Abstract
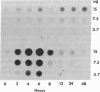
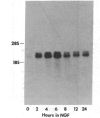
The mechanism by which nerve growth factor (NGF) stimulates ornithine decarboxylase (OrnDCase; EC 4.1.1.17) activity in the rat pheochromocytoma cell line PC12 was investigated. As demonstrated previously, NGF rapidly induces OrnDCase activity in a dose-dependent manner, with maximal enzymatic activity at 4-6 hr after exposure to NGF. Activity subsequently returns to near basal levels. A cloned OrnDCase cDNA was used to analyze the levels of OrnDCase RNA. In response to NGF administration, OrnDCase RNA levels were induced. The time course of the OrnDCase RNA induction paralleled that of the enzyme activity induction, and the magnitude of both inductions was quantitatively the same. Increased concentration of OrnDCase RNA was clearly detected at the earliest time point examined, 2 hr. No change was observed in the size of OrnDCase RNA. The dose-response curves for both RNA and enzyme activity inductions were also similar. Thus, increased OrnDCase RNA levels fully account for, and are responsible for, the induction of activity. Further, one-third of the OrnDCase RNA induction was unaffected by cycloheximide treatment but was fully blocked by actinomycin D treatment, suggesting that NGF acts through at least two mechanisms to mediate the OrnDCase induction. The first mechanism is cycloheximide insensitive and the second is mediated through an event requiring ongoing protein synthesis. Both mechanisms require ongoing transcription, as evidenced by the complete sensitivity of the induction process to actinomycin D.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atmar V. J., Kuehn G. D. Phosphorylation of ornithine decarboxylase by a polyamine-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5518–5522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger F. G., Szymanski P., Read E., Watson G. Androgen-regulated ornithine decarboxylase mRNAs of mouse kidney. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7941–7946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bethell D. R., Pegg A. E. Polyamines are needed for the differentiation of 3T3-L1 fibroblasts into adipose cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):272–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Rosbash M. Polynucleotide sequences in eukaryotic DNA and RNA that form ribonuclease-resistant complexes with polyuridylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 5;85(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazitt Y., Friend C. Polyamine biosynthesis enzymes in the induction and inhibition of differentiation in Friend erythroleukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1980 May;40(5):1727–1732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., Liem R. K., Shelanski M. L. Regulation of a high molecular weight microtubule-associated protein in PC12 cells by nerve growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):76–83. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. A., McGuire J. C. Induction of ornithine decarboxylase by nerve growth factor dissociated from effects on survival and neurite outgrowth. Nature. 1978 Nov 9;276(5684):191–194. doi: 10.1038/276191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guroff G., Dickens G., End D. The induction of ornithine decarboxylase by nerve growth factor and epidermal growth factor in PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 1981 Aug;37(2):342–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb00461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka H., Otten U., Thoenen H. Nerve growth factor-mediated selective induction of ornithine decarboxylase in rat pheochromocytoma; a cyclic AMP-independent process. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80777-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heby O. Role of polyamines in the control of cell proliferation and differentiation. Differentiation. 1981;19(1):1–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller J. S., Fong W. F., Canellakis E. S. Induction of a protein inhibitor to ornithine decarboxylase by the end products of its reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry I. A. The effect of the retrograde axonal transport of nerve growth factor on the morphology of adrenergic neurones. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 7;134(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)91068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry I. A. The retrograde trans-synaptic control of the development of cholinergic terminals in sympathetic ganglia. Brain Res. 1975 Mar 28;86(3):483–487. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90900-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heumann R., Korsching S., Scott J., Thoenen H. Relationship between levels of nerve growth factor (NGF) and its messenger RNA in sympathetic ganglia and peripheral target tissues. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3183–3189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isomaa V. V., Pajunen A. E., Bardin C. W., Jänne O. A. Ornithine decarboxylase in mouse kidney. Purification, characterization, and radioimmunological determination of the enzyme protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6735–6740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Jr, Gorin P. D., Brandeis L. D., Pearson J. Dorsal root ganglion neurons are destroyed by exposure in utero to maternal antibody to nerve growth factor. Science. 1980 Nov 21;210(4472):916–918. doi: 10.1126/science.7192014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänne J., Pösö H., Raina A. Polyamines in rapid growth and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 6;473(3-4):241–293. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahana C., Nathans D. Isolation of cloned cDNA encoding mammalian ornithine decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3645–3649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kontula K. K., Torkkeli T. K., Bardin C. W., Jänne O. A. Androgen induction of ornithine decarboxylase mRNA in mouse kidney as studied by complementary DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):731–735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsching S., Thoenen H. Nerve growth factor in sympathetic ganglia and corresponding target organs of the rat: correlation with density of sympathetic innervation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3513–3516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsching S., Thoenen H. Quantitative demonstration of the retrograde axonal transport of endogenous nerve growth factor. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Aug 19;39(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käpyaho K., Jänne J. Stimulation of melanotic expression in murine melanoma cells exposed to polyamine antimetabolites. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 31;113(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90425-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk G. D., Civin C. I., Weissman R. M., Baylin S. B. Ornithine decarboxylase: essential in proliferation but not differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells. Science. 1982 Apr 2;216(4541):75–77. doi: 10.1126/science.6950518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonnell P. C., Nagaiah K., Lakshmanan J., Guroff G. Nerve growth factor increases activity of ornithine decarboxylase in superior cervical ganglia of young rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4681–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCann P. P., Tardif C., Mamont P. S. Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase by ODC-antizyme in HTC cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Apr 25;75(4):948–954. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91474-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConlogue L. C., Marton L. J., Coffino P. Growth regulatory effects of cyclic AMP and polyamine depletion are dissociable in cultured mouse lymphoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):762–767. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConlogue L., Coffino P. Ornithine decarboxylase in difluoromethylornithine-resistant mouse lymphoma cells. Two-dimensional gel analysis of synthesis and turnover. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8384–8388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConlogue L., Gupta M., Wu L., Coffino P. Molecular cloning and expression of the mouse ornithine decarboxylase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):540–544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire J. C., Greene L. A., Furano A. V. NGF stimulates incorporation of fucose or glucosamine into an external glycoprotein in cultured rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvihill E. R., Palmiter R. D. Relationship of nuclear estrogen receptor levels to induction of ovalbumin and conalbumin mRNA in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2060–2068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Stallcup B. alpha-Bungarotoxin binding and cholinergic receptor function on a rat sympathetic nerve line. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8629–8633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B., Kirschenbaum B., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor-induced increase in saxitoxin binding to rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Neurosci. 1982 Oct;2(10):1405–1411. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-10-01405.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. H., Snyder S. H. Amine synthesis in regenerating rat liver: extremely rapid turnover of ornithine decarboxylase. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 May;5(3):253–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler J., Kelly M., McCann P. P. Inhibition of ornithine decarboxylase induces embryonal carcinoma cell differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 18;114(1):410–417. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91642-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seely J. E., Pösö H., Pegg A. E. Effect of androgens on turnover of ornithine decarboxylase in mouse kidney. Studies using labeling of the enzyme by reaction with [14C] alpha-difluoromethylornithine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7549–7553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekar V., Atmar V. J., Krim M., Kuehn G. D. Interferon induction of polyamine-dependent protein kinase activity in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):305–311. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91110-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelton D. L., Reichardt L. F. Expression of the beta-nerve growth factor gene correlates with the density of sympathetic innervation in effector organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7951–7955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. P., Varon S., Shooter E. M. Multiple forms of the nerve growth factor protein and its subunits. Biochemistry. 1968 Sep;7(9):3259–3268. doi: 10.1021/bi00849a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steglich C., Scheffler I. E. An ornithine decarboxylase-deficient mutant of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4603–4609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Takigawa M., Suzuki F. Role of polyamines in expression of the differentiated phenotype of chondrocytes: effect of DL-alpha-hydrazino-delta-aminovaleric acid (DL-HAVA), an inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase, on chondrocytes treated with parathyroid hormone. J Biochem. 1983 Feb;93(2):591–598. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Physiology of nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1980 Oct;60(4):1284–1335. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.4.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tischler A. S., Greene L. A. Nerve growth factor-induced process formation by cultured rat pheochromocytoma cells. Nature. 1975 Nov 27;258(5533):341–342. doi: 10.1038/258341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu M. W., Hori S., Tolson N., Huff K., Guroff G. Increased phosphorylation of a specific nuclear protein in rat superior cervical ganglia in response to nerve growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 14;81(3):941–946. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91442-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]