Abstract
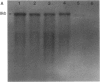
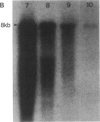
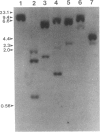
A cDNA clone for nonerythroid alpha-spectrin was identified by direct immunological screening of a chicken smooth muscle cDNA library. A library prepared in the expression plasmids pUC8 and pUC9 was screened with an antiserum specific for chicken alpha-spectrin. Blots of poly(A)+ RNA from various tissues of chicken and mouse show that the cDNA hybridizes to an 8-kilobase mRNA. The cDNA hybridizes to a single-copy sequence on Southern blots of chicken genomic DNA. The complete nucleic acid sequence of the clone has a single 1419-base open reading frame. The derived amino acid sequence is organized into two partial and three complete 106-amino-acid repeats that show homology to the repeats described for human erythroid alpha- and beta-spectrin. Immunological and biochemical data indicate that chicken nonerythroid and human erythroid alpha-spectrin are two of the more widely diverged members of the spectrin family of proteins. In this respect, the degree of homology found between them was unexpected. Our data suggest a common evolutionary origin for these two alpha-spectrins and allow some predictions concerning spectrin gene structure.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Davis J., Fowler W. E. Brain spectrin, a membrane-associated protein related in structure and function to erythrocyte spectrin. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):126–131. doi: 10.1038/299126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodine D. M., 4th, Birkenmeier C. S., Barker J. E. Spectrin deficient inherited hemolytic anemias in the mouse: characterization by spectrin synthesis and mRNA activity in reticulocytes. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90408-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., Elshourbagy N., Taylor J. M., Gordon J. I. Rat apolipoprotein A-IV contains 13 tandem repetitions of a 22-amino acid segment with amphipathic helical potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Cohen C. M., Tyler J. Interaction of cytoskeletal proteins on the human erythrocyte membrane. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Kelly T., Mangeat P. Nonerythrocyte spectrins: actin-membrane attachment proteins occurring in many cell types. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):478–486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cioe L., Curtis P. Detection and characterization of a mouse alpha-spectrin cDNA clone by its expression in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1367–1371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M. The molecular organization of the red cell membrane skeleton. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):141–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P. Fodrin is the general spectrin-like protein found in most cells whereas spectrin and the TW protein have a restricted distribution. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P., Weber K. Erythroid spectrin, brain fodrin, and intestinal brush border proteins (TW-260/240) are related molecules containing a common calmodulin-binding subunit bound to a variant cell type-specific subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4002–4005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Shiffer K. The spectrin membrane skeleton of normal and abnormal human erythrocytes: a review. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):C121–C141. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.3.C121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Zagon I. S., Kulikowski R. R. Identification of a spectrin-like protein in nonerythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7570–7574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Ricci W. M., Hughes S. H. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone that contains the entire coding region for chicken smooth-muscle alpha-tropomyosin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14136–14143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn C. L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Phillips S. J., Weaver S., Haigwood N. L., Voliva C. F., Edgell M. H. DNA sequence organization of the beta-globin complex in the BALB/c mouse. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak L. P., Birkenmeier E. H. Mouse sn-glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: molecular cloning and genetic mapping of a cDNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3020–3024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota Y., Takahashi S., Nishikawa K., Ooi T. Homology in protein sequences expressed by correlation coefficients. J Theor Biol. 1981 Jul 21;91(2):347–361. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(81)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Nelson W. J. Erythrocyte form of spectrin in cerebellum: appearance at a specific stage in the terminal differentiation of neurons. Science. 1983 Nov 25;222(4626):931–933. doi: 10.1126/science.6356364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Nelson W. J., Kasamatsu T. Segregation of two spectrin forms in the chicken optic system: a mechanism for establishing restricted membrane-cytoskeletal domains in neurons. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J., Willard M. Fodrin: axonally transported polypeptides associated with the internal periphery of many cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):631–642. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T., Steers E., Jr Selective solubilization of a protein component of the red cell membrane. Science. 1968 Jan 12;159(3811):203–204. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3811.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T. The red cell membrane skeleton: recent progress. Blood. 1983 Jan;61(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. T., Ngai J., Wold B. J., Lazarides E. Tissue-specific expression of distinct spectrin and ankyrin transcripts in erythroid and nonerythroid cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):152–160. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Lazarides E. Expression of the beta subunit of spectrin in nonerythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):363–367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Lazarides E. Switching of subunit composition of muscle spectrin during myogenesis in vitro. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):364–368. doi: 10.1038/304364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repasky E. A., Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Widespread occurrence of avian spectrin in nonerythroid cells. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):821–833. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90444-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Gonda M. A., Flickinger G. H., Hahn B. H., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Genomes of evolutionarily divergent members of the human T-cell leukemia virus family (HTLV-I and HTLV-II) are highly conserved, especially in pX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4544–4548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher D. W., Davis G., Marchesi V. T. Structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. II. The sequence of the alpha-I domain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14938–14947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher D. W., Davis G., Yurchenco P. D., Marchesi V. T. Structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. I. Isolation of the alpha-I domain and its cyanogen bromide peptides. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14931–14937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher D. W., Marchesi V. T. Erythrocyte spectrin is comprised of many homologous triple helical segments. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):177–180. doi: 10.1038/311177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasenius V. M., Saraste M., Knowles J., Virtanen I., Lehto V. P. Sequencing of the chicken non-erythroid spectrin cDNA reveals an internal repetitive structure homologous to the human erythrocyte spectrin. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1425–1430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]