Abstract
Purpose
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) is defined by a perturbed B-cell receptor-mediated signaling machinery. We aimed to model differential signaling behavior between B cells from CLL and healthy individuals to pinpoint modes of dysregulation.
Experimental Design
We developed an experimental methodology combining immunophenotyping, multiplexed phosphospecific flow cytometry, and multifactorial statistical modeling. Utilizing patterns of signaling network covariance, we modeled BCR signaling in 67 CLL patients using Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR). Results from multidimensional modeling were validated using an independent test cohort of 38 patients.
Results
We identified a dynamic and variable imbalance between proximal (pSYK, pBTK) and distal (pPLCγ2, pBLNK, ppERK) phosphoresponses. PLSR identified the relationship between upstream tyrosine kinase SYK and its target, PLCγ2, as maximally predictive and sufficient to distinguish CLL from healthy samples, pointing to this juncture in the signaling pathway as a hallmark of CLL B cells. Specific BCR pathway signaling signatures that correlate with the disease and its degree of aggressiveness were identified. Heterogeneity in the PLSR response variable within the B cell population is both a characteristic mark of healthy samples and predictive of disease aggressiveness.
Conclusion
Single-cell multidimensional analysis of BCR signaling permitted focused analysis of the variability and heterogeneity of signaling behavior from patient-to-patient, and from cell-to-cell. Disruption of the pSYK/pPLCγ2 relationship is uncovered as a robust hallmark of CLL B cell signaling behavior. Together, these observations implicate novel elements of the BCR signal transduction as potential therapeutic targets.
Introduction
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) results from the accumulation of mature monoclonal CD5+ B cells in the bone marrow, lymphoid organs and peripheral blood. CLL B cells are characterized by low expression of surface CD20 and co-expression of CD19 and CD5 [1]. While some patients have rapidly progressive disease that is characterized by early need for treatment, resistance to chemotherapy and short survival, others have a stable, indolent course over many years and often succumb from other causes [2]. In patients with evidence of clinically indolent course, treatment is generally delayed and a period of “watch and wait” is typically indicated [3]. Over the past decade molecular and cellular prognostic markers have been identified that correlate with response to treatment and/or overall survival (among which one of the most accurately predictive is the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGHV) gene mutation status), though the discriminatory power of these known prognosticators is not absolute [4]–[8].
At the cellular level, clonal expansion of B cells depends on the efficient propagation of signal from the cell membrane to target genes following antigenic stimulation of the BCR [9], [10]. It has been proposed that unmutated surface immunoglobulins in CLL are more responsive to antigenic stimulation, resulting in strong BCR-mediated signal transduction and induction of anti-apoptotic proteins such as XIAP and MCL-1 [11]–[13], while CLL cells with mutated IGHV more closely resembles anergic B cells [14], with incomplete responsiveness through the BCR pathway and induction of tolerogenic signals. CLL B cells have been described to have constitutive activation of several members of the BCR signalosome. For instance, levels of phosphorylated Lyn and Syk have been shown to be higher in CLL cells [15], [16]. Similarly, the PI3K/Akt pathway has been shown to be aberrantly activated in CLL cells [17], [18]. BCR signaling aberrancy has been shown to correlate with prognostic clinical parameters or disease stage at the time of diagnosis. Recent work from the Jumaa laboratory identified a possibly parallel BCR activation mechanism, whereby a structural motif of the CLL BCR drives antigen-independent autonomous signaling [19]. Regardless of the initial activating event, the BCR pathway is clearly an ideal target for new drug development in CLL. Small molecule inhibitors of the BCR signaling pathway are demonstrating remarkable activity in clinical trials. The target specificity, off-target activity and exact mechanism of action of these novel drugs, however, are not completely understood at this time [20]–[25].
Single-cell network profiling is a method that allows the investigation of cell signaling events with single-cell resolution and requires minimal sample manipulation [26]. Using combined immunophenotyping and multiplexed phosphospecific flow cytometry Irish et al. identified a subpopulation of lymphoma cells with impaired BCR signaling from tumor samples of patients with follicular lymphoma [27], [28]. A negative impact of these low-responding cells on patients overall survival was noted. More recently, using a similar methodology, Palazzo et al. demonstrated that CLL B cells could be stratified into two groups depending on the efficiency of BCR signal amplification caused by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a broad tyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Furthermore, in vitro response to the nucleotide analog F-Ara-A by primary CLL cells was highly associated with the ability of CLL B cells to undergo peroxide-augmented signaling [29].
We applied phosphospecific flow cytometry to study the heterogeneous response of stimulated B cells with the goal of identifying BCR pathway signaling signatures that correlate with the disease and with its degree of aggressiveness. We hypothesized that this method would allow the identification of CLL-specific signaling behavior that would be highly predictive of the presence of disease in a B cell population. To do this, we stimulated the cells with anti-IgM and H2O2, a highly standardized, widely published method for probing the signaling pathway of B cells [28]–[30]. We found that the development of a sophisticated computational method was essential to analyze the phospho-flow data in its multidimensional nature, rather than as a series of individual results.
Materials and Methods
Sample preparation
We used samples from 67 CLL patients and 10 healthy volunteers who signed informed consent to have their sample used for research purposes, in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approval by the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) institutional review board. Treated and untreated CLL patient samples were randomly selected. Patients were not treated uniformly under a specific clinical trial. Clinical characteristics are described in Supplementary Table S1. 38 additional samples from another institution (a generous gift of Dr. Sami Malek, University of Michigan) were used as a validating cohort for BCR signaling analysis, or combined with the MSKCC samples for selected analysis.
Isolation, storage, and thawing of primary cells
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated using density gradient separation (Ficoll-Paque Plus; GE Healthcare) and frozen within 6 hours from collection, without further manipulation. For signaling analysis, cells were thawed and washed in RMPI+10% FBS. Mononuclear cells were resuspended at 107 cells/mL, and allowed to rest at 37°C for up to 2 hours.
Immunophenotyping and total cytoplasmic Zap-70 analysis
For immunophenotyping, cells were stained anti-CD3, -CD5, -CD19, -CD20 (cytoplasmic), and -CD38 (all BD-Biosciences), and anti-IgM F(ab′)2 (Biosource International). For cytoplasmic Zap-70 analysis, resting cells were fixed with a 1.6% paraformaldehyde solution for 10 minutes at 37°C then permeabilized with cold methanol at −20°C for 10 minutes. Cells were then washed with PBS with 2% FBS and stained with anti-Zap-70 antibody (clone 1E7.2, BD Biosciences) for 30 minutes. Cells were washed once with PBS+2% FBS, and collected on an LSRII cytometer (BD Biosciences).
IGHV gene sequencing
DNA was amplified using BIOMED-2 multiplex PCR assays with consensus primers that have been previously developed and standardized for detecting clonally rearranged immunoglobulins [1]. The DNA was sequenced using Applied Biosystem's BigDye Terminator v3.1 Cycle Sequencing Kit. Mutation levels were analyzed by comparison to known germline sequences using VBASE.
BCR stimulation
After thawing, cells were rested in FBS-containing medium, then stimulated by adding goat polyclonal anti-IgM F(ab′)2 (Biosource International) to a final concentration of 10 µg/mL at 37°C. A resting time of 2 hours was chosen based on time course experiments that demonstrated that, while a 15 minute resting time was sufficient to achieve maximum stimulation in highly responding samples, continued incubation in FBS-containing medium up to 2 hours provided enhanced phosphoresponses in the lower responders (Supp. Fig. S1A). Addition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) further enhanced observed phosphoresponses in non-maximally activated samples, in a dose-dependent manner (Supp. Fig. S1B and S1C). A working concentration of 3.3 mM H2O2 was chosen. Fixation was achieved with the addition of pre-warmed paraformaldehyde (BD Biosciences) to a final concentration of 1.6%. Cells were fixed for 10 minutes at 37°C, permeabilized with cold methanol at −20°C for 10 minutes, and stored at −80°C until staining step, no longer than 48 hours.
