Abstract
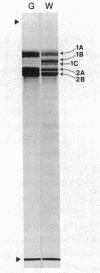
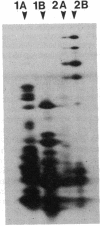
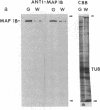
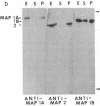
The major nontubulin proteins in purified brain microtubules are high molecular weight species traditionally classified into two groups known as microtubule-associated proteins 1 and 2 (MAP 1 and MAP 2). In an earlier study, we found that MAP 1 consisted of a complex of polypeptides and we characterized the highest molecular weight species--MAP 1A--with the use of a monoclonal antibody. In the current report, we describe four monoclonal antibodies raised against electrophoretically purified MAP 1B. All of the antibodies reacted exclusively with this protein. Together with peptide mapping, these results indicated that MAP 1B was structurally distinct from the other MAPs. Another distinctive property of MAP 1B was that most of it remained soluble during microtubule polymerization, resulting in an extreme underestimate of its abundance in the brain. Immunofluorescence microscopy of rat brain sections and cultured rat brain cells indicated that compared to MAP 1A and MAP 2, MAP 1B was particularly prominent in axonal as well as dendritic processes. Together, these data indicate that MAP 1B is a major, previously undescribed component of the neuronal cytoskeleton.
Full text
PDF


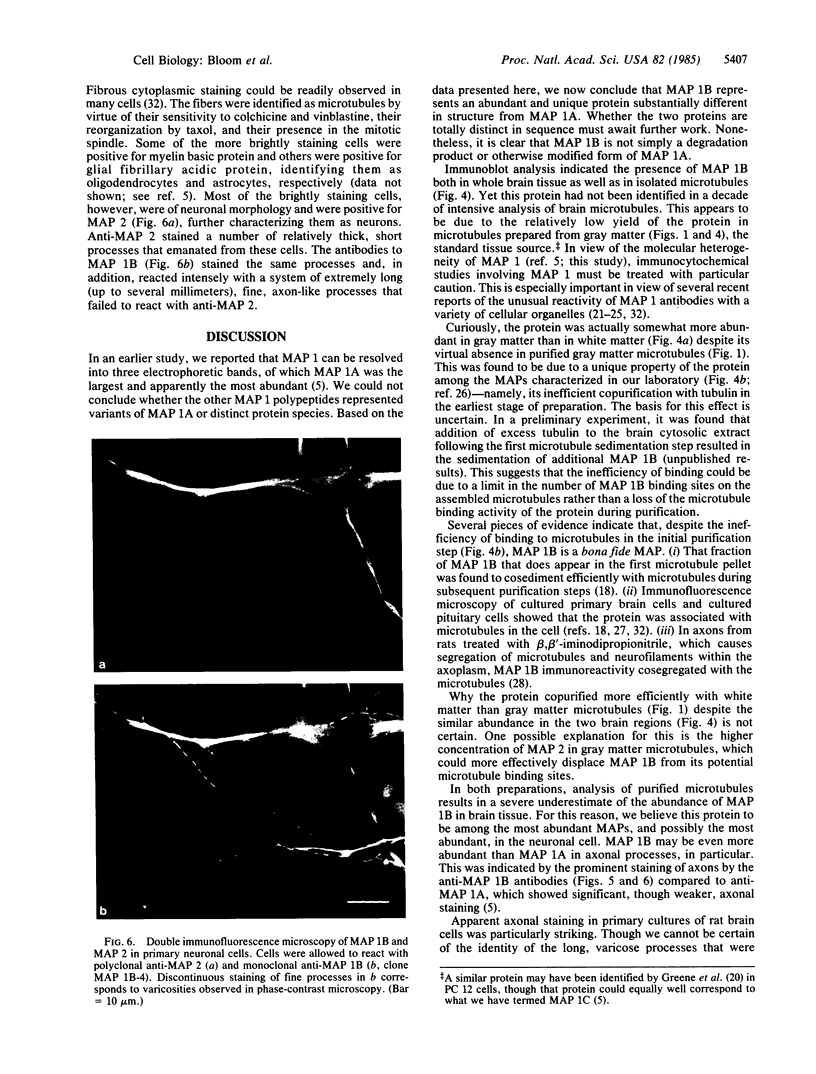

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asai D. J., Thompson W. C., Wilson L., Dresden C. F., Schulman H., Purich D. L. Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs): a monoclonal antibody to MAP 1 decorates microtubules in vitro but stains stress fibers and not microtubules in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1434–1438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Luca F. C., Vallee R. B. Identification of high molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins in anterior pituitary tissue and cells using taxol-dependent purification combined with microtubule-associated protein specific antibodies. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):4185–4191. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Luca F. C., Vallee R. B. Widespread cellular distribution of MAP-1A (microtubule-associated protein 1A) in the mitotic spindle and on interphase microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):331–340. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Schoenfeld T. A., Vallee R. B. Widespread distribution of the major polypeptide component of MAP 1 (microtubule-associated protein 1) in the nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):320–330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom G. S., Vallee R. B. Association of microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP 2) with microtubules and intermediate filaments in cultured brain cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1523–1531. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D., Sandoval I. V. A widely distributed nuclear protein immunologically related to the microtubule-associated protein MAP1 is associated with the mitotic spindle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1146–1150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Cumming R. Ontogeny of microtubule-associated protein 2 in rat cerebellum: differential expression of the doublet polypeptides. Neuroscience. 1984 Jan;11(1):156–167. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caceres A., Banker G., Steward O., Binder L., Payne M. MAP2 is localized to the dendrites of hippocampal neurons which develop in culture. Brain Res. 1984 Apr;315(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(84)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Miller P. E., Navone F., Theurkauf W. E., Vallee R. B. Distribution of microtubule-associated protein 2 in the nervous system of the rat studied by immunofluorescence. Neuroscience. 