Abstract
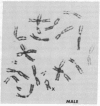
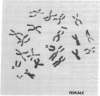
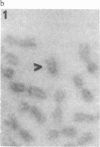
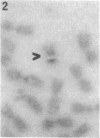
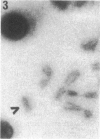
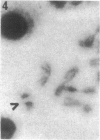
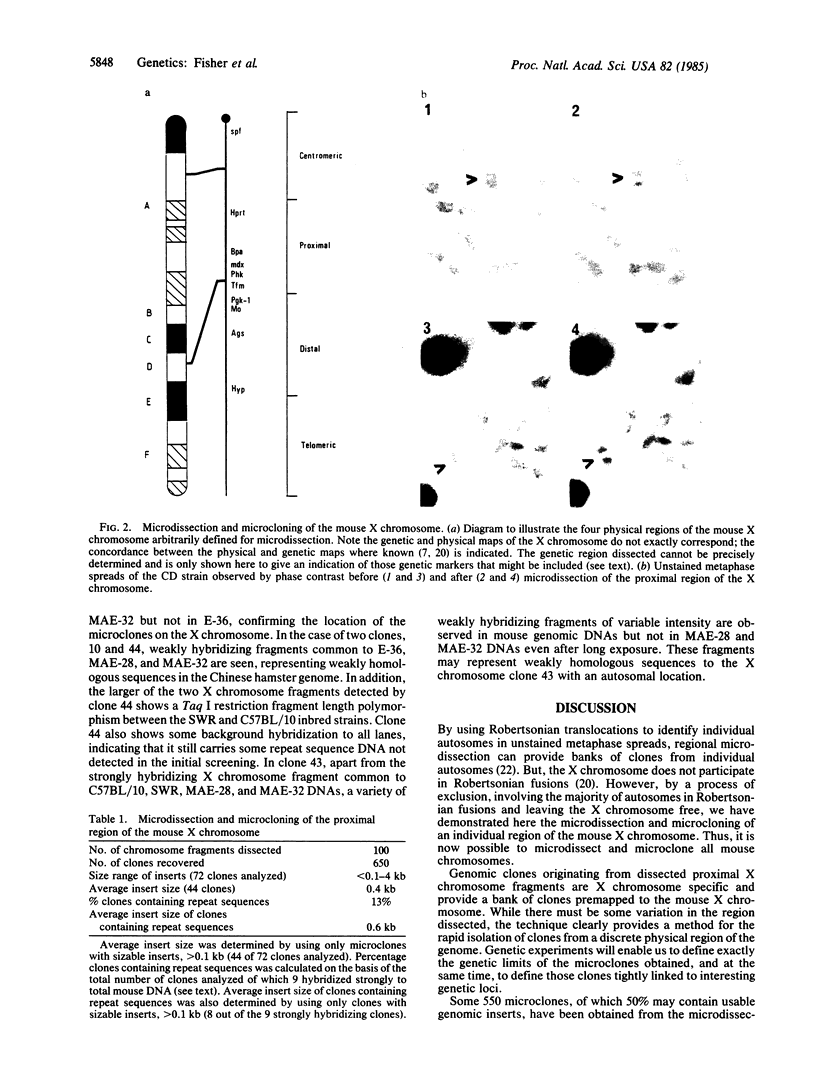
A wild mouse (CD) karyotype in which all the chromosomes bar the X, 19, and Y, are fused as metacentrics has been used for the microdissection and microcloning of a specific mouse X chromosome region. Dissection of a proximal region of the X chromosome encompassing the genetic loci Hprt to Tfm and including mdx has yielded 650 clones. A number of the recovered clones containing sizable inserts have been confirmed as X chromosome specific. This X chromosome bank of clones provides a start point for the isolation of the mdx locus. It is now clear that microdissection and microcloning can be applied to all mouse chromosomes, including the X chromosome, yielding premapped banks of clones that will greatly aid in the isolation and characterization of important genetic loci.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belfort M., Wulff D. L. An analysis of the processes of infection and induction of E. coli mutant hfl-1 by bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1973 Sep;55(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(73)81020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birg F., Favaloro J., Kamen R. Analysis of polyoma virus nuclear RNA by mini-blot hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3138–3142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breckon G., Goy P. Routine chromosome screening in Syrian hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus) using orbital sinus blood. Lab Anim. 1979 Oct;13(4):301–304. doi: 10.1258/002367779780943260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Dover G. A. The specific organisation of satellite DNA sequences on the X-chromosome of Mus musculus: partial independence of chromosome evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 25;8(4):781–792. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulfield G., Siller W. G., Wight P. A., Moore K. J. X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1189–1192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cappana E., Cristaldi M., Perticone P., Rizzoni M. Identification of chromosomes involved in the 9 Robertsonian fusions of the Apennine mouse with a 22-chromosome karyotype. Experientia. 1975 Mar 15;31(3):294–296. doi: 10.1007/BF01922545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattanach B. M., Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M. D., Barlow J. Male, female and intersex development in mice of identical chromosome constitution. Nature. 1982 Dec 2;300(5891):445–446. doi: 10.1038/300445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Eustachio P., Bothwell A. L., Takaro T. K., Baltimore D., Ruddle F. H. Chromosomal location of structural genes encoding murine immunoglobulin lambda light chains. Genetics of murine lambda light chains. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):793–800. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M. D., Cattanach B. M. Meitoic crossing-over between the X and Y chromosomes of male mice carrying the sex-reversing (Sxr) factor. Nature. 1982 Dec 2;300(5891):443–445. doi: 10.1038/300443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F. Mechanisms and evolutionary origins of variable X-chromosome activity in mammals. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1974 Nov 5;187(1088):243–268. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1974.0073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren A., Monk M. Fertile females produced by inactivation of an X chromosome of "sex-reversed' mice. Nature. 1982 Dec 2;300(5891):446–448. doi: 10.1038/300446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizusawa S., Ward D. F. A bacteriophage lambda vector for cloning with BamHI and Sau3A. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90200-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. M., Davies K. E., Harper P. S., Meredith L., Mueller C. R., Williamson R. Linkage relationship of a cloned DNA sequence on the short arm of the X chromosome to Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):69–71. doi: 10.1038/300069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastan S., Cattanach B. M. Interaction between the Xce locus and imprinting of the paternal X chromosome in mouse yolk-sac endoderm. Nature. 1983 Jun 16;303(5918):635–637. doi: 10.1038/303635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhme D., Fox H., Herrmann B., Frischauf A. M., Edström J. E., Mains P., Silver L. M., Lehrach H. Molecular clones of the mouse t complex derived from microdissected metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scalenghe F., Turco E., Edström J. E., Pirrotta V., Melli M. Microdissection and cloning of DNA from a specific region of Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1981;82(2):205–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00286105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh L., Phillips C., Jones K. W. The conserved nucleotide sequences of Bkm, which define Sxr in the mouse, are transcribed. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Efficient isolation of genes by using antibody probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1194–1198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]