Phosphospecific flow cytometry
Fixed and permeabilized cells were washed once with PBS with 2% FBS. An antibody mix containing conjugated phosphospecific antibodies was added, and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. Phosphospecific Alexa Fluor 488 and Alexa Fluor 647, or R-PE-conjugated antibodies (all from BD-Biosciences) against pBLNK(Y84), pBTK(Y551)/Itk(Y511), pERK1/2(T202/Y204), pPLCγ2(Y759) and pSYK(Y348) were used. Detection of PBMC subsets was achieved with Pacific Blue-conjugated anti-CD3 (clone UCHT1, BD Bioscience), PerCPCy5.5-conjugated anti-CD20 (clone H1, BD Biosciences), and PE-Cy7-conjugated anti-CD5 (clone L17F12, BD Biosciences) antibodies.
Data analysis
Flow cytometry data were acquired on an LSR II Flow cytometer (Beckton Dickinson). After gating out doublets and dead cells, the CD3−/CD20+ gate was used to identify B cells within the healthy PBMCs. The clonal CD20low/CD5+/CD3− population of each patient with CLL was manually gated.
Phosphoresponses for kinase X (pX = pBLNK, pBTK, ppERK, PLCγ2, or pSYK) were quantified by computing the frequency F(X) of cells whose Mean Fluorescence Intensity (MFI) for stimulated cells was 99% higher than the MFI for unstimulated cells. To reduce the dimensionality of the data, we applied a partial-least square regression (PLSR) using the Matlab statistical toolbox (Mathworks): the F(X) matrix for all phosphoresponses of all the samples (CLL or healthy controls) were pooled together in one matrix and linearly-regressed against a one-dimensional matrix of 0 for CLL patients and 1 for healthy individuals. The linear combination of F(X) yielded a one-dimensional variable VPLSR.
Results
CLL B cells exhibit wide variability in their responsiveness to BCR stimulation and pathological dysregulation of proximal signaling components
PBMCs from CLL patients and healthy volunteers were isolated by density gradient without further B-cell separation. All samples were collected, frozen and thawed following a uniform protocol to prevent inter-sample variations due to handling. BCR-mediated activation with anti-IgM and H2O2 was optimized to a stimulation time of 4 minutes.
In the CLL samples, CD20+/CD5+ cells represented a variable proportion of the total cells for each individual patient, depending on the extent of the circulating CLL clone. As expected, the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of the CD20 staining was generally dim, though some samples were strongly CD20+. Similarly, CD5 expression varied among patients.
At baseline, both CLL and healthy B cells had no or minimal constitutive activation of each of the upstream or downstream BCR signaling proteins analyzed. Addition of H2O2 amplified the stimulatory effect of BCR cross-linking, significantly more so in CLL B cells than in healthy controls (Supp. Fig. S1C). This confirms that CLL B cells are overall anergic, possibly because of an excess of phosphatase activity that can be blocked upon H2O2 treatment [31]–[33]. Following H2O2 exposure and BCR cross-linking for 4 minutes, we analyzed the intensity of activation, measured as MFI of five specific phosphoepitopes of a selected number of BCR signaling pathway members ( Fig. 1A ). The detectable fraction of cells responding with phosphorylation of SYK, BLNK, BTK, PLCγ2, or ERK1/2 was highly variable among the 105 CLL patient samples analyzed. Examples of “high responder” and “low responder” CLL samples, compared with B cells from one healthy individual, are shown in Fig. 1B . Preliminary analysis of sample phosphoresponses revealed strong correlation between each pairwise pX and pY (i.e. pPLCγ2 and pSYK) (Supp. Fig. S2A, S2B). Contour plots of MFI illustrate bimodal patterns of stimulation within all CLL patient samples; bimodality is absent from healthy B cell populations ( Fig. 1C , Supp. Fig. S2C). Therefore, within a single population, the B cells of healthy individuals show modest variability (yielding mostly uniformly intermediate responses), while the CLL B cells can be distinguished by their all-or-none response (visualized by two populations separated by phosphoresponse). Importantly, we checked that cell viability was homogeneous among all samples, thus variable bimodality of the B cell response to stimulation is not an artifact of our cell preparation protocol (Supp. Fig. S3). Bimodality of the stimulated response is a novel observation of BCR signaling pathway dynamics in CLL patients [34].
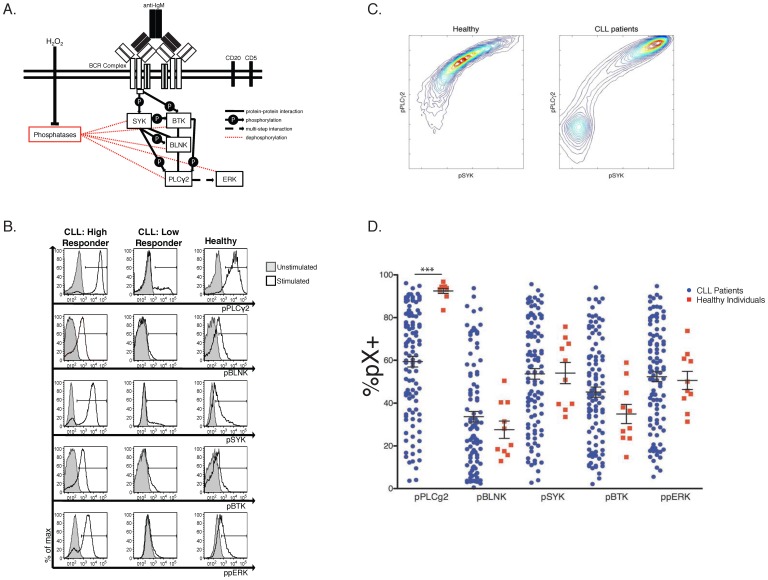
Figure 1. Phosphoprofiling of the Proximal BCR Signaling Pathway Uncovers High Variability in BCR Signaling Pathway Behavior in CLL B cells.
A. Simplified diagram of the BCR signaling pathway components investigated in this study. B. Representative histograms of phosphoresponses of B- cells for two CLL patients (a high and a low responder) and one healthy individual. CLL and healthy B cells were gated as described in the methods section. Stimulated samples (anti-IgM+H2O2) are indicated by a black line, unstimulated samples are shaded grey. C. Contour maps of the average B cell population: For each cohort, CLL and healthy, the cellular phosphoresponse fluorescence intensity values are averaged and viewed two dimensionally. Bimodality in the phosphoresponse of CLL B cells can be seen for the pairwise pPLCγ2 vs. pSYK) (see also Supp. Fig. S2 for other combinations of phosphoresponses). Healthy B cells show modest variability within the B-cell population, while the CLL B cells can be distinguished by their all-or-none response. D. Following IgM crosslinking, phosphoresponses are shown as the percentage of responding cells for each patient over an unstimulated matched control. This view of the wide, continuous range of each CLL patients' phosphoprofile highlights the high variability in the behavior of the BCR signaling pathway. Only the pPLCγ2 response showed statistical significance when comparing healthy to CLL cells (***p<0.0001).
Comparison of the percentage of responding cells over the corresponding unstimulated control in all CLL samples and healthy controls is shown in Fig. 1D . This representation reveals the wide, continuous range of CLL patients' phosphoprofiles and highlights the high variability in the responsiveness of the BCR signaling pathway in this patients' population. Importantly, this analysis reveals that while CLL cell populations all have some degree of bimodality in their signaling response, the fraction of the population with a stimulated phenotype is widely variable between CLL patients. Surface IgM staining revealed no correlation between expression of IgM and magnitude of signaling response, indicating that the changes in %pX+ among CLL patients is due to alterations in the signal transduction mechanism (data not shown).
Using this simple comparison of each isolated phosphoresponse, only the PLCγ2 activation showed statistical significance when comparing healthy to CLL samples (p<0.0001) ( Fig. 1D ). Analysis of the percentage of pX+ and of the MFI values of all phosphoresponses in every possible pairwise combination shows good linear correlation of the entity of phosphoresponses, and again highlights the greater variability observed in CLL patients (Supp. Fig. S2A, S2B).
Multidimensional phosphoresponse signatures partition CLL patients into clinically relevant subgroups
For more than 75% of the CLL cases analyzed, CLL B cells were either uniformly high-responders to IgM cross-linking (n = 17/105), low-responders (n = 28/105), or healthy-like with intermediate response (n = 36/105). Hence, we defined a five-dimensional filter based on the amplitude of the signaling responses ( Fig. 2A ) for these three populations and tested their ability to match known indicators of clinical outcome (time to first treatment, TTFT, or mutational status of IGHV genes).
