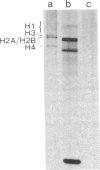
Abstract
We have cloned histone cDNAs from total RNA isolated from testis and from gastrula-stage embryos of the sea urchin Psammechinus miliaris. The reverse transcription of histone mRNAs was specifically primed with an oligonucleotide that is complementary to the conserved palindromic sequence present at the 3' end of nonpolyadenylated histone mRNAs. Two sperm H2B, two late H2B, and three late H2A variant cDNA clones were isolated and characterized by DNA sequence analysis. These cDNA clones were used to study the accumulation of histone mRNA during sea urchin embryogenesis. The different late H2A and H2B mRNAs are present in as few as 200 copies in the egg and each accumulate to 3-5 X 10(5) molecules in the gastrula embryo. One of the late mRNAs, the H2A-3 mRNA, is also abundant in testis RNA and codes for the H2A variant present in sperm chromatin. The late H2A-3 protein is therefore a more prevalent H2A variant of the sea urchin. In contrast, the two sperm H2B mRNAs are found in testes but not ovaries and embryos of the sea urchin, suggesting that the sperm H2B genes are expressed only during spermatogenesis. In addition, evidence for gene conversion between two late H2A gene variants is presented.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busslinger M., Moschonas N., Flavell R. A. Beta + thalassemia: aberrant splicing results from a single point mutation in an intron. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90412-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Portmann R., Birnsteil M. L. A regulatory sequence near the 3' end of sea urchin histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 11;6(9):2997–3008. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. G., Ozaki H. Changes in the histones of the sea urchin Stronglylocentrotus purpuratus at fertilization. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Mar 15;119(2):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs G., Nocente-McGrath C., Lieber T., Holt C., Knowles J. A. Sea urchin (lytechinus pictus) late-stage histone H3 and H4 genes: characterization and mapping of a clustered but nontandemly linked multigene family. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):383–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90132-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. H., Newrock K. M., Zweidler A. Stage-specific switches in histone synthesis during embryogenesis of the sea urchin. Science. 1975 Dec 5;190(4218):994–997. doi: 10.1126/science.1237932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Andrea R., Harvey R., Wells J. R. Vertebrate histone genes: nucleotide sequence of a chicken H2A gene and regulatory flanking sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3119–3128. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Hough-Evans B. R., Britten R. J. Molecular biology of the sea urchin embryo. Science. 1982 Jul 2;217(4554):17–26. doi: 10.1126/science.6178156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green G. R., Poccia D. L. Phosphorylation of sea urchin sperm H1 and H2B histones precedes chromatin decondensation and H1 exchange during pronuclear formation. Dev Biol. 1985 Mar;108(1):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K., Probst E., Schaffner W., Birnstiel M. Molecular analysis of the histone gene cluster of Psammechinus miliaris: I. Fractionation and identification of five individual histone mRNAs. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):455–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90213-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Hatching in the sea urchin Lytechinus pictus is accompanied by a shift in histone H4 gene activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4135–4139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C. C., Birnstiel M. L. The organization and expression of histone gene families. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hentschel C., Irminger J. C., Bucher P., Birnstiel M. L. Sea urchin histone mRNA termini are located in gene regions downstream from putative regulatory sequences. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):147–151. doi: 10.1038/285147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles J. A., Childs G. J. Temporal expression of late histone messenger RNA in the sea urchin Lytechinus pictus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2411–2415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauron A., Kedes L., Hough-Evans B. R., Davidson E. H. Accumulation of individual histone mRNAs during embryogenesis of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1982 Dec;94(2):425–434. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90359-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R. E., Jr, Wilt F. H. Accumulation of the early histone messenger RNAs during the development of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1982 Dec;94(2):435–440. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R., Cohn R., Kedes L., Mohun T. Expression and organization of histone genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:239–277. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxson R., Mohun T., Gormezano G., Childs G., Kedes L. Distinct organizations and patterns of expression of early and late histone gene sets in the sea urchin. Nature. 1983 Jan 13;301(5896):120–125. doi: 10.1038/301120a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman A. F., De Boer P. A., De Laaf R. T., Destrée O. H. Primary structure of the histone H2A and H2B genes and their flanking sequences in a minor histone gene cluster of Xenopus laevis. FEBS Lett. 1982 Aug 2;144(2):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80645-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newrock K. M., Alfageme C. R., Nardi R. V., Cohen L. H. Histone changes during chromatin remodeling in embryogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):421–431. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newrock K. M., Cohen L. H., Hendricks M. B., Donnelly R. J., Weinberg E. S. Stage-specific mRNAs coding for subtypes of H2A and H2B histones in the sea urchin embryo. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock S. L., McIver C. M., Monahan J. J. Transformation of E. coli using homopolymer-linked plasmid chimeras. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 28;655(2):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. B., Weisser K. E., Childs G. Sequence comparisons of non-allelic late histone genes and their early stage counterparts. Evidence for gene conversion within the sea urchin late stage gene family. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 25;174(4):647–662. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W., Kunz G., Daetwyler H., Telford J., Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. Genes and spacers of cloned sea urchin histone DNA analyzed by sequencing. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):655–671. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90249-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland M., Strickland W. N., Brandt W. F., von Holt C. The partial amino acid sequences of the two H2B histones from sperm of the sea urchin Psammechinus miliaris. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 26;536(1):289–297. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90076-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland W. N., Strickland M. S., de Groot P. C., von Holt C. The primary structure of histone H2A from the sperm cell of the sea urchin Parechinus angulosus. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(1):151–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04779.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. C., Carlson S. S., White T. J. Biochemical evolution. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:573–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters D., Sautiere P., Biserte G. Primary structure of histone H2A from gonad of the sea urchin Psammechinus miliaris. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct;90(2):231–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong R., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. The primary structure and expression of four cloned human histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7409–7425. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]