Abstract
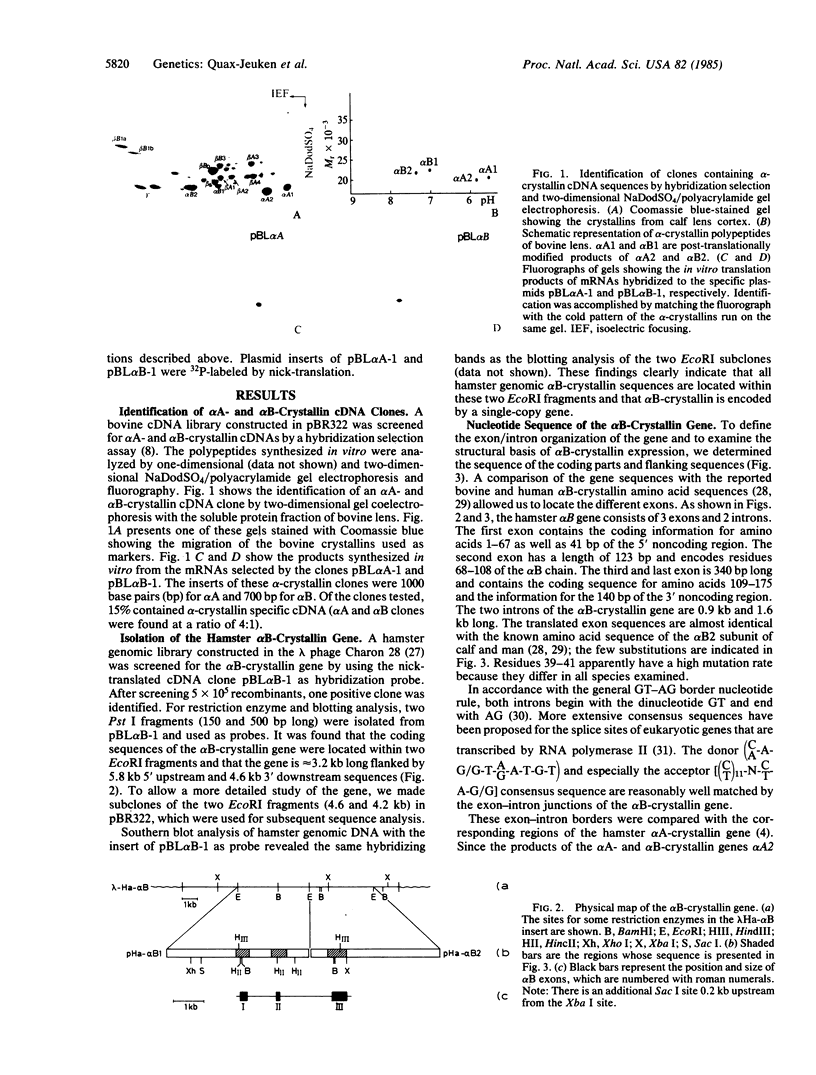
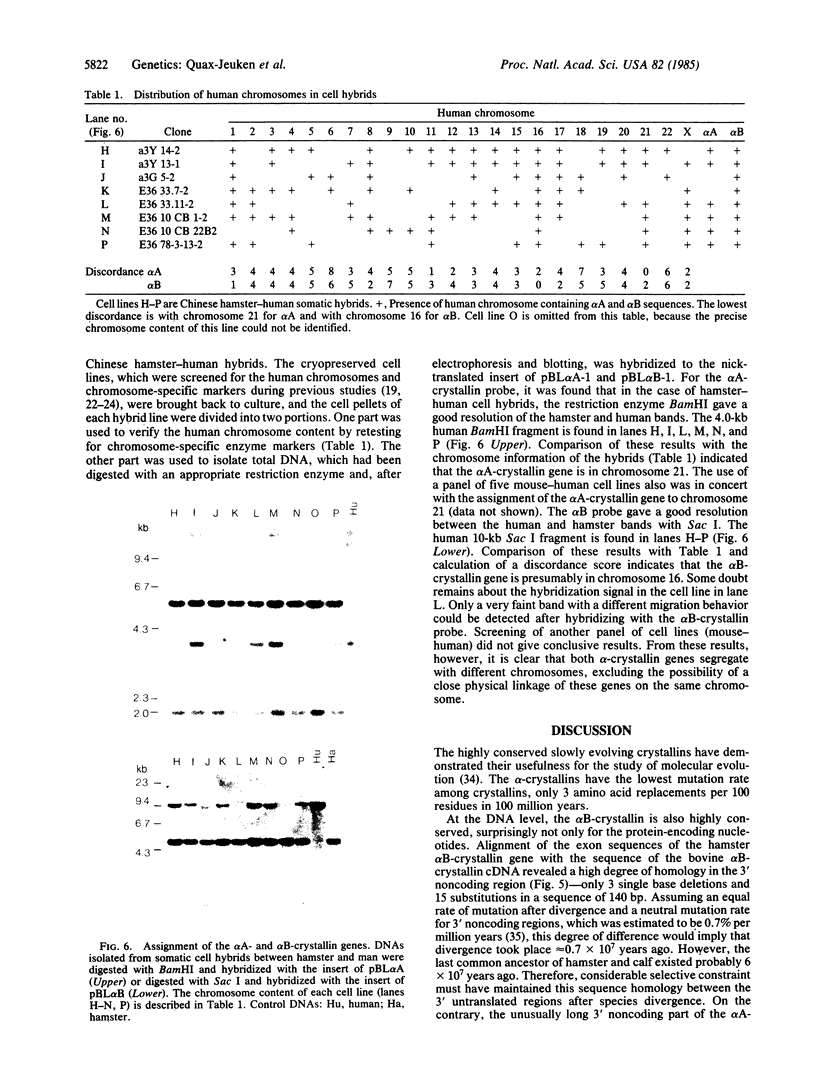
We isolated bovine complementary DNA clones for the alpha A- and alpha B-crystallin subunits. The alpha B cDNA clone was used to isolate an alpha B-crystallin gene. This gene, derived from hamster, occurs as a single copy in the genome and is 3.2 kilobases long. The coding sequences are spread on three exons with a total length of 709 nucleotides. The exon-intron distribution of the hamster alpha B-crystallin gene is similar to that of the alpha A-crystallin gene except for the 69 nucleotides that specify the 23 "insert" residues of the alpha AIns chain by means of differential splicing. The 3' noncoding region of the alpha B mRNA (140 bases), which is short compared with the alpha A mRNA (520 bases), shows a remarkable homology between calf and hamster. Both alpha-crystallin cDNA clones have been used to assign the chromosomal location of the corresponding human genes with the aid of somatic cell hybrids. It is shown that the single-copy alpha A- and alpha B-crystallin genes are located on different chromosomes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloemendal H. Lens proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;12(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238209105849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloemendal H. The vertebrate eye lens. Science. 1977 Jul 8;197(4299):127–138. doi: 10.1126/science.877544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chepelinsky A. B., King C. R., Zelenka P. S., Piatigorsky J. Lens-specific expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene promoted by 5' flanking sequences of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene in explanted chicken lens epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2334–2338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. H., Westerhuis L. W., de Jong W. W., Bloemendal H. Rat alpha-crystallin A chain with an insertion of 22 residues. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Aug 15;89(1):259–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb20921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan N. J., Dobner P. R., Fuchs E. V., Cleveland D. W. Expression of human alpha-tubulin genes: interspecies conservation of 3' untranslated regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1738–1745. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodemont H. J., Andreoli P. M., Moormann R. J., Ramaekers F. C., Schoenmakers J. G., Bloemendal H. Molecular cloning of mRNA sequences encoding rat lens crystallins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5320–5324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins J. W., Nickerson J. M., Sullivan M. A., Piatigorsky J. The chicken delta-crystallin gene family. Two genes of similar structure in close chromosomal approximation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9821–9825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbschleb-Voogt E., Grzeschik K. H., Pearson P. L., Meera Khan P. Assignment of adenosine deaminase complexing protein (ADCP) gene(s) to human chromosome 2 in rodent-human somatic cell hybrids. Hum Genet. 1981;59(4):317–323. doi: 10.1007/BF00295464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbschleb-Voogt E., Pearson P. L., Vossen J. M., Meera Khan P. Basic defect in the expression of adenosine deaminase in ADA- SCID disease investigated through the cells of an obligate heterozygote. Hum Genet. 