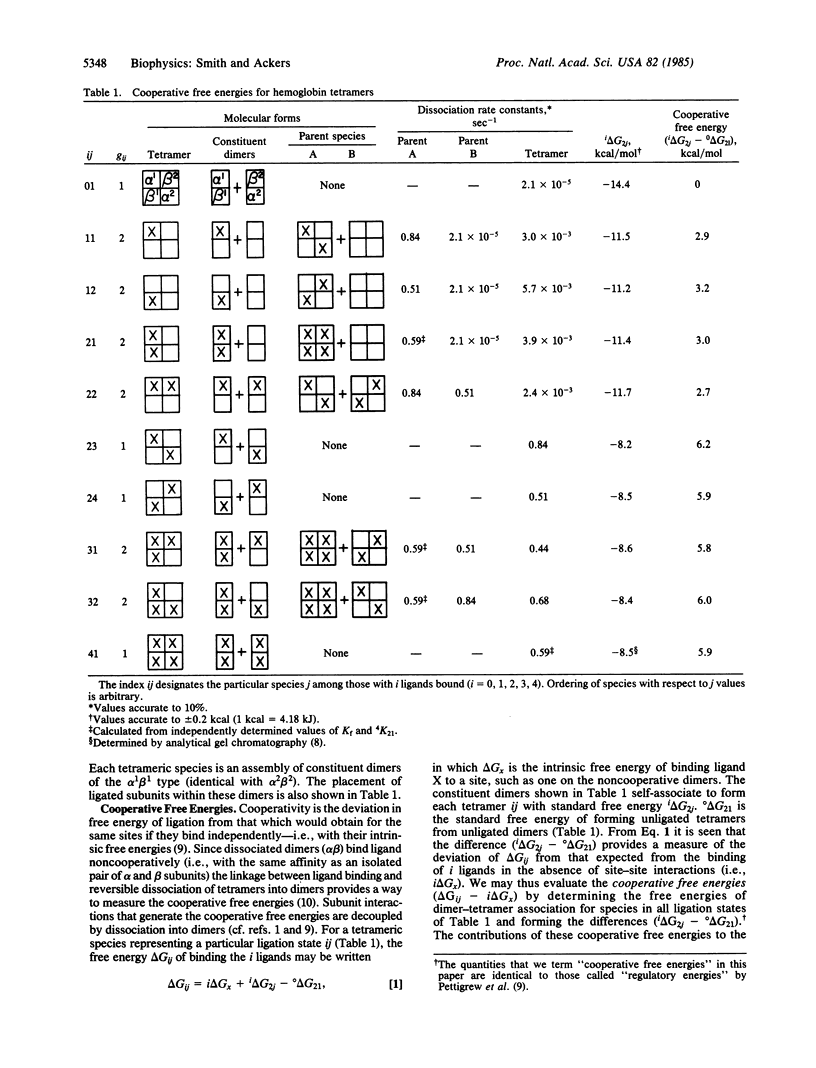
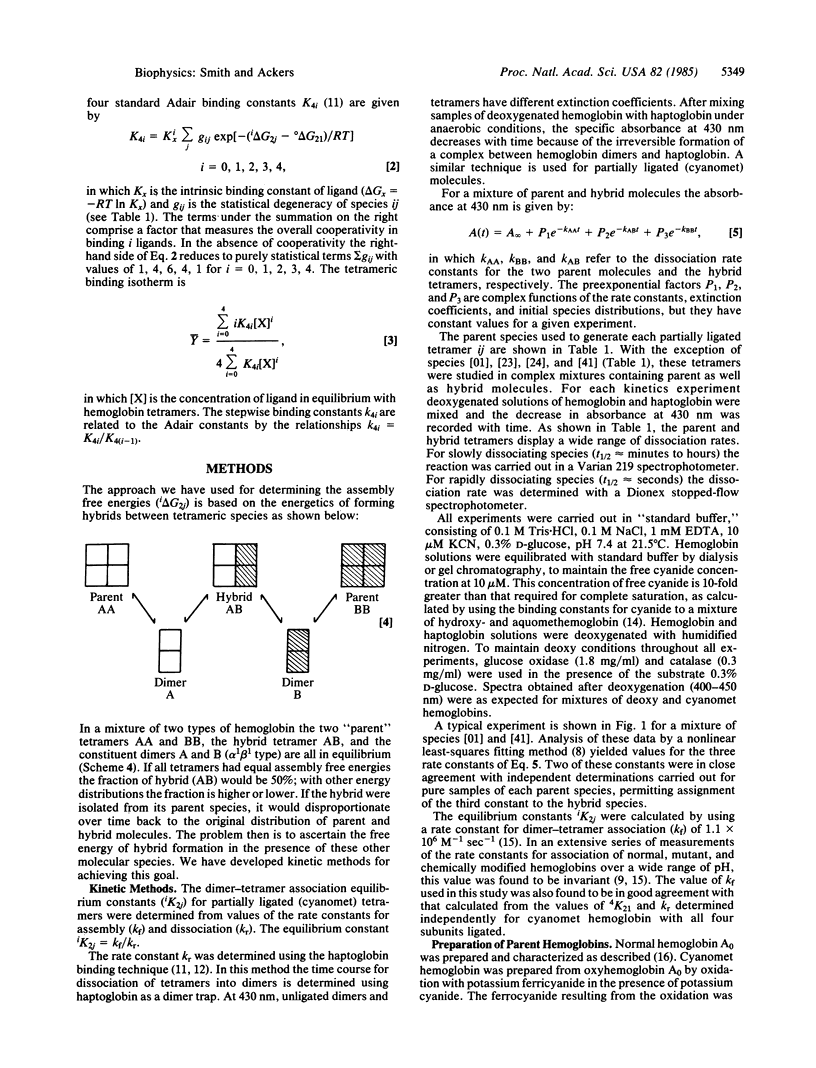
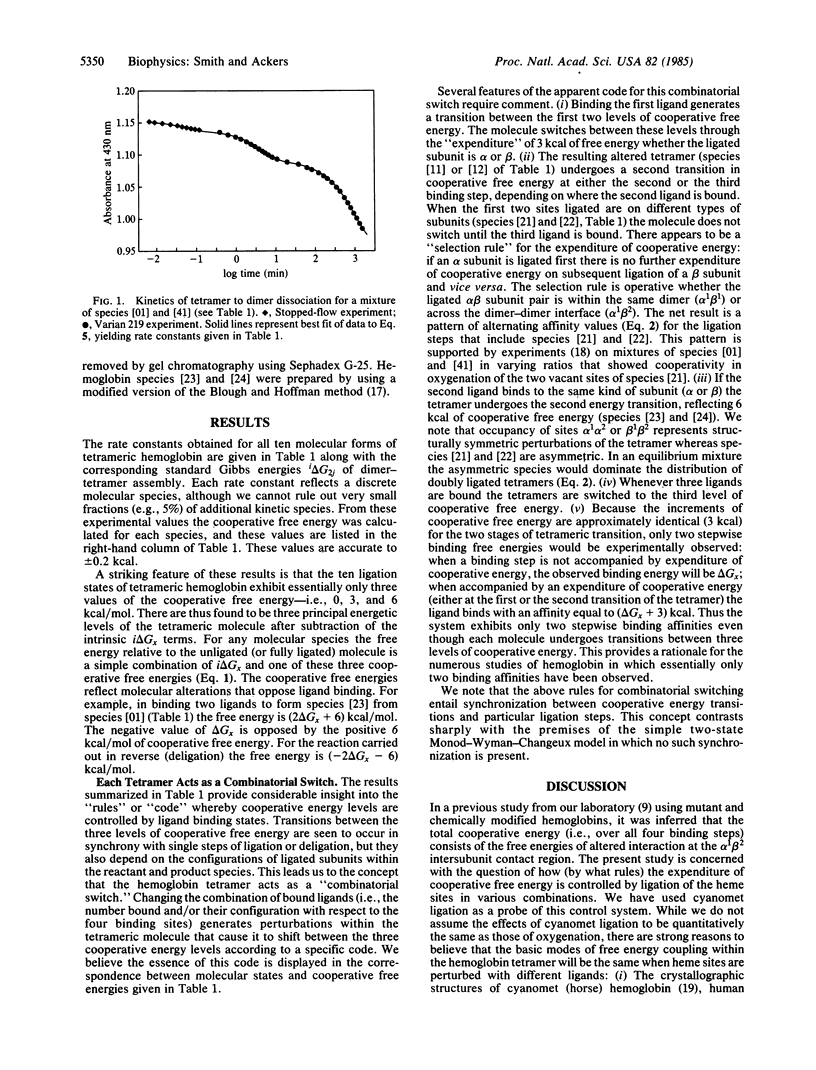
Tetrameric human hemoglobin can assume ten molecular forms that differ in the number and configuration of ligands bound at the four heme sites. For each of these species we have determined the cooperative free energy--i.e., the deviation in free energy of ligation from that which would obtain for the same sites binding as independent alpha and beta subunits. These cooperative free energies were resolved from measurements on the dissociation into dimers of tetramers in which each subunit is either unligated (Fe2+ deoxy) or "ligated" by conversion into the cyanomet form (Fe3+ CN). The results indicate that each hemoglobin tetramer acts as a three-level molecular switch. During the course of ligation, the total cooperative free energy (6 kcal/mol over all four binding steps) is expended in two transitions that are synchronized with particular ligation steps. Whether a cooperative energy transition occurs or not depends upon how the ligation step changes both the number and configuration of ligated subunits. The hemoglobin tetramer is thus a "combinatorial switch." The finding of three distinct free energy levels for the ten ligation states suggests the existence of three major structural forms of the hemoglobin tetramer.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackers G. K., Halvorson H. R. The linkage between oxygenation and subunit dissociation in human hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4312–4316. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackers G. K., Johnson M. L. Linked functions in allosteric proteins. Extension of the concerted (MWC) model for ligand-linked subunit assembly and its application to human hemoglobins. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 25;147(4):559–582. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90400-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. Intermediate structure of normal human haemoglobin: methaemoglobin in the deoxy quaternary conformation. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 25;79(3):495–506. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J., Chothia C. Haemoglobin: the structural changes related to ligand binding and its allosteric mechanism. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 5;129(2):175–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blough N. V., Hoffman B. M. Carbon monoxide binding to the ferrous chains of [Mn,Fe(II)] hybrid hemoglobins: pH dependence of the chain affinity constants associated with specific hemoglobin ligation pathways. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 19;23(13):2875–2882. doi: 10.1021/bi00308a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassoly R. Use of nitric oxide as a probe for assessing the formation of asymmetrical hemoglobin hybrids. An attempted comparison between alphaNObetaNOalphadeoxybetadeoxy, alpha2NObeta2deoxy, and alpha2deoxybeta2NO hybrids. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3602–3606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu A. H., Ackers G. K. Mutual effects of protons, NaCl, and oxygen on the dimer-tetramer assembly of human hemoglobin. The dimer Bohr effect. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1199–1205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deatherage J. F., Loe R. S., Anderson C. M., Moffat K. Structure of cyanide methemoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):687–706. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fermi G., Perutz M. F., Shaanan B., Fourme R. The crystal structure of human deoxyhaemoglobin at 1.74 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1984 May 15;175(2):159–174. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90472-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzfeld J., Stanley H. E. A general approach to co-operativity and its application to the oxygen equilibrium of hemoglobin and its effectors. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 15;82(2):231–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90343-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip S. H., Ackers G. K. Thermodynamic studies on subunit assembly in human hemoglobin. Temperature dependence of the dimer-tetramer association constants for oxygenated and unliganded hemoglobins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):82–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip S. H., Johnson M. L., Ackers G. K. Kinetics of deoxyhemoglobin subunit dissociation determined by haptoglobin binding: estimation of the equilibrium constant from forward and reverse rates. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):654–660. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. L., Turner B. W., Ackers G. K. A quantitative model for the cooperative mechanism of human hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1093–1097. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Némethy G., Filmer D. Comparison of experimental binding data and theoretical models in proteins containing subunits. Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):365–385. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura S., Ho C. Preparation and proton nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of cross-linked mixed valency hybrid hemoglobins: models for partially oxygenated species. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6280–6287. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S., Shulman R. G. High resolution nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of hemoglobin. 3. The half-ligated state and allosteric interactions. J Mol Biol. 1972 Sep 28;70(2):315–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90542-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrella M., Benazzi L., Cremonesi L., Vesely S., Viggiano G., Rossi-Bernardi L. Isolation of intermediate compounds between hemoglobin and carbon monoxide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4511–4517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettigrew D. W., Romeo P. H., Tsapis A., Thillet J., Smith M. L., Turner B. W., Ackers G. K. Probing the energetics of proteins through structural perturbation: sites of regulatory energy in human hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaanan B. Structure of human oxyhaemoglobin at 2.1 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 25;171(1):31–59. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo A., Karplus M. A mathematical model for structure-function relations in hemoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 14;72(1):163–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. W., Pettigrew D. W., Ackers G. K. Measurement and analysis of ligand-linked subunit dissociation equilibria in human hemoglobins. Methods Enzymol. 1981;76:596–628. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)76147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Jr, Tsay K. Y. A convenient chromatographic method for the preparation of human hemoglobin. Anal Biochem. 1973 Jul;54(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90256-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



