Abstract
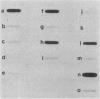
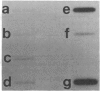
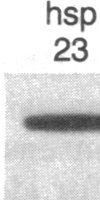
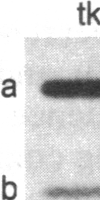
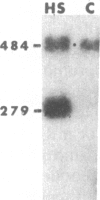
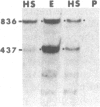
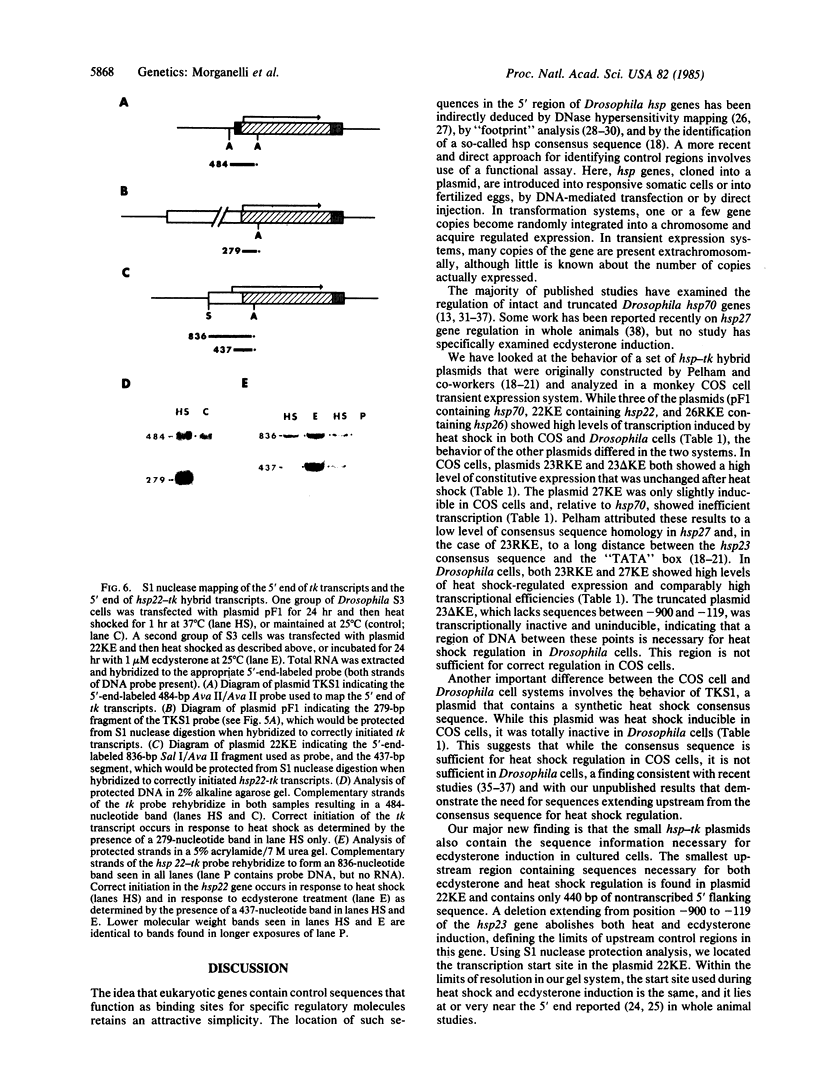
Hybrid genes containing the 5' region of Drosophila heat shock protein (hsp) genes, ligated to the herpesvirus thymidine kinase (tk) gene, were transfected into Drosophila line S3 cells. Constructions containing sequences upstream from hsp70, or from any of the small hsp genes, showed heat-inducible tk expression. Ecdysterone-inducible tk expression was seen only in transfections with small hsp-tk hybrid genes. Plasmids containing a synthetic "heat shock consensus sequence" or a deletion of the hsp23 upstream region were totally inactive in transfection studies.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin J., Mestril R., Lawson R., Klapper H., Voellmy R. The heat shock consensus sequence is not sufficient for hsp70 gene expression in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):197–203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. M., Woodward M. P. Small heat shock proteins in Drosophila may confer thermal tolerance. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Sep;147(2):437–442. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E., Wyss C. Acetylcholinesterase induction by beta-ecdysone in Drosophila cell lines and their hybrids. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Sep;6(5):631–640. doi: 10.1007/BF01538642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz M., Pelham H. R. Expression of a Drosophila heat-shock protein in Xenopus oocytes: conserved and divergent regulatory signals. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1583–1588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01359.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. J. Induction of Drosophila heat-shock puffs in isolated polytene nuclei. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90199-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheney C. M., Shearn A. Developmental regulation of Drosophila imaginal disc proteins: synthesis of a heat shock protein under non-heat-shock conditions. Dev Biol. 1983 Feb;95(2):325–330. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. S., Meselson M. Inducible transcription and puffing in Drosophila melanogaster transformed with hsp70-phage lambda hybrid heat shock genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5509–5513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corces V., Pellicer A., Axel R., Meselson M. Integration, transcription, and control of a Drosophila heat shock gene in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):7038–7042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.7038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corces V., Pellicer A. Identification of sequences involved in the transcriptional control of a Drosophila heat-shock gene. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14812–14817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craine B. L., Kornberg T. Activation of the major drosophila heat-shock genes in vitro. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):671–681. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90174-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Dawid I. B. Transient expression of genes introduced into cultured cells of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7095–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudler R., Travers A. A. Upstream elements necessary for optimal function of the hsp 70 promoter in transformed flies. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90494-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Corces V. G. Correct temperature induction and developmental regulation of a cloned heat shock gene transformed into the Drosophila germ line. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2883–2889. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A. Primary sequence of the 5' flanking regions of the Drosophila heat shock genes in chromosome subdivision 67B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1627–1642. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland R. C., Berger E. M. Synthesis of low molecular weight heat shock peptides stimulated by ecdysterone in a cultured Drosophila cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):855–859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland R. C., Berger E., Sirotkin K., Yund M. A., Osterbur D., Fristrom J. Ecdysterone induces the transcription of four heat-shock genes in Drosophila S3 cells and imaginal discs. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):498–507. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson R., Mestril R., Schiller P., Voellmy R. Expression of heat shock-beta-galactosidase hybrid genes in cultured Drosophila cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):116–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00328710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroy P., Dennis R., Beckers C., Sage B. A., O'Connor J. D. Demonstration of an ecdysteroid receptor in a cultured cell line of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6035–6038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayrand S., Pederson T. Heat shock alters nuclear ribonucleoprotein assembly in Drosophila cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):161–171. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirault M. E., Southgate R., Delwart E. Regulation of heat-shock genes: a DNA sequence upstream of Drosophila hsp70 genes is essential for their induction in monkey cells. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1279–1285. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00025.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morganelli C. M., Berger E. M. Transient expression of homologous genes in Drosophila cells. Science. 1984 Jun 1;224(4652):1004–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4652.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Bienz M. A synthetic heat-shock promoter element confers heat-inducibility on the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1473–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southgate R., Ayme A., Voellmy R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the Drosophila small heat shock gene cluster at locus 67B. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 25;165(1):35–57. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitek M. P., Morganelli C. M., Berger E. M. Stimulation of cytoplasmic actin gene transcription and translation in cultured Drosophila cells by ecdysterone. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1738–1743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Two protein-binding sites in chromatin implicated in the activation of heat-shock genes. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):229–234. doi: 10.1038/309229a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yund M. A., King D. S., Fristrom J. W. Ecdysteroid receptors in imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6039–6043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman J. L., Petri W., Meselson M. Accumulation of a specific subset of D. melanogaster heat shock mRNAs in normal development without heat shock. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1161–1170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]