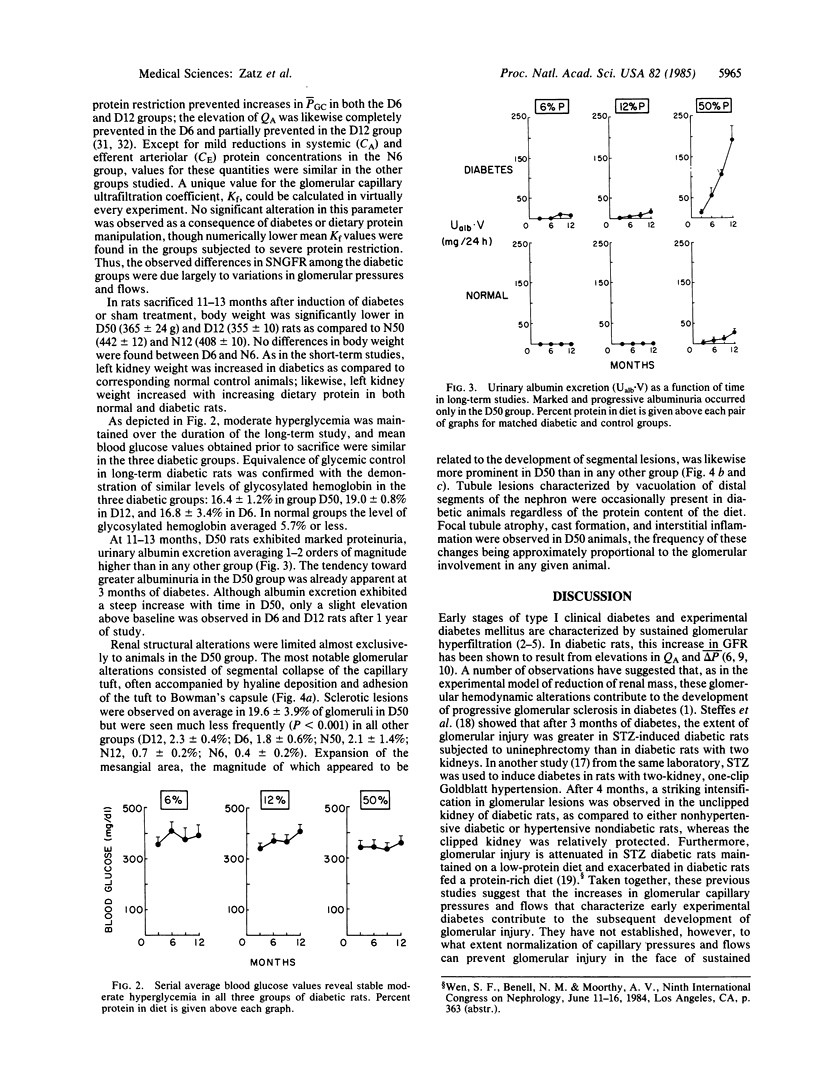
Abstract
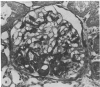
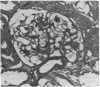
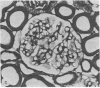
Six groups of Munich-Wistar rats underwent micropuncture study 2-10 weeks and morphologic studies 11-13 months after induction of streptozotocin diabetes or after sham treatment. Diabetic rats received diets containing 6% (group D6), 12% (D12), or 50% protein (D50) and were maintained under similar conditions of moderate hyperglycemia by daily injections of ultralente insulin. Age- and weight-matched normal control rats were also given 6% (Group N6), 12% (N12), or 50% protein (N50). Kidney weight, whole-kidney and single-nephron glomerular filtration rate, glomerular plasma flow, and mean glomerular transcapillary hydraulic pressure difference were higher in D50 rats than in all other groups and predisposed this group to marked and progressive albuminuria. Likewise, histological examination of the kidneys disclosed areas of sclerosis in 19.6% of glomeruli in D50 rats; the frequency of such lesions was less than 2.5% in all other groups. These findings indicate that the metabolic disorder seen in stable, moderately hyperglycemic diabetic rats does not lead to glomerulopathy as long as elevations in glomerular pressures and flows are prevented.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballermann B. J., Skorecki K. L., Brenner B. M. Reduced glomerular angiotensin II receptor density in early untreated diabetes mellitus in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 2):F110–F116. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.1.F110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baylis C., Deen W. M., Myers B. D., Brenner B. M. Effects of some vasodilator drugs on transcapillary fluid exchange in renal cortex. Am J Physiol. 1976 Apr;230(4):1148–1158. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.4.1148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton W. K., Benton F. R., Maclay J. G., Sturgill B. C. Spontaneous glomerular sclerosis in aging Sprague-Dawley rats. I. Lesions associated with mesangial IgM deposits. Am J Pathol. 1976 Nov;85(2):277–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Meyer T. W., Hostetter T. H. Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease: the role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 Sep 9;307(11):652–659. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198209093071104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brochner-Mortensen J. The glomerular filtration rate during moderate hyperglycemia in normal man. Acta Med Scand. 1973 Jul-Aug;1-2(1):31–37. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1973.tb19410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney S. L., Wong N. L., Dirks J. H. Acute effects of streptozotocin diabetes on rat renal function. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jun;93(6):950–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J. S., Frandsen M., Svendsen P. A., Gammelgaard J., Parving H. H. Rapid changes in kidney function--factors influencing kidney function in diabetics and normal man. Acta Endocrinol Suppl (Copenh) 1981;242:11–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J. S., Gammelgaard J., Frandsen M., Parving H. H. Increased kidney size, glomerular filtration rate and renal plasma flow in short-term insulin-dependent diabetics. Diabetologia. 1981 Apr;20(4):451–456. doi: 10.1007/BF00253406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J. S., Gammelgaard J., Orskov H., Andersen A. R., Telmer S., Parving H. H. Kidney function and size in normal subjects before and during growth hormone administration for one week. Eur J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;11(6):487–490. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1981.tb02018.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen J. S., Gammelgaard J., Tronier B., Svendsen P. A., Parving H. H. Kidney function and size in diabetics before and during initial insulin treatment. Kidney Int. 1982 May;21(5):683–688. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin L. D., Hostetter T. H., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. Hemodynamic basis for glomerular injury in rats with desoxycorticosterone-salt hypertension. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1448–1461. doi: 10.1172/JCI111349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feld L. G., Van Liew J. B., Galaske R. G., Boylan J. W. Selectivity of renal injury and proteinuria in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Kidney Int. 1977 Nov;12(5):332–343. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick R. L., Mazer J. S., Higgins P. J., Bunn H. F. Characterization of glycosylated hemoglobins. Relevance to monitoring of diabetic control and analysis of other proteins. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1062–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI110856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Olson J. L., Rennke H. G., Venkatachalam M. A., Brenner B. M. Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons: a potentially adverse response to renal ablation. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):F85–F93. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.1.F85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M. The case for intrarenal hypertension in the initiation and progression of diabetic and other glomerulopathies. Am J Med. 1982 Mar;72(3):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90490-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter T. H., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Glomerular hemodynