Abstract
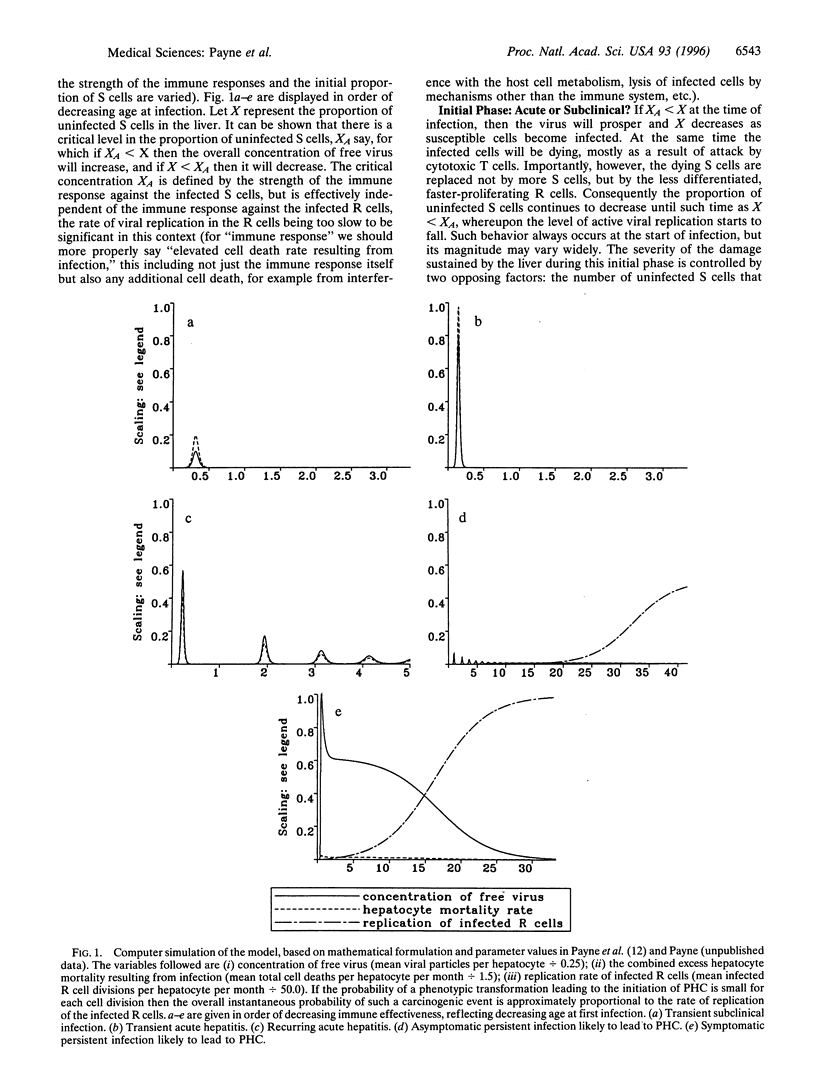
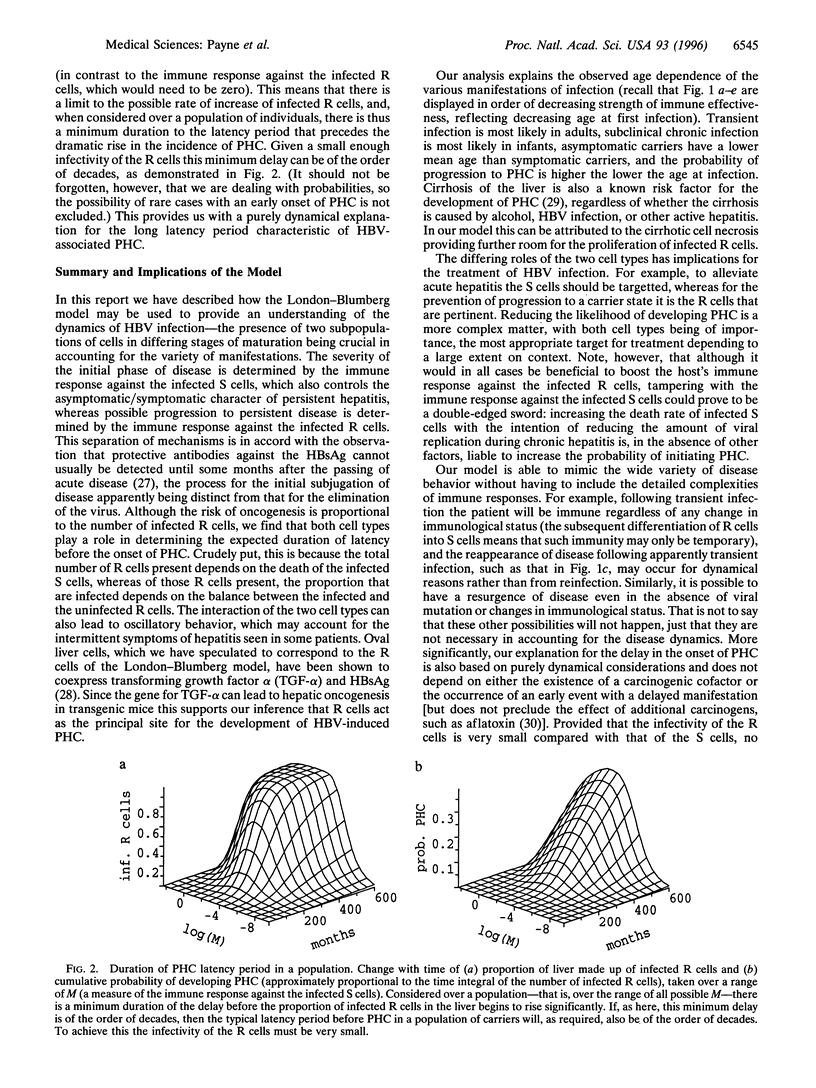
We consider a cellular model of infection by the hepatitis B virus and describe how it may be used to account for two important features of the disease, namely (i) the wide variety of manifestations of infection and the age dependence thereof, and (ii) the typically long delay before the development of virus-induced liver cancer (primary hepatocellular carcinoma). The model is based on the assumption that the liver is comprised of both immature and mature hepatocytes, with these two subpopulations of cells responding contrastingly upon infection by the virus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander G. J. Immunology of hepatitis B virus infection. Br Med Bull. 1990 Apr;46(2):354–367. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y., Lin C. C., Chien C. S. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brechot C., Hadchouel M., Scotto J., Degos F., Charnay P., Trepo C., Tiollais P. Detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in liver and serum: a direct appraisal of the chronic carrier state. Lancet. 1981 Oct 10;2(8250):765–768. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman W. B., Wennerberg A. E., Smith G. J., Grisham J. W. Regulation of the differentiation of diploid and some aneuploid rat liver epithelial (stemlike) cells by the hepatic microenvironment. Am J Pathol. 1993 May;142(5):1373–1382. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley F. J., Scheuer P. J., Sherlock S. Natural history of hepatitis-associated antigen-positive chronic liver disease. Lancet. 1972 Dec 30;2(7792):1388–1393. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92963-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusheiko G. M. Hepatocellular carcinoma associated with chronic viral hepatitis. Aetiology, diagnosis and treatment. Br Med Bull. 1990 Apr;46(2):492–511. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmunds W. J., Medley G. F., Nokes D. J., Hall A. J., Whittle H. C. The influence of age on the development of the hepatitis B carrier state. Proc Biol Sci. 1993 Aug 23;253(1337):197–201. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1993.0102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Factor V. M., Radaeva S. A., Thorgeirsson S. S. Origin and fate of oval cells in dipin-induced hepatocarcinogenesis in the mouse. Am J Pathol. 1994 Aug;145(2):409–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto Y., Hampton L. L., Wirth P. J., Wang N. J., Xie J. P., Thorgeirsson S. S. Alterations of tumor suppressor genes and allelic losses in human hepatocellular carcinomas in China. Cancer Res. 1994 Jan 1;54(1):281–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Dusheiko G. M., Seeff L. B., Jones E. A., Waggoner J. G., Bales Z. B. Seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to antibody in chronic type B hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jun;94(6):744–748. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-6-744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia C. C., Thorgeirsson S. S., Tabor E. Expression of hepatitis B surface and core antigens and transforming growth factor-alpha in "oval cells" of the liver in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med Virol. 1994 Jul;43(3):216–221. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890430304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kekulé A. S., Lauer U., Weiss L., Luber B., Hofschneider P. H. Hepatitis B virus transactivator HBx uses a tumour promoter signalling pathway. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):742–745. doi: 10.1038/361742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. M., Koike K., Saito I., Miyamura T., Jay G. HBx gene of hepatitis B virus induces liver cancer in transgenic mice. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):317–320. doi: 10.1038/351317a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maynard J. E. Hepatitis B: global importance and need for control. Vaccine. 1990 Mar;8 (Suppl):S18–S23. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli M., Vergani G. M., Alberti A., Vergani D., Portmann B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Specificity of T lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: evidence that T cells are directed against HBV core antigen expressed on hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2773–2778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne R. J., Nowak M. A., Blumberg B. S. A cellular model to explain the pathogenesis of infection by the hepatitis B virus. Math Biosci. 1994 Sep;123(1):25–58. doi: 10.1016/0025-5564(94)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Realdi G., Alberti A., Rugge M., Bortolotti F., Rigoli A. M., Tremolada F., Ruol A. Seroconversion from hepatitis B e antigen to anti-HBe in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):195–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S. The role of determined stem-cells in the cellular lineage of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Dev Biol. 1993 Mar;37(1):189–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Shouval D., Sherman H. I., Hadziyannis S. J., Kew M. C. Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA into the genome of liver cells in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies in percutaneous liver biopsies and post-mortem tissue specimens. N Engl J Med. 1981 Oct 29;305(18):1067–1073. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198110293051807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S. Hepatitis B: the disease. Vaccine. 1990 Mar;8 (Suppl):S6–S23. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(90)90206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slagle B. L., Zhou Y. Z., Butel J. S. Hepatitis B virus integration event in human chromosome 17p near the p53 gene identifies the region of the chromosome commonly deleted in virus-positive hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 1;51(1):49–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorgeirsson S. S. Hepatic stem cells. Am J Pathol. 1993 May;142(5):1331–1333. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thung S. N., Gerber M. A., Sarno E., Popper H. Distribution of five antigens in hepatocellular carcinoma. Lab Invest. 1979 Aug;41(2):101–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toshkov I., Hacker H. J., Roggendorf M., Bannasch P. Phenotypic patterns of preneoplastic and neoplastic hepatic lesions in woodchucks infected with woodchuck hepatitis virus. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1990;116(6):581–590. doi: 10.1007/BF01637078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viola L. A., Barrison I. G., Coleman J. C., Paradinas F. J., Fluker J. L., Evans B. A., Murray-Lyon I. M. Natural history of liver disease in chronic hepatitis B surface antigen carriers. Survey of 100 patients from Great Britain. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1156–1159. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90600-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaman S. N., Melia W. M., Johnson R. D., Portmann B. C., Johnson P. J., Williams R. Risk factors in development of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: prospective study of 613 patients. Lancet. 1985 Jun 15;1(8442):1357–1360. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91785-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