1981;56(3):379–386. doi: 10.1007/BF00274697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A. Four small Drosophila heat shock proteins are related to each other and to mammalian alpha-crystallin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2360–2364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Piatigorsky J. Alternative RNA splicing of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene: protein-coding information within an intron. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):707–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Shinohara T., Piatigorsky J. alpha A-crystallin messenger RNA of the mouse lens: more noncoding than coding sequences. Science. 1982 Feb 19;215(4535):985–987. doi: 10.1126/science.7156978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramps J. A., de Man B. M., de Jong W. W. The primary structure of the B2 chain of human alpha-crystallin. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 15;74(1):82–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80757-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P., Wijnen L. M., Hagemeijer A., Pearson P. L. Human formaldehyde dehydrogenase (FDH) and its assignment to chromosome 4. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(2):112–115. doi: 10.1159/000132041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P., Wijnen L. M., Hagemeijer A., Pearson P. L. Human formaldehyde dehydrogenase (FDH) and its assignment to chromosome 4. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(2):112–115. doi: 10.1159/000132041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meera Khan P., Wijnen L. M., Wijnen J. T., Grzeschik K. H. Electrophoretic characterization and genetics of human biliverdin reductase (BLVR; EC 1.3.1.24); assignment of BLVR to the p14 leads to cen region of human chromosome 7 in mouse-human somatic cell hybrids. Biochem Genet. 1983 Feb;21(1-2):123–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski K., Wlodarski K., Aden D. Heterotopic chondrogenesis and osteogenesis induced by transformed cells: use of nude mice as a model system. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Oct;1(4):391–395. doi: 10.1007/BF01538670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F., Efstratiadis A., Lomedico P., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Dodgson J. The evolution of genes: the chicken preproinsulin gene. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90641-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J. Delta crystallins and their nucleic acids. Mol Cell Biochem. 1984;59(1-2):33–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00231304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gunning P., Blau H., Kedes L. Human actin genes are single copy for alpha-skeletal and alpha-cardiac actin but multicopy for beta- and gamma-cytoskeletal genes: 3' untranslated regions are isotype specific but are conserved in evolution. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1783–1791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax-Jeuken Y., Janssen C., Quax W., van den Heuvel R., Bloemendal H. Bovine beta-crystallin complementary DNA clones. Alternating proline/alanine sequence of beta B1 subunit originates from a repetitive DNA sequence. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):457–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., Egberts W. V., Hendriks W., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. The structure of the vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimm D. L., Horness D., Kucera J., Blattner F. R. Construction of coliphage lambda Charon vectors with BamHI cloning sites. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(3-4):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russnak R. H., Jones D., Candido E. P. Cloning and analysis of cDNA sequences coding for two 16 kilodalton heat shock proteins (hsps) in Caenorhabditis elegans: homology with the small hsps of Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3187–3205. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöffl F., Raschke E., Nagao R. T. The DNA sequence analysis of soybean heat-shock genes and identification of possible regulatory promoter elements. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2491–2497. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. A strategy of DNA sequencing employing computer programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2601–2610. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomarev S. I., Zinovieva R. D., Dolgilevich S. M., Krayev A. S., Skryabin K. G., Gause G. G., Jr The absence of the long 3'-non-translated region in mRNA coding for eye lens alpha A2-crystallin of the frog (Rana temporaria). FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 3;162(1):47–51. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Ouderaa F. J., De Jong W. W., Hilderink A., Bloemendal H. The amino-acids sequence of the alphaB2 chain of bovine alpha-crystallin. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 1;49(1):157–168. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03821.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerveld A., Visser R. P., Meera Khan P., Bootsma D. Loss of human genetic markers in man--Chinese hamster somatic cell hybrids. Nat New Biol. 1971 Nov 3;234(44):20–24. doi: 10.1038/newbio234020a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnen L. M., Grzeschik K. H., Pearson P. L., Meera Khan P. Direct assignment of citrate synthase (CS) gene to human chromosome 12 in man-mouse somatic cell hybrids. Hum Genet. 1977 Dec 23;39(3):339–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00295429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijnen L. M., Grzeschik K. H., Pearson P. L., Meera Khan P. The human PGM-2 and its chromosomal localization in man-mouse hybrids. Hum Genet. 1977 Jul 26;37(3):271–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00393608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong W. W., Cohen L. H., Leunissen J. A., Zweers A. Internally elongated rodent alpha-crystallin A chain: resulting from incomplete RNA splicing? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Sep 30;96(2):648–655. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91404-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Putten H., Terwindt E., Berns A., Jaenisch R. The integration sites of endogenous and exogenous Moloney murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90359-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]