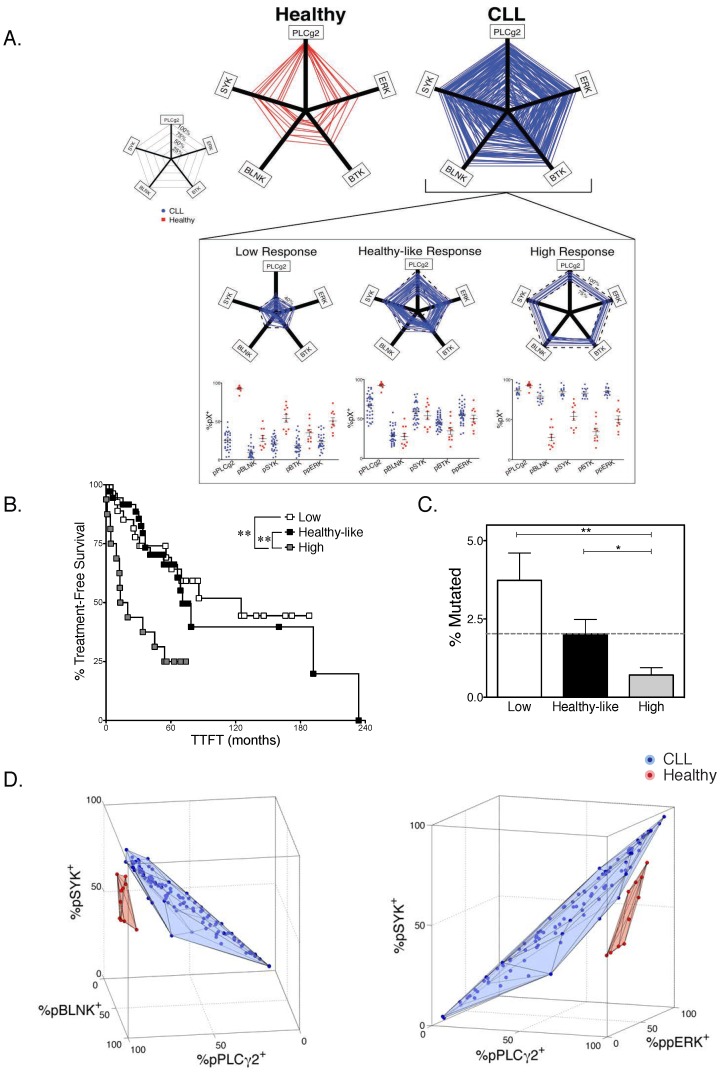
Figure 2. Variability in the Signaling Profile Allows Partioning of CLL Patients Into Distinct Prognostic Groups.
A Graphic representation of all five phosphoresponses for CLL patients (blue, n = 110) as compared to the healthy controls (red, n = 11). A pentagon was created for each sample by connecting the percent of responding cells (over unstimulated control) recorded on the axes. A wide variability in extent of response was observed in the CLL group, encompassing all possible level of responsiveness. Three distinct groups of CLL could be defined based on the responsiveness (inset): patients with uniformly low response (left, at least 4 of the 5 pX+<40%), patients with uniformly high response (right, at least 4 pX+>75%), and patients with intermediate, healthy-like response (middle, at least 4 pX+ within the range of healthy samples). This groups of patients yielded n = 28 among low-responders, n = 36 among intermediate (healthy-like) responders and n = 17 among high-responders. B Kaplan-Meyer curves showing time from diagnosis to first treatment (TTFT) was plotted for the three distinct CLL subgroups described in D. Patients whose phosphoprofile consists of uniformly high phosphoresponses had a statistically significant (p<0.01) shorter time to first treatment (TTFT). Furthermore, high responders had a larger fraction that had required treatment (p<0.04). Those patients whose %pX+ values were uniformly low or similar to healthy individuals across the 5 responses studied had a significantly longer time to first treatment, and fewer patients within this cohort have required treatment at the time of this analysis. C Distinct IGHV status (% deviation from germline sequence) is also observed between these three subgroups. The dashed line indicates the 2% cutoff for mutational status, mutated vs. unmutated. Mean ± Std. Error % Mutated: Healthy-like = 2.02±0.43; High = 0.73±.21; Low = 3.9±.86. D Three-dimensional visualization of three phosphoresponses ([%pPLCγ2+, %pBLNK+ and %pSYK+], or ([%pPLCγ2+, %pSYK+ and %ppERK+]) for (blue) all CLL and (red) healthy samples. Each panel demonstrates the clear separation of the healthy patient samples from the CLL patient samples solely by virtue of the combined %pX+ values for the three phosphoresponses.
Patients whose CLL B cells responded to IgM cross-linking with high BCR responsiveness required treatment after shorter periods of expectant monitoring (50% of cases treated by 12.4 months), compared to patients whose CLL B cells exhibited intermediate (healthy-like)-responsiveness (26.9 months) or low-responsiveness (36.3 months) (p<0.01). Hence, it appears that stronger B cell signaling response to BCR cross-linking in CLL B cells when compared to healthy B cells correlates with the severity of the disease ( Fig. 2B ). We also found that the degree of BCR responsiveness inversely correlated with the percentage of mutation in the IGHV genes compared to the germline BCR ( Fig. 2C ). Specifically, patients with high BCR responsiveness were more likely to have unmutated IGHV genes (using the standard 2% mutation cut-off compared to germ-line sequences), while patients with low responsiveness had overall mostly mutated IGHV genes. IGHV genes mutation rate in patients with intermediate, healthy-like responsiveness fell, on average, on the 2% cutoff. When comparing clinical parameters of disease aggressiveness (TTFT, treatment status, ZAP70 abundance) to individual phosphoresponses only pPLCγ2 correlated significantly with treatment status (Supp. Fig. S4), thus further supporting the multidimensional view of the BCR signaling pathway as an independent indicator of disease state. Indeed, visualization of the phosphoresponses in higher dimensions is a powerful tool to resolve disease status between a CLL and healthy B cell. Three-dimensional visualization of three phosphoresponses (pPLCγ2+, pSYK+ and either pBLNK+ or ppERK+) for all CLL and healthy samples demonstrated a clear separation of the healthy individuals' samples from the CLL patients' samples solely by virtue of the combined %pX+ values ( Fig. 2D ). Unlike other biomolecular factors utilized as diagnostic tools in CLL, the phosphorylation of BCR proximal signaling components unambiguously distinguishes aberrant signaling pathway behavior from healthy functionality.
Multifactorial statistical modeling of CLL-specific BCR signaling behavior reveals key sources of dysfunction
The immunophenotypic diagnosis of CLL relies on the identification of CD5+CD3−CD23+CD20low light chain-restricted lymphocytes in the blood or bone marrow of affected patients. Here, we use only phosphoresponses following BCR stimulation to reliably identify CLL patients. Partial-least square regression (PLSR) was applied to correlate the measured phosphoresponses with the disease status; creating a novel variable that accurately distinguishes and classifies pathological from healthy B cells.
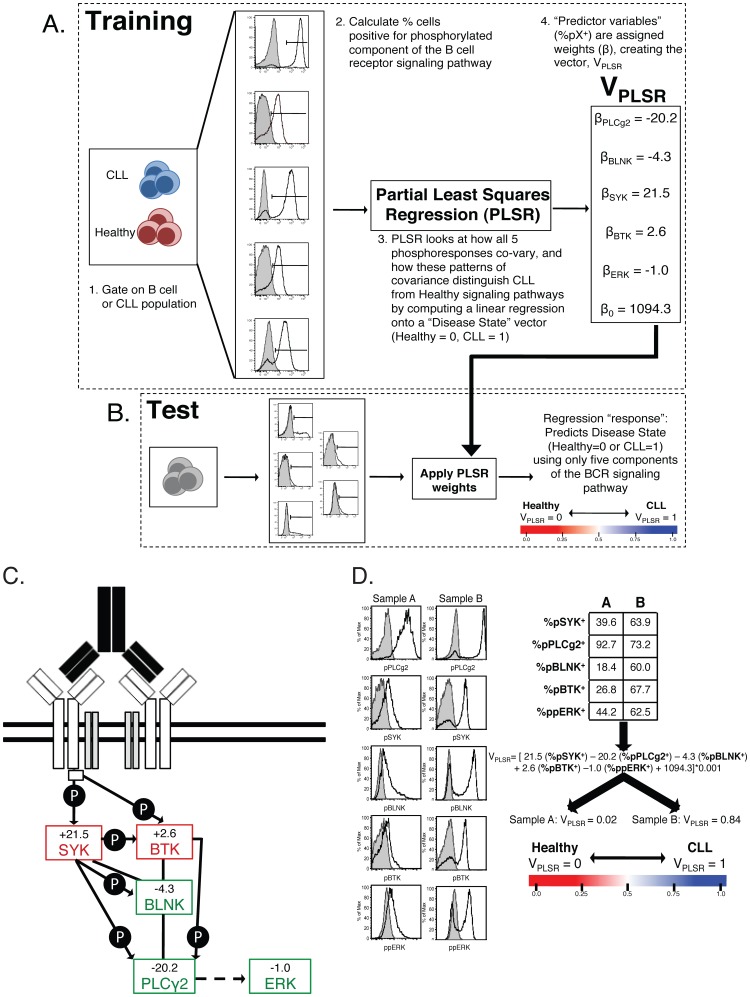
Figure 3A depicts in detail the practical application of PLSR analysis of phosphoflow data. CLL B cells or healthy B cells were isolated using the gating strategy previously described. Phosphospecific antibodies allowed detection of bimodal phosphoresponses for pPLCγ2, pSYK, pBTK, pBLNK and ppERK. The percentage of cells positive for each phosphospecific antibody was calculated based on the unstimulated histograms. These %pX+ (X = pPLCγ2, pSYK, pBLNK, pBTK, ppERK) provide the raw data for PLSR analysis. PLSR correlates the magnitude of each patient's phosphoresponse (%pX+) with a variable defining disease status (0 for healthy individuals and 1 for CLL patients; 7 healthy and 67 CLL pooled together). The PLSR algorithm attempts to optimize weights (β, in Fig. 3A, B ) to match the differences between healthy and CLL phosphoprofiles. The output of PLSR analysis is a linear combination, VPLSR, that applies weights to each observed “predictor” variable (%pX+). Thus, we created the following metric (VPLSR) that encodes Healthy vs. CLL BCR signaling behavior, given the inputs %pX+. ( Fig. 3C, D ):
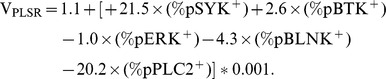 |
100% of the variance in phosphoresponse fluorescence intensity and 66% of the variance in clinical status is encompassed in this VPLSR component. This weighted sum of individual phosphoresponses includes negative contributions from distal pPLCγ2, pBLNK and ppERK and positive contributions from more proximal kinases pSYK and pBTK. This implies that CLL B cells respond to BCR cross-linking with hypo-responsiveness for the distal pPLCγ2, pBLNK and ppERK, relatively to the proximal signaling events, compared to B cells from healthy individuals ( Fig. 3C ). By nature of the regression methodology, this dysregulation between proximal and distal signaling components is among the factors that most maximally distinguish a CLL BCR signaling pathway from that of a healthy B cell. PLSR on the most significant variable phosphoresponses (pPLCγ2 and pSYK) is in fact sufficient to deliver the same discrimination between CLL and healthy individuals (Supp. Fig. S5).
Figure 3. Statistical Analysis of CLL B-cell Phosphoprofile using Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR) against disease status.
This figure details our method for analyzing phosphoflow data by Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR) against disease status: A Training: 1 CLL B cells or healthy B cells were isolated using the gating described in the methods section. 2 Phosphospecific antibodies allowed detection of the phosphoresponse for pPLCγ2, pSYK, pBTK, pBLNK and ppERK. The percentage of cells positive for each phosphospecific antibody was calculated based on the unstimulated histograms. These %pX+ provide the raw data for Partial Least Squares Regression analysis, PLSR. 3 PLSR was applied to best correlate a linear combination of these phosphoprofiles for each patient (all healthy controls and all CLL samples pooled together) with a variable defining disease status (arbitrarily set to 0 for healthy individuals and 1 for CLL patients). This step of the analysis is referred to as “Training” as the PLSR algorithm uses a subset of CLL B cells and Healthy B cells to model the covariance of each phosphoresponse. 4 The output of PLSR analysis is a linear combination VPLSR with weights (βi) to each observed “predictor” variable (%pXi +). The PLSR algorithm output attempts to find weights that best match the differences between healthy and CLL patient phosphoprofiles with disease status. B Test: Using the model (VPLSR) defined during the training phase, we tested the power of our model by its ability to correctly predict the disease status of independently-acquired CLL patients and healthy individuals. Phosphoresponses are measured and linearly-combined into a VPLSR variable as specified by the training step. C BCR signaling diagram highlighting pathway-based understanding of the VPLSR score and weights. D Example of VPLSR predictive power: two samples (one CLL and one healthy control) were tested side-by-side. As predicted, VPLSR helps discriminate their differences in phosphoresponses. As illustrated in Fig. 3A, %pX+ values over an unstimulated control are calculated and linearly combined to yield VPLSR for the sample under consideration. Sample 1119, yields VPLSR = 0.02, while Sample 1062, yields VPLSR = 0.84, consistently with disease status (healthy and CLL, respectively).
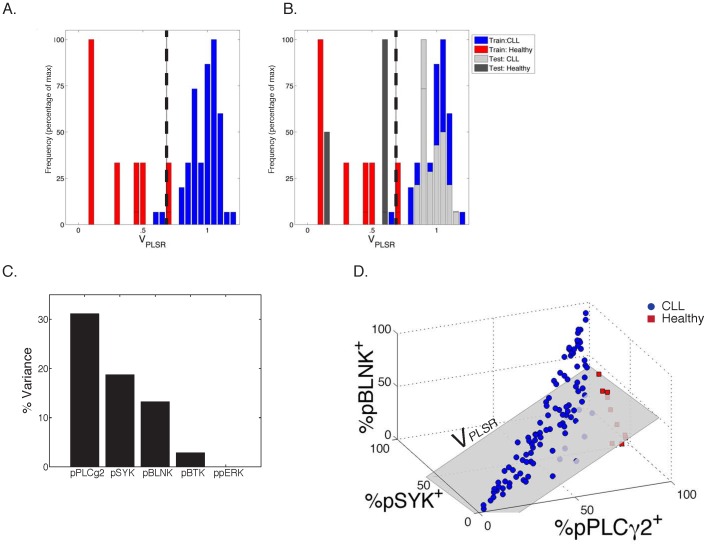
We then demonstrated how differential responsiveness in signaling responses discriminates between CLL and healthy individuals with high statistical significance (p<2×10−5). ( Fig. 4A ). Optimization of a VPLSR threshold found that VPLSR = 0.695 best discriminated between our training set of CLL and healthy individuals (Supp. Fig. S6, S7). Utilizing the VPLSR model defined during our training phase, we tested the validity of our model using a “test set” from a separate CLL patient cohort (38 independently-acquired CLL patient samples, 3 healthy samples). We measured the stimulated signaling response of the test cohort, applied our VPLSR classifier and found it 100% accurate ( Fig. 4B , Supp. Fig. S6B). As pPLCγ2, pSYK and pBLNK account for 63% of the variability in the output, “response” variables (healthy vs. CLL) ( Fig. 4C ), we generated a 3D-representation of these phosphoresponses ( Fig. 4D ). This multidimensional visualization of the VPLSR variable illustrates how CLL B cells respond with colinearity in these three critical phosphoresponses (pPLCγ2, pSYK and pBLNK) while healthy individuals display a deviation from this strict colinearity (grey plane in Fig. 4D , Supp. Fig. S2A).
Figure 4. PLSR Model Results.
A Distributions of VPLSR scores for CLL and healthy samples from the training cohort. The x-axis shows the range of VPLSR solutions, with healthy individuals significantly clustering on the lower extreme, and CLL patients' phosphoprofiles producing high VPLSR scores (p<0.0001). This plot shows only patients included in the training set. The vertical black line at VPLSR = 0.695 represents the optimized cutoff between CLL and healthy phosphoprofiles (see Supp. Fig. S7). B Distribution of VPLSR scores for CLL and healthy samples from the training set (light and dark grey bars), overlaid to the VPLSR distribution of the training set. The model is upheld as the test set data is correctly partitioned by disease status (p<0.0001). Root mean squared error (RMSE) measurements quantify the regression error, supporting the validity and applicability of the model to other datasets: RMSEtraining = 0.1750; RMSEtest = 0.1576; RMSEall = 0.1644. Training set: CLL = 67; Healthy = 7. Test set: CLL = 38; Healthy = 3. C Percent variance between the disease states, according to VPLSR weight. Each phosphor-epitope individually accounts for the indicated percentage of the variability between CLL samples and healthy samples within the PLSR model. As shown, pPLCγ2+ has the strongest power in distinguishing healthy from CLL. D 3D-representation of VPLSR: a compendium of phosphoresponses best discriminating between CLL and healthy individuals. Each samples is represented as a datapoint, positioned in space according to the value of %pX+, for each axis. The grey plane corresponds to VPLSR = 0.695, which best separates CLL from healthy individuals.
Our multidimensional PLSR analysis demonstrates that the malignant properties of CLL B cells are evident and detectable in the B cell signaling response. PLSR analysis offered a robust filter to process multiple signaling readouts into a single discriminating variable, VPLSR. Comparison of VPLSR with CD5 and CD20 MFI indicates independence of the BCR signaling dysregulation in CLL from these established phenotypic features of CLL B cells. (Supp. Fig. S8) This independence of VPLSR from CD5 supports the ability of using the BCR signaling pathway phospho-signature as an independent measure of CLL disease status.
Cell-to-cell heterogeneity in VPLSR within the B cell population is both a characteristic hallmark of healthy samples and predictive of disease aggressiveness
Parsing of signaling responses in conjunction with CD5 and CD20 levels demonstrates heterogeneity of responsiveness within a CLL population. We applied cell-to-cell variability analysis (CCVA) [35], [36] to our single-cell phosphoprofiling measurements of CLL B cells. For each sample of stimulated B cells, CCVA parsed cells into subpopulations according to their abundance of CD20 and CD5 ( Fig. 5A ). Within each subpopulation, we computed the average VPLSR and obtained the distribution VPLSR(CD20,CD5). We then estimated the variability of BCR signaling by computing the standard deviation σ of the distribution VPLSR(CD20,CD5): σ (CD20, CD5) quantifies the heterogeneity of BCR signaling conditioned by the abundance of CD20 and CD5. Using the definition of subgroups of patients based on their responsiveness as defined in Figure 2A (“low responders”, “intermediate, healthy-like responders” and “high responders”), we found that healthy-like responders were individuals whose B cells displayed significantly larger σ (CD20, CD5) i.e. larger variability in signaling compared to low- or high-responders ( Fig. 5B ).
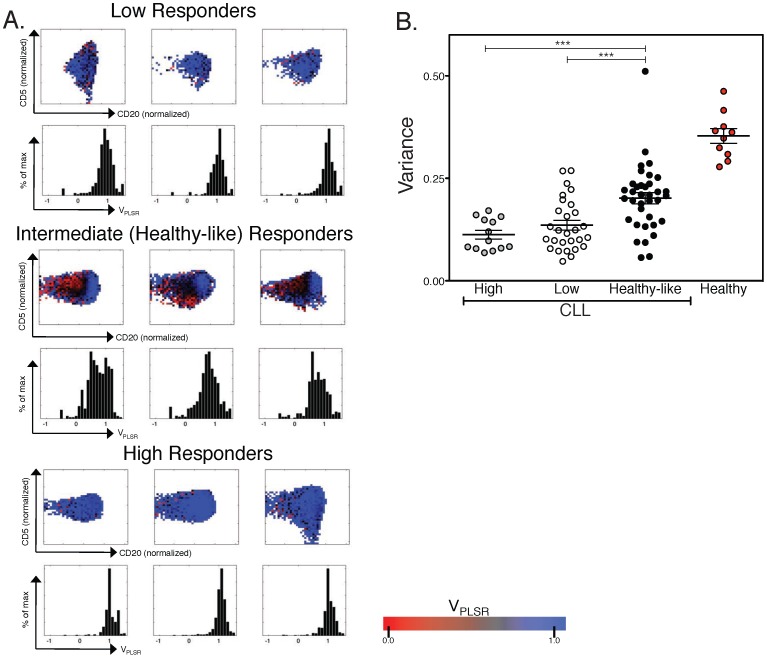
Figure 5. Cell-to-cell variability analysis for VPLSR as a function of CD20 and CD5 abundance.
A VPLSR analysis of high responder, low responder, and healthy-like responder groups. Three representative patient samples are shown for each responder type. All CLL B-cell samples have a majority of their cellular population exhibiting a VPLSR>0.695 consistent with the CLL range (blue, as shown in the scale bar). Histograms represent the mean and spread of the VPLSR values within each sample's B-cell population for low, high, and healthy-like responders. While low and high responders have a VPLSR score centered around 1, the width of this peak is highly variable, but much more so in the healthy-like CLL. Healthy samples uniformly have a large variance of VPLSR scores. B Evaluation of the heterogeneity within the samples as a measure of the variance of VPLSR within the B cell population. Healthy-like responders exhibited a significantly larger variance compared to high or how responders (healthy-like vs. high: p = 0.0005; healthy-like vs. low: p = 0.0008; high vs. low: p = 0.23). The variance of VPLSR within the B cell population of healthy samples is also shown.
Discussion
The ability of CLL cells to defy apoptosis is the result of a series of signaling events that favor survival over cell death. Gene expression profiling analyses have demonstrated that normal B cells and CLL B cells differ by thousands of differentially expressed genes. However, only a relatively small number of genes can differentiate between CLL with mutated and unmutated IGHV genes [37], [38]. The CLL genes that distinguished between the two subtypes were enriched for genes that are modulated upon BCR stimulation, particularly in the unmutated samples. Additionally, the presence of stereotyped IGHV genes in a significant proportion of CLL patients further supports the hypothesis of chronic antigenic BCR stimulation [39]–[41]. A recent study revealed a mechanism of cell-autonomous BCR stimulation in CLL, totally independent of antigenic stimulation, but requiring the presence of distinct epitopes intrinsic to the BCR itself [19]. Such variation in the degrees of autonomous or antigen-dependent signaling response via the BCR might explain the variation in clinical behavior among CLL patients.
We postulated that a quantitative assay probing CLL-specific signaling signatures in a large patient cohort could distinguish between CLL and healthy B cells, and that specific signatures could correlate with the heterogeneity of the disease. Heterogeneity has been shown by phospho-flow cytometry in recently published work. A recent small-scale study of 11 CLL samples showed generally impaired CLL signaling responses to BCR stimulation compared to healthy B cells, and an association was noted between signaling ability and outcome [42]. In a separate study, phosphoprofiling of 23 CLL samples demonstrated that, while anti-IgM crosslinking alone produced minimal phosphoresponses, addition of H2O2 as a mean of signal amplification via tyrosine phosphatase inhibition could segregate patients' CLL cells in high and low responders, implying variability in the differential proximal BCR modulation within the clonal population. Furthermore, the apoptotic response to F-Ara-A exposure was directly correlated to the size of the H2O2-responsive population, indicating that there is a direct association between BCR signaling ability and apoptotic response [29].
Our methodology combining flow cytometry and multifactorial statistical analysis of phosphoresponse profiles for 105 CLL patients uncovered a robust signaling defect in CLL B cells. Though activation of B cells with anti-IgM and H2O2, a commonly used in vitro method of stimulation, likely does not perfectly reproduce in vivo conditions, it shifts the system into a state of maximal activation. This permits insights into signaling mechanisms that differentiate CLL from healthy B-cells. Multidimensional regression analysis (PLSR) of B cell phosphoresponses against disease status assigned positive weights for activation of proximal kinases (SYK and BTK) and negative weights for activation of distal kinases (PLCγ2, BLNK and ERK). The resulting PLSR variable from our study was found to strongly correlate with disease status (high for CLL versus low for healthy). Thus we analyzed the overall 5-dimensional phosphoprofile as a whole in order to uncover the defect in the pathologic CLL clone compared to healthy cells. Other groups have utilized similar methodologies to analyze multidimensional data, in which complex statistical models are summarized in a practical mathematical procedure [43], [44]. Yet, none have applied these approaches to flow cytometric data, nor focused on defined biochemical networks to uncover mechanistic properties.
The critical utility of the PLSR analysis lies in its ability to model and probe mechanistic differences between CLL and healthy B cell; it is not meant to be used as a diagnostic tool for CLL. Furthermore, the information contained in the PLSR model is independent from established prognosticators. In fact, our discovery may be of fundamental biological significance as PLCγ2 is a critical signaling regulator of B-cell activation, whose hypoactivation could be used as a biomarker for response to therapies targeting the BCR signaling pathway, in CLL and other lymphoproliferative disorders. Along those lines, Song et al. reported how total SYK and PLCγ2 phosphorylation upon dasatinib treatment (a SRC inhibitor) predicted the apoptotic response to the drug [45]. Previous studies of BCR signaling response may have failed to discover the differential pSYK vs pPLCγ2 defect that we report here, because it is not absolute. Indeed, we found that there exists vast variability in signaling behavior between patients, which prevents using PLCγ2 or SYK phosphorylation alone as a direct readout of BCR aberrant signaling. This is particularly significant for future studies as the identity of the dysfunctional regulators in CLL BCR signaling (possibly a differentially-regulated phosphatase) must carry more specificity towards pPLCγ2 inhibition compared to other kinases. Relating VPLSR to other diagnostic and prognostic readouts, we found that those of worse outcome (treatment status, CD38 expression, cytogenetic defects associated with poor prognosis) did correlate, though with only modest statistical significance, with lower VPLSR (data not shown).
Our study also confirmed bimodality in the phosphoresponse of CLL patients, as previously described by Palazzo et al. [29], here for each of the five kinases under study; this is characteristic of a globally-perturbed kinase network structure in CLL. Furthermore, while vast variability was observed between the stimulation signatures of different CLL patients, the tightly-controlled activation of the healthy donors was found to be robust, reproducible, and independent of healthy donor age (Supp. Fig. S9). This is particularly significant as access to blood samples from age-matched healthy donors can be limiting, yet unnecessary in the case of our methodology. Our study also identified two groups of patients, based on differential responsiveness within their CLL B cell population: patients whose majority of CLL cells strongly responded to antigenic activation were found to require treatment earlier and to harbor more frequently unmutated IGHV genes (both indicators of poor prognosis).
To conclude, this work demonstrates that a combination of phospho-specific flow cytometry and PLSR analysis can quantify how different neoplastic and benign cells behave within the same sample. Our multiparametric methodology can help identify mechanisms of dysregulation, that otherwise could never be explored by less sophisticated techniques. Hence, with minimal manipulation in a clinical setting, direct activation and probing of signaling responses with single–cell resolution by flow cytometry can yield new measurements to further classify subtypes of CLL with statistical significance.
Supporting Information
Patient Profiles and Clinical Characteristics.
(PDF)
Optimization and Validation of thaw, rest, and stimulation procedure. A. Rest time: Two CLL (blue) and two healthy donors (red) were rested for varied amount of time (as indicated on the x-axis), followed by a 4-min stimulation with anti-IgM and 3.3 mM hydrogen peroxide. These data demonstrate that B cells rapidly reach a steady-state of BCR-responsiveness after thawing and we conservatively chose a 2 hr-rest period for all our assays. B. H2O2 Titration: Four CLL patients (blue) and two healthy samples (red) were stimulated with anti-IgM and various concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (3.3 µM, 33 µM, 330 µM and 3.3 mM). %pBLNK+, %pPLC2+, %pSYK+ and %pBTK+ was used to measure the stimulation outcomes. We chose to use 3.3 mM H2O2 to boost the signaling responses of B cells in our assay. C. Stimulation conditions employed represent optimal setting for analysis of signaling mechanisms in CLL: Four experimental conditions and their effects on the signaling pathway response of CLL and healthy samples are shown. Data presented here justify the combined use of hydrogen peroxide and anti-IgM to achieve maximal discriminatory power among samples.
(TIFF)
Pairwise comparison of two-dimensional phosphoresponses. A %pX+ values for all CLL (blue) and healthy (red) samples. Each possible pairwise combination is shown. B MFI of cells responding with phosphorylation of X (X = PLC2, BLNK, SYK, BTK and ERK) in all possible pairwise combination. C Contour maps of the average B cell population: For each cohort, CLL and healthy, the cellular phosphoresponse fluorescence intensity values are averaged and viewed two dimensionally. Bimodality in the phosphoresponse of CLL B cells can be seen for 3 pairwise combinations (pBLNK vs pSYK, pPLCγ2 vs pBLNK and ppERK vs. pBTK). Healthy individuals show modest variability within a single population, while the CLL B-cells can be distinguished by their all-or-none response; a novel observation of BCR signaling pathway dynamics in CLL patients.
(TIFF)
Assessment of Apoptosis after 2-hour rest. A. Apoptosis measured with Annexin V and 7-AAD, herein double-positive cells used to identify the percentage of dead cells within the CD19+ B cells. There is no significant difference of the mean percent dead cells between high CLL responders, low CLL responders, or healthy PBMCs. B. No correlation exists between %pPLCg2 and the percentage of dead B cells (R2 = 0.07, p-value = 0.44, not significant).
(TIFF)
Correlating CLL patients' phosphoresponses with treatment status. Only PLC2 phosphoresponse is significantly different for treated and untreated patients (***: p<0.001).
(TIFF)
PLSR using only %pSYK+ and %pPLCγ2+ illustrates how these two factors, which accounted for the majority of the variance in the 5-phosphoresponse PLSR, are sufficient in partitioning CLL from healthy samples. A VPLSR(pPLCγ2, pSYK) equation. This new PLSR variable only takes into account a sample's %pPLCγ2+ and %pSYK+ values. Note the similarity in the PLSR weights between this equation and the original VPLSR. B BCR signaling diagram highlighting pathway-based understanding of the VPLSR score and weights. C Plot of %pPLCγ2+ vs %pSYK+ for all samples. Datapoints represent individual samples, blue denotes CLL patients, red denotes healthy individuals. The dashed line represents the VPLSR(pPLCγ2, pSYK) variable solved such that the disease states are maximally differentiated. D Frequency distribution of VPLSR(pPLCγ2, pSYK) values for all CLL and healthy controls. This variable is able to distinguish samples by disease state (p<0.0001).
(TIFF)
Two-dimensional representation of CLL vs Healthy discrimination based on PLSR values. A. Training Set CLL and Healthy individuals. VPLSR partitioning line (VPLSR = 0.695) is shown in black. B. Training and Test set. VPLSR discriminating line correctly partitions the test data (p<0.0001) by disease state.
(TIFF)
Cross Validation Justifies PLSR Power and the Use of Other Datasets. A Using Leave-One-Out Cross Validation, the RMSE remains small, and separation between the BCR signaling responses of CLL patients and healthy individuals remains strong. The results here are visualized using a cumulative distribution function plot, showing that the separation between the two disease states is consistent. B Using Leave-One-Out Cross Validation, we can determine frequency of error in the PLSR discrimination between disease states. A cutoff of VPLSR scores to distinguish CLL vs. healthy is optimized based on these error frequencies: cutoff = 0.695. At this cutoff, <1/10 Healthy samples are falsely defined as CLL, and 4/105 CLL samples are falsely defined as Healthy based on their VPLSR score. C Validation of PLSR Model. The relationship between the number of regression components included and the root mean squared error (RMSE) is shown here. Five components, or latent variables, are used to minimize error without overfitting.
(TIFF)
VPLSR does not correlate with the abundance of CD5 (A) and CD20 (B) in B cells for CLL patients and healthy individuals.
(TIFF)
The ability of VPLSR to discriminate between CLL and healthy patients is independent of donor age. Our original healthy donors (used for training and testing the VPLSR) were not agematched (HD median age: 36 year-old, CLL median age: 66 year-old). To test if the donor age affected the reliability of our method, we collected a separate cohort of agematched healthy donors (median age = 69 year-old) and young healthy donors (median age = 24 year-old). We applied the BCR stimulation and VPLSR processing protocol (as outlined in our methods) to (n = 7) CLL patients, (n = 7) age-matched healthy donors and (n = 6) young healthy donors. A) VPLSR of CLL patients (blue) and healthy donors (red) from “training” and “test” cohorts as a function of age. Note the lack of correlation (CLL: R2 = 0.004; Healthy: R2 = 0.03, n.s.), which justifies using samples collected from non age-matched healthy donors. B) Stimulation and analysis protocols (Fig. 3) were applied to a novel group of CLL patients (blue), age-matched healthy donors (dark red), and younger healthy donors (red). Independent of age, our methodology discriminates between disease states in this new experimental cohort. This figure is representative of two repeats.
(TIFF)
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Alan Houghton for his longstanding support, Sidney Lu, Jonathan Irish and Gary Nolan for helpful discussions, and Jay Patel and Uttam Rao for technical help. This work was supported by the following funding sources: NIH U54 CA148967 (MLP, KP, CZ, JWC, MvdB, GA-B), Lymphoma Foundation (MLP, MvdB), NIH K08 CA118260 (MLP), The Laskin Charitable Foundation (MLP), NSF 0848030 (JWC, GA-B), NIH R01-HL069929 (MvdB), NIH R01-CA107096 (MvdB), NIH R01- AI080455 (MvdB), DOD-USAMRAA award W81XWH-09-1-0294 (MvdB), RERF-NIAID (MvdB), MSKCC Experimental Therapeutics Center (MvdB), Lymphoma Foundation (MvdB), Alex's Lemonade Stand (MvdB), MSKCC Geoffrey Beene Cancer Research Center (MvdB), Peter Solomon Fund (MvdB), NIH AI083408 (CZ, GA-B).
Funding Statement
NIH U54 CA148967 (MLP, KP, CZ, DB, JWC, MvdB, GA-B) Lymphoma Foundation (MLP) NIH K08 CA118260 (MLP) The Laskin Charitable Foundation (MLP) NIH R01-HL069929 (MvdB) NIH R01-CA107096 (MvdB) NIH R01- AI080455 (MvdB) DOD-USAMRAA award W81XWH-09-1-0294 (MvdB) RERF-NIAID (MvdB) MSKCC Experimental Therapeutics Center (MvdB) Lymphoma Foundation (MvdB) Alex's Lemonade Stand (MvdB) MSKCC Geoffrey Beene Cancer Research Center (MvdB) Peter Solomon Fund (MvdB) NSF 0848030 (JWC, GA-B) NIH AI083408 (CZ, GA-B) The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Chiorazzi N, Rai KR, Ferrarini M (2005) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 352: 804–815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Dighiero G, Binet JL (2000) When and how to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 343: 1799–1801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Grever M, Kay N, Keating MJ, et al. (1996) National Cancer Institute-sponsored Working Group guidelines for chronic lymphocytic leukemia: revised guidelines for diagnosis and treatment. Blood 87: 4990–4997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Crespo M, Bosch F, Villamor N, Bellosillo B, Colomer D, et al. (2003) ZAP-70 expression as a surrogate for immunoglobulin-variable-region mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 348: 1764–1775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Ibrahim S, Keating M, Do KA, O'Brien S, Huh YO, et al. (2001) CD38 expression as an important prognostic factor in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 98: 181–186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Zupo S, Isnardi L, Megna M, Massara R, Malavasi F, et al. (1996) CD38 expression distinguishes two groups of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemias with different responses to anti-IgM antibodies and propensity to apoptosis. Blood 88: 1365–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, et al. (1999) Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 94: 1840–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Dohner H, Stilgenbauer S, Benner A, Leupolt E, Krober A, et al. (2000) Genomic aberrations and survival in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med 343: 1910–1916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Ghia P, Chiorazzi N, Stamatopoulos K (2008) Microenvironmental influences in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: the role of antigen stimulation. J Intern Med 264: 549–562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Stevenson FK, Krysov S, Davies AJ, Steele AJ, Packham G (2011) B-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 118: 4313–4320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Grzybowska-Izydorczyk O, Cebula B, Robak T, Smolewski P (2010) Expression and prognostic significance of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) family and its antagonists in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Eur J Cancer 46: 800–810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Schliep S, Decker T, Schneller F, Wagner H, Hacker G (2004) Functional evaluation of the role of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Exp Hematol 32: 556–562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Baudot AD, Jeandel PY, Mouska X, Maurer U, Tartare-Deckert S, et al. (2009) The tyrosine kinase Syk regulates the survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells through PKC[delta] and proteasome-dependent regulation of Mcl-1 expression. Oncogene 28: 3261–3273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Chiorazzi N, Ferrarini M (2003) B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: lessons learned from studies of the B cell antigen receptor. Annu Rev Immunol 21: 841–894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Buchner M, Fuchs S, Prinz G, Pfeifer D, Bartholome K, et al. (2009) Spleen tyrosine kinase is overexpressed and represents a potential therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res 69: 5424–5432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Contri A, Brunati AM, Trentin L, Cabrelle A, Miorin M, et al. (2005) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells contain anomalous Lyn tyrosine kinase, a putative contribution to defective apoptosis. J Clin Invest 115: 369–378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Ringshausen I, Schneller F, Bogner C, Hipp S, Duyster J, et al. (2002) Constitutively activated phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI-3K) is involved in the defect of apoptosis in B-CLL: association with protein kinase Cdelta. Blood 100: 3741–3748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Cuni S, Perez-Aciego P, Perez-Chacon G, Vargas JA, Sanchez A, et al. (2004) A sustained activation of PI3K/NF-kappaB pathway is critical for the survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Leukemia 18: 1391–1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Duhren-von Minden M, Ubelhart R, Schneider D, Wossning T, Bach MP, et al. (2012) Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia is driven by antigen-independent cell-autonomous signalling. Nature 489: 309–312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.JP Sharman JI, G Coffey, D Czerwinski, Y Hitoshi, R Levy (2007) Targeting Syk kinase for the treatment of B-cell lymphoma. ASCO Meeting Abstracts: 162s.
- 21. Hoellenriegel J, Meadows SA, Sivina M, Wierda WG, Kantarjian H, et al. (2011) The phosphoinositide 3′-kinase delta inhibitor, CAL-101, inhibits B-cell receptor signaling and chemokine networks in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Advani RH, Buggy JJ, Sharman JP, Smith SM, Boyd TE, et al. (2013) Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Ibrutinib (PCI-32765) Has Significant Activity in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Malignancies. Journal of Clinical Oncology 31: 88–94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Amrein PC, Attar EC, Takvorian T, Hochberg EP, Ballen KK, et al. (2011) Phase II Study of Dasatinib in Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clinical Cancer Research 17: 2977–2986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Friedberg JW, Sharman J, Sweetenham J, Johnston PB, Vose JM, et al. (2010) Inhibition of Syk with fostamatinib disodium has significant clinical activity in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 115: 2578–2585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, Flinn IW, Burger JA, et al. (2013) Targeting BTK with Ibrutinib in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. New England Journal of Medicine 369: 32–42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Irish JM, Hovland R, Krutzik PO, Perez OD, Bruserud O, et al. (2004) Single cell profiling of potentiated phospho-protein networks in cancer cells. Cell 118: 217–228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Irish JM, Czerwinski DK, Nolan GP, Levy R (2006) Altered B-cell receptor signaling kinetics distinguish human follicular lymphoma B cells from tumor-infiltrating nonmalignant B cells. Blood 108: 3135–3142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Irish JM, Myklebust JH, Alizadeh AA, Houot R, Sharman JP, et al. (2010) B-cell signaling networks reveal a negative prognostic human lymphoma cell subset that emerges during tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 12747–12754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Palazzo AL, Evensen E, Huang YW, Cesano A, Nolan GP, et al. (2011) Association of reactive oxygen species-mediated signal transduction with in vitro apoptosis sensitivity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. PLoS One 6: e24592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Khalil AM, Cambier JC, Shlomchik MJ (2012) B cell receptor signal transduction in the GC is short-circuited by high phosphatase activity. Science 336: 1178–1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Lee K, Esselman WJ (2002) Inhibition of PTPs by H(2)O(2) regulates the activation of distinct MAPK pathways. Free Radic Biol Med 33: 1121–1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Reth M (2002) Hydrogen peroxide as second messenger in lymphocyte activation. Nat Immunol 3: 1129–1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Behbehani GK, Bendall SC, Clutter MR, Fantl WJ, Nolan GP (2012) Single-cell mass cytometry adapted to measurements of the cell cycle. Cytometry A 81: 552–566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Mukherjee S, Zhu J, Zikherman J, Parameswaran R, Kadlecek TA, et al. (2013) Monovalent and Multivalent Ligation of the B Cell Receptor Exhibit Differential Dependence upon Syk and Src Family Kinases. Sci Signal 6: ra1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Cotari JW, Voisinne G, Altan-Bonnet G (2013) Diversity training for signal transduction: leveraging cell-to-cell variability to dissect cellular signaling, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Biotechnol 24: 760–766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Cotari JW, Voisinne G, Dar OE, Karabacak V, Altan-Bonnet G (2013) Cell-to-cell variability analysis dissects the plasticity of signaling of common gamma chain cytokines in T cells. Sci Signal 6: ra17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Klein U, Tu Y, Stolovitzky GA, Mattioli M, Cattoretti G, et al. (2001) Gene expression profiling of B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia reveals a homogeneous phenotype related to memory B cells. J Exp Med 194: 1625–1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Rosenwald A, Alizadeh AA, Widhopf G, Simon R, Davis RE, et al. (2001) Relation of gene expression phenotype to immunoglobulin mutation genotype in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Exp Med 194: 1639–1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Ghiotto F, Fais F, Valetto A, Albesiano E, Hashimoto S, et al. (2004) Remarkably similar antigen receptors among a subset of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Invest 113: 1008–1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Stamatopoulos K, Belessi C, Moreno C, Boudjograh M, Guida G, et al. (2007) Over 20% of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia carry stereotyped receptors: Pathogenetic implications and clinical correlations. Blood 109: 259–270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Widhopf GF 2nd, Rassenti LZ, Toy TL, Gribben JG, Wierda WG, et al. (2004) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells of more than 1% of patients express virtually identical immunoglobulins. Blood 104: 2499–2504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Blix ES, Irish JM, Husebekk A, Delabie J, Forfang L, et al. (2012) Phospho-specific flow cytometry identifies aberrant signaling in indolent B-cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer 12: 478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Agnelli L, Mereu E, Pellegrino E, Limongi T, Kwee I, et al. (2012) Identification of a 3-gene model as a powerful diagnostic tool for the recognition of ALK-negative anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood 120: 1274–1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Ralfkiaer U, Hagedorn PH, Bangsgaard N, Lovendorf MB, Ahler CB, et al. (2011) Diagnostic microRNA profiling in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). Blood 118: 5891–5900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Song Z, Lu P, Furman RR, Leonard JP, Martin P, et al. Activities of SYK and PLCgamma2 predict apoptotic response of CLL cells to SRC tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib. Clin Cancer Res 16: 587–599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Patient Profiles and Clinical Characteristics.
