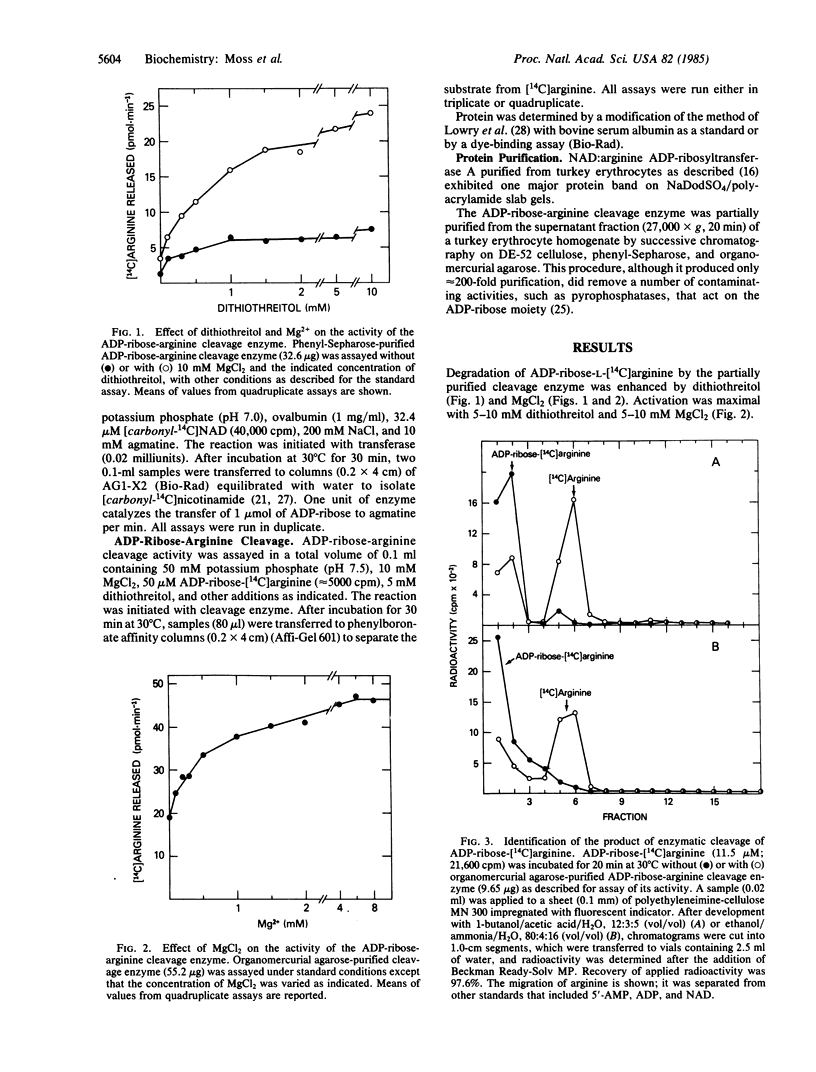
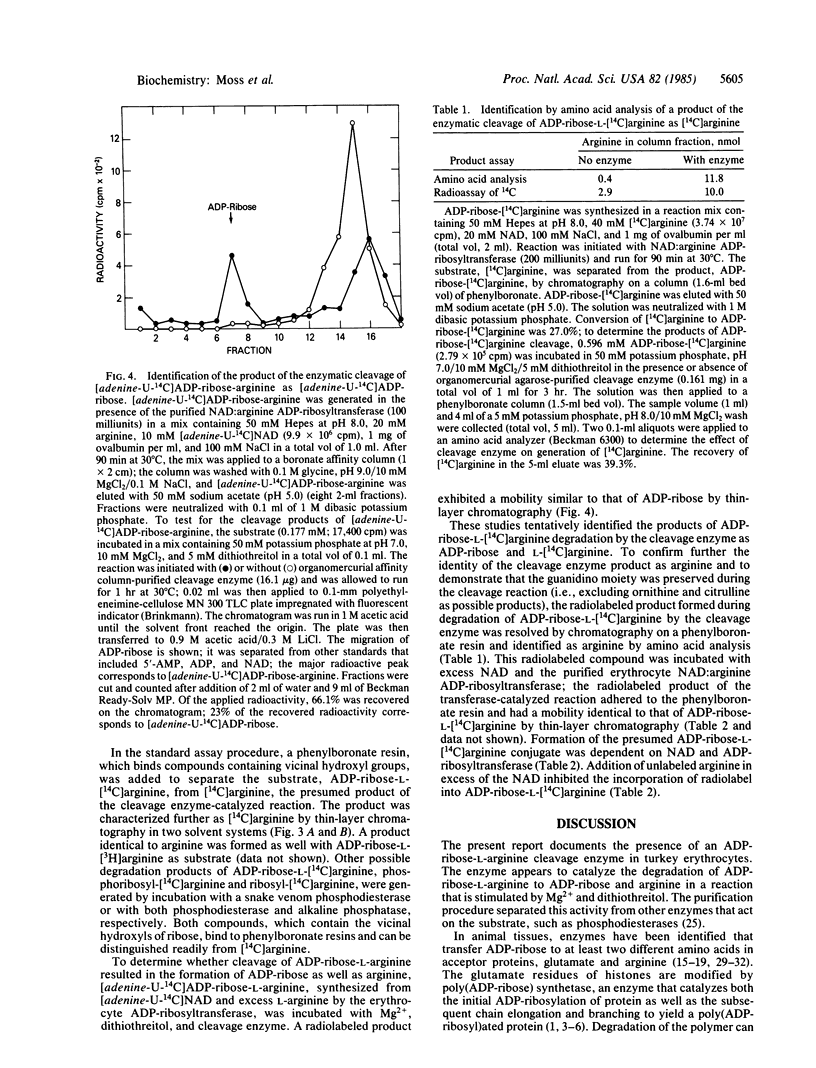
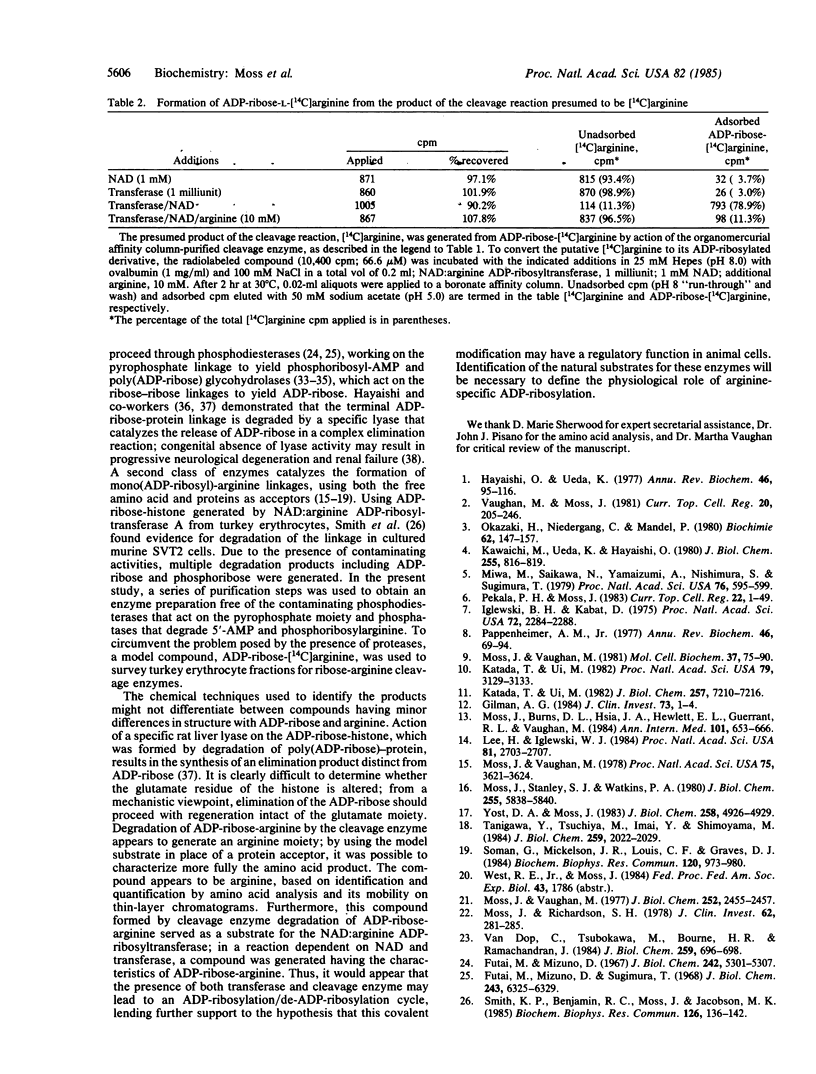
Abstract
Enzymes have been identified in animal tissues that catalyze the mono(ADP-ribosyl)ation of arginine and proteins. Since these NAD:arginine ADP-ribosyltransferases under physiological conditions do not appear to catalyze the degradation of the product ADP-ribose-arginine, the possibility was investigated that a different family of enzymes exists that cleaves the ADP-ribose-arginine linkage. An enzyme was identified in and partially purified from turkey erythrocytes that catalyzed the degradation of ADP-ribose-[14C]arginine synthesized by a salt-activated NAD:arginine ADP-ribosyl-transferase, resulting in the release of a radiolabeled compound that was characterized chromatographically and by amino acid analysis as arginine. This putative arginine product was converted in a reaction dependent on NAD and the NAD:arginine ADP-ribosyltransferase to a compound exhibiting properties characteristic of ADP-ribose-arginine. Action of cleavage enzyme on [adenine-U-14C]ADP-ribose-arginine resulted in the release of a radiolabeled compound that behaved chromatographically like [adenine-U-14C]ADP-ribose. Since degradation of ADP-ribose-arginine appears to generate an arginine moiety that is a substrate for the NAD:arginine ADP-ribosyltransferase, it appears that ADP-ribosylation may be a reversible modification of proteins.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burzio L. O., Riquelme P. T., Koide S. S. ADP ribosylation of rat liver nucleosomal core histones. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3029–3037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burzio L. O., Riquelme P. T., Ohtsuka E., Koide S. S. Evidence for two variants of poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) glycohydrolase in rat testis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Mar;173(1):306–319. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Mizuno D. A new phosphodiesterase forming nucleoside 5'-monophosphate from rat liver. Its partial purification and substrate specificity for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and oligonucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1967 Nov 25;242(22):5301–5307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Mizuno D., Sugimura T. Mode of action of rat liver phosphodiesterase on a polymer of phosphoribosyl adenosine monophosphate and related compounds. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6325–6329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. Guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):1–4. doi: 10.1172/JCI111179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayaishi O., Ueda K. Poly(ADP-ribose) and ADP-ribosylation of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:95–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglewski B. H., Kabat D. NAD-dependent inhibition of protein synthesis by Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin,. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. ADP ribosylation of the specific membrane protein of C6 cells by islet-activating protein associated with modification of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7210–7216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Ui M. Direct modification of the membrane adenylate cyclase system by islet-activating protein due to ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaichi M., Ueda K., Hayaishi O. Initiation of poly(ADP-ribosyl) histone synthesis by poly(ADP-ribose) synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):816–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H., Iglewski W. J. Cellular ADP-ribosyltransferase with the same mechanism of action as diphtheria toxin and Pseudomonas toxin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2703–2707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa M., Saikawa N., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., Sugimura T. Structure of poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose): identification of 2'-[1''-ribosyl-2''-(or 3''-)(1'''-ribosyl)]adenosine-5',5'',5'''-tris(phosphate) as a branch linkage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):595–599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa M., Tanaka M., Matsushima T., Sugimura T. Purification and properties of glycohydrolase from calf thymus splitting ribose-ribose linkages of poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose). J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3475–3482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Burns D. L., Hsia J. A., Hewlett E. L., Guerrant R. L., Vaughan M. NIH conference. Cyclic nucleotides: mediators of bacterial toxin action in disease. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Nov;101(5):653–666. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-5-653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Manganiello V. C., Vaughan M. Hydrolysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide by choleragen and its A protomer: possible role in the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4424–4427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Richardson S. H. Activation of adenylate cyclase by heat-labile Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Evidence for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity similar to that of choleragen. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):281–285. doi: 10.1172/JCI109127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Stanley S. J., Watkins P. A. Isolation and properties of an NAD- and guanidine-dependent ADP-ribosyltransferase from turkey erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5838–5840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Isolation of an avian erythrocyte protein possessing ADP-ribosyltransferase activity and capable of activating adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3621–3624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Mechanism of action of choleragen and E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin: activation of adenylate cyclase by ADP-ribosylation. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Jul 7;37(2):75–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02354931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Mechanism of action of choleragen. Evidence for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity with arginine as an acceptor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2455–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata N., Ueda K., Hayaishi O. ADP-ribosylation of histone H2B. Identification of glutamic acid residue 2 as the modification site. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7610–7615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata N., Ueda K., Kagamiyama H., Hayaishi O. ADP-ribosylation of histone H1. Identification of glutamic acid residues 2, 14, and the COOH-terminal lysine residue as modification sites. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7616–7620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka J., Ueda K., Hayaishi O., Komura H., Nakanishi K. ADP-ribosyl protein lyase. Purification, properties, and identification of the product. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):986–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Honda M., Hayaishi O. Novel enzyme from rat liver that cleaves an ADP-ribosyl histone linkage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2254–2257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki H., Niedergang C., Mandel P. Adenosine diphosphate ribosylation of histone H1 by purified calf thymus polyadenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase. Biochimie. 1980;62(2-3):147–157. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(80)80190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Diphtheria toxin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pekala P. H., Moss J. Poly ADP-ribosylation of protein. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1983;22:1–49. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152822-5.50005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riquelme P. T., Burzio L. O., Koide S. S. ADP ribosylation of rat liver lysine-rich histone in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3018–3028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. P., Benjamin R. C., Moss J., Jacobson M. K. Identification of enzymatic activities which process protein bound mono(ADP-ribose). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):136–142. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90582-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman G., Mickelson J. R., Louis C. F., Graves D. J. NAD: guanidino group specific mono ADP-ribosyltransferase activity in skeletal muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):973–980. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanigawa Y., Tsuchiya M., Imai Y., Shimoyama M. ADP-ribosyltransferase from hen liver nuclei. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):2022–2029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Oka J., Naruniya S., Miyakawa N., Hayaishi O. Poly ADP-ribose glycohydrolase from rat liver nuclei, a novel enzyme degrading the polymer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):516–523. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dop C., Tsubokawa M., Bourne H. R., Ramachandran J. Amino acid sequence of retinal transducin at the site ADP-ribosylated by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):696–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan M., Moss J. Mono (ADP-ribosyl)transferases and their effects on cellular metabolism. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;20:205–246. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152820-1.50010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. C., Chambers J. P., Liehr J. G. Glutamyl ribose 5-phosphate storage disease. A hereditary defect in the degradation of poly(ADP-ribosylated) proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1037–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost D. A., Moss J. Amino acid-specific ADP-ribosylation. Evidence for two distinct NAD:arginine ADP-ribosyltransferases in turkey erythrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4926–4929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



