Abstract
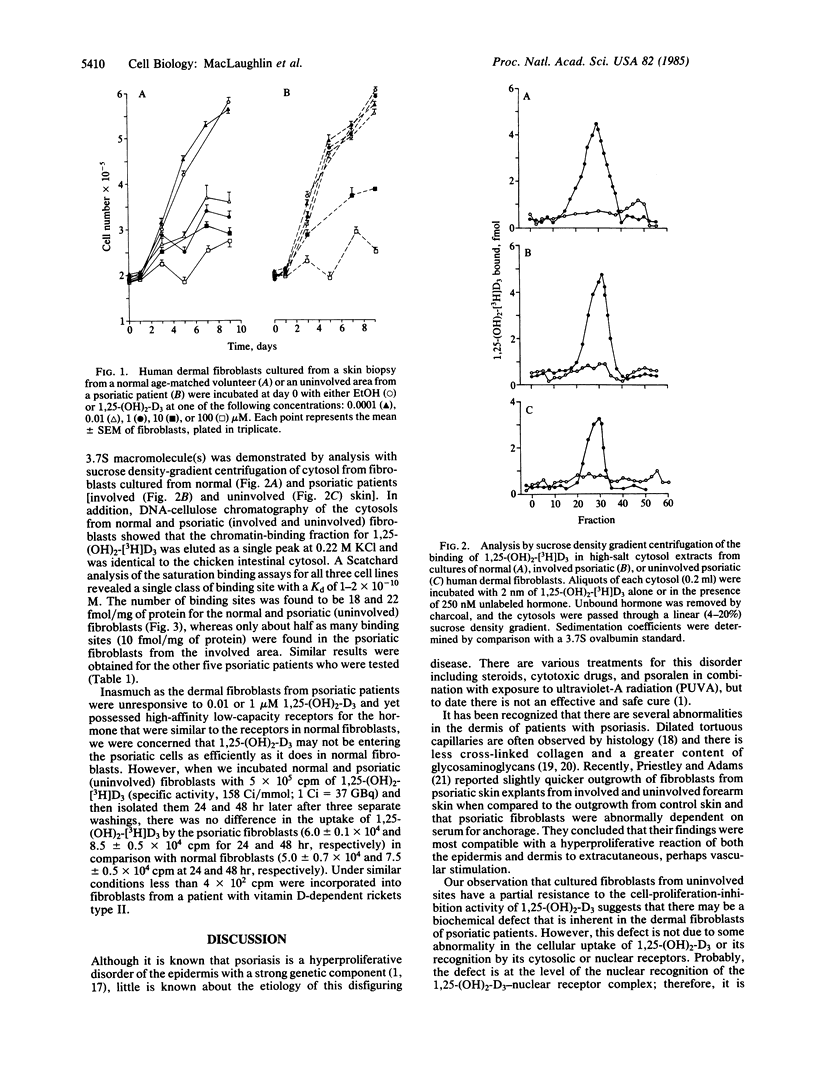
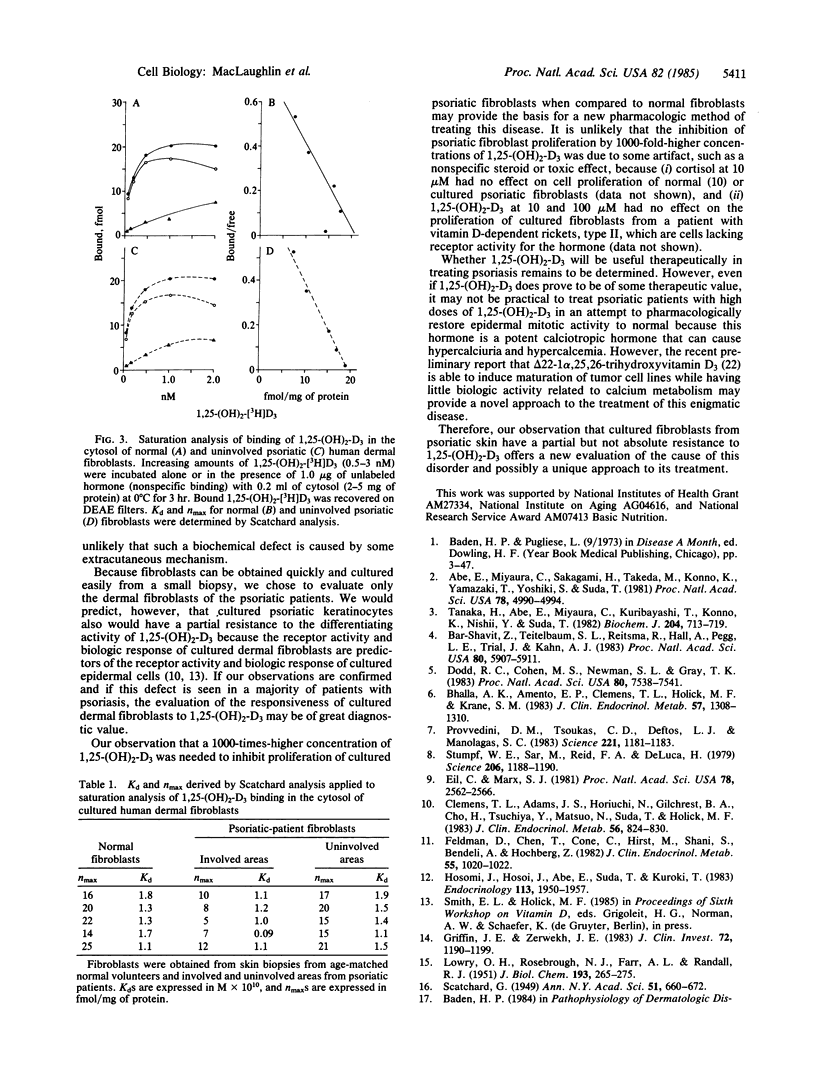
We examined the responsiveness of cultured dermal fibroblasts from biopsies of uninvolved and involved areas of skin from six patients with psoriasis to the cell-proliferation-inhibition activity of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (1,25-(OH)2-D3). Cultured fibroblasts from age-matched controls responded to 1,25-(OH)2-D3 (at 0.01, 1, 10, and 100 microM) in a dose-dependent fashion, whereas cultured psoriatic fibroblasts from involved or uninvolved skin showed no inhibition of proliferation when exposed to 0.01 or 1 microM of 1,25-(OH)2-D3. However, 1,25-(OH)2-D3 did inhibit proliferation of cultured psoriatic fibroblasts when the concentrations were increased to 10 and 100 microM. An analysis of the 1,25-(OH)2-D3 receptors in cultured psoriatic fibroblasts from uninvolved skin revealed that the Kd, nmax, and sedimentation coefficient were identical to the receptors found in the fibroblasts from age-matched controls. Therefore, cultured psoriatic fibroblasts from involved and uninvolved skin have a partial resistance to 1,25-(OH)2-D3, suggesting that there may be a biochemical defect that is inherent in the dermal fibroblasts of psoriatic patients. Recognition of this defect may provide a new approach for the evaluation of the cause and treatment of this disfiguring skin disorder.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe E., Miyaura C., Sakagami H., Takeda M., Konno K., Yamazaki T., Yoshiki S., Suda T. Differentiation of mouse myeloid leukemia cells induced by 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4990–4994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Shavit Z., Teitelbaum S. L., Reitsma P., Hall A., Pegg L. E., Trial J., Kahn A. J. Induction of monocytic differentiation and bone resorption by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5907–5911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhalla A. K., Amento E. P., Clemens T. L., Holick M. F., Krane S. M. Specific high-affinity receptors for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: presence in monocytes and induction in T lymphocytes following activation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Dec;57(6):1308–1310. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-6-1308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens T. L., Adams J. S., Horiuchi N., Gilchrest B. A., Cho H., Tsuchiya Y., Matsuo N., Suda T., Holick M. F. Interaction of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin-D3 with keratinocytes and fibroblasts from skin of normal subjects and a subject with vitamin-D-dependent rickets, type II: a model for study of the mode of action of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Apr;56(4):824–830. doi: 10.1210/jcem-56-4-824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd R. C., Cohen M. S., Newman S. L., Gray T. K. Vitamin D metabolites change the phenotype of monoblastic U937 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7538–7541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eil C., Marx S. J. Nuclear uptake of 1,25-dihydroxy[3H]cholecalciferol in dispersed fibroblasts cultured from normal human skin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2562–2566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman D., Chen T., Cone C., Hirst M., Shani S., Benderli A., Hochberg Z. Vitamin D resistant rickets with alopecia: cultured skin fibroblasts exhibit defective cytoplasmic receptors and unresponsiveness to 1,25(OH)2D3. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):1020–1022. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischmajer R., Blumenkrantz N. Fractionation of glycosaminoglycans from psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1970 Oct;55(4):274–276. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12259980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin J. E., Zerwekh J. E. Impaired stimulation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D-24-hydroxylase in fibroblasts from a patient with vitamin D-dependent rickets, type II. A form of receptor-positive resistance to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1190–1199. doi: 10.1172/JCI111074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath A., Tábora E. Alterations of collagen in psoriatic skin. Dermatologica. 1972;144(2):83–91. doi: 10.1159/000252101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosomi J., Hosoi J., Abe E., Suda T., Kuroki T. Regulation of terminal differentiation of cultured mouse epidermal cells by 1 alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Endocrinology. 1983 Dec;113(6):1950–1957. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-6-1950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priestley G. C., Adams L. W. Hyperactivity of fibroblasts cultured from psoriatic skin: I. Faster proliferation and effect of serum withdrawal. Br J Dermatol. 1983 Aug;109(2):149–156. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1983.tb07075.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priestley G. C. Hyperactivity of fibroblasts cultured from psoriatic skin: II. Synthesis of macromolecules. Br J Dermatol. 1983 Aug;109(2):157–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1983.tb07076.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provvedini D. M., Tsoukas C. D., Deftos L. J., Manolagas S. C. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors in human leukocytes. Science. 1983 Sep 16;221(4616):1181–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.6310748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpf W. E., Sar M., Reid F. A., Tanaka Y., DeLuca H. F. Target cells for 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in intestinal tract, stomach, kidney, skin, pituitary, and parathyroid. Science. 1979 Dec 7;206(4423):1188–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.505004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka H., Abe E., Miyaura C., Kuribayashi T., Konno K., Nishii Y., Suda T. 1 alpha,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol and a human myeloid leukaemia cell line (HL-60). Biochem J. 1982 Jun 15;204(3):713–719. doi: 10.1042/bj2040713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