(PDF)
Optimization and Validation of thaw, rest, and stimulation procedure. A. Rest time: Two CLL (blue) and two healthy donors (red) were rested for varied amount of time (as indicated on the x-axis), followed by a 4-min stimulation with anti-IgM and 3.3 mM hydrogen peroxide. These data demonstrate that B cells rapidly reach a steady-state of BCR-responsiveness after thawing and we conservatively chose a 2 hr-rest period for all our assays. B. H2O2 Titration: Four CLL patients (blue) and two healthy samples (red) were stimulated with anti-IgM and various concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (3.3 µM, 33 µM, 330 µM and 3.3 mM). %pBLNK+, %pPLC2+, %pSYK+ and %pBTK+ was used to measure the stimulation outcomes. We chose to use 3.3 mM H2O2 to boost the signaling responses of B cells in our assay. C. Stimulation conditions employed represent optimal setting for analysis of signaling mechanisms in CLL: Four experimental conditions and their effects on the signaling pathway response of CLL and healthy samples are shown. Data presented here justify the combined use of hydrogen peroxide and anti-IgM to achieve maximal discriminatory power among samples.
(TIFF)
Pairwise comparison of two-dimensional phosphoresponses. A %pX+ values for all CLL (blue) and healthy (red) samples. Each possible pairwise combination is shown. B MFI of cells responding with phosphorylation of X (X = PLC2, BLNK, SYK, BTK and ERK) in all possible pairwise combination. C Contour maps of the average B cell population: For each cohort, CLL and healthy, the cellular phosphoresponse fluorescence intensity values are averaged and viewed two dimensionally. Bimodality in the phosphoresponse of CLL B cells can be seen for 3 pairwise combinations (pBLNK vs pSYK, pPLCγ2 vs pBLNK and ppERK vs. pBTK). Healthy individuals show modest variability within a single population, while the CLL B-cells can be distinguished by their all-or-none response; a novel observation of BCR signaling pathway dynamics in CLL patients.
(TIFF)
Assessment of Apoptosis after 2-hour rest. A. Apoptosis measured with Annexin V and 7-AAD, herein double-positive cells used to identify the percentage of dead cells within the CD19+ B cells. There is no significant difference of the mean percent dead cells between high CLL responders, low CLL responders, or healthy PBMCs. B. No correlation exists between %pPLCg2 and the percentage of dead B cells (R2 = 0.07, p-value = 0.44, not significant).
(TIFF)
Correlating CLL patients' phosphoresponses with treatment status. Only PLC2 phosphoresponse is significantly different for treated and untreated patients (***: p<0.001).
(TIFF)
PLSR using only %pSYK+ and %pPLCγ2+ illustrates how these two factors, which accounted for the majority of the variance in the 5-phosphoresponse PLSR, are sufficient in partitioning CLL from healthy samples. A VPLSR(pPLCγ2, pSYK) equation. This new PLSR variable only takes into account a sample's %pPLCγ2+ and %pSYK+ values. Note the similarity in the PLSR weights between this equation and the original VPLSR. B BCR signaling diagram highlighting pathway-based understanding of the VPLSR score and weights. C Plot of %pPLCγ2+ vs %pSYK+ for all samples. Datapoints represent individual samples, blue denotes CLL patients, red denotes healthy individuals. The dashed line represents the VPLSR(pPLCγ2, pSYK) variable solved such that the disease states are maximally differentiated. D Frequency distribution of VPLSR(pPLCγ2, pSYK) values for all CLL and healthy controls. This variable is able to distinguish samples by disease state (p<0.0001).
(TIFF)
Two-dimensional representation of CLL vs Healthy discrimination based on PLSR values. A. Training Set CLL and Healthy individuals. VPLSR partitioning line (VPLSR = 0.695) is shown in black. B. Training and Test set. VPLSR discriminating line correctly partitions the test data (p<0.0001) by disease state.
(TIFF)
Cross Validation Justifies PLSR Power and the Use of Other Datasets. A Using Leave-One-Out Cross Validation, the RMSE remains small, and separation between the BCR signaling responses of CLL patients and healthy individuals remains strong. The results here are visualized using a cumulative distribution function plot, showing that the separation between the two disease states is consistent. B Using Leave-One-Out Cross Validation, we can determine frequency of error in the PLSR discrimination between disease states. A cutoff of VPLSR scores to distinguish CLL vs. healthy is optimized based on these error frequencies: cutoff = 0.695. At this cutoff, <1/10 Healthy samples are falsely defined as CLL, and 4/105 CLL samples are falsely defined as Healthy based on their VPLSR score. C Validation of PLSR Model. The relationship between the number of regression components included and the root mean squared error (RMSE) is shown here. Five components, or latent variables, are used to minimize error without overfitting.
(TIFF)
VPLSR does not correlate with the abundance of CD5 (A) and CD20 (B) in B cells for CLL patients and healthy individuals.
(TIFF)
The ability of VPLSR to discriminate between CLL and healthy patients is independent of donor age. Our original healthy donors (used for training and testing the VPLSR) were not agematched (HD median age: 36 year-old, CLL median age: 66 year-old). To test if the donor age affected the reliability of our method, we collected a separate cohort of agematched healthy donors (median age = 69 year-old) and young healthy donors (median age = 24 year-old). We applied the BCR stimulation and VPLSR processing protocol (as outlined in our methods) to (n = 7) CLL patients, (n = 7) age-matched healthy donors and (n = 6) young healthy donors. A) VPLSR of CLL patients (blue) and healthy donors (red) from “training” and “test” cohorts as a function of age. Note the lack of correlation (CLL: R2 = 0.004; Healthy: R2 = 0.03, n.s.), which justifies using samples collected from non age-matched healthy donors. B) Stimulation and analysis protocols (Fig. 3) were applied to a novel group of CLL patients (blue), age-matched healthy donors (dark red), and younger healthy donors (red). Independent of age, our methodology discriminates between disease states in this new experimental cohort. This figure is representative of two repeats.
(TIFF)