1984 Apr;11(4):817–846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dentler W. L., Granett S., Rosenbaum J. L. Ultrastructural localization of the high molecular weight proteins associated with in vitro-assembled brain microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1975 Apr;65(1):237–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellisman M. H., Porter K. R. Microtrabecular structure of the axoplasmic matrix: visualization of cross-linking structures and their distribution. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):464–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Liem R. K., Shelanski M. L. Regulation of a high molecular weight microtubule-associated protein in PC12 cells by nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):76–83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Bloom G. S., Vallee R. B. Cytoskeletal architecture and immunocytochemical localization of microtubule-associated proteins in regions of axons associated with rapid axonal transport: the beta,beta'-iminodipropionitrile-intoxicated axon as a model system. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;101(1):227–239. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N. Cross-linker system between neurofilaments, microtubules, and membranous organelles in frog axons revealed by the quick-freeze, deep-etching method. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):129–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber G., Matus A. Differences in the cellular distributions of two microtubule-associated proteins, MAP1 and MAP2, in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):151–160. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00151.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim H., Binder L. I., Rosenbaum J. L. The periodic association of MAP2 with brain microtubules in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):266–276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P., Walter U., Theurkauf W. E., Vallee R. B., De Camilli P. Frozen tissue sections as an experimental system to reveal specific binding sites for the regulatory subunit of type II cAMP-dependent protein kinase in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5562–5566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. B., Borisy G. G. Association of high-molecular-weight proteins with microtubules and their role in microtubule assembly in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2696–2700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato C., Nishizawa K., Nakamura H., Ueda R. Nuclear immunofluorescence by a monoclonal antibody against microtubule-associated protein-1 as it is associated with cell proliferation and transformation. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Nov;155(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90765-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherline P., Mascardo R. Epidermal growth factor-induced centrosomal separation: mechanism and relationship to mitogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):316–322. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theurkauf W. E., Vallee R. B. Molecular characterization of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase bound to microtubule-associated protein 2. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3284–3290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B. A taxol-dependent procedure for the isolation of microtubules and microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs). J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):435–442. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., Bloom G. S. Isolation of sea urchin egg microtubules with taxol and identification of mitotic spindle microtubule-associated proteins with monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6259–6263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallee R. B., Davis S. E. Low molecular weight microtubule-associated proteins are light chains of microtubule-associated protein 1 (MAP 1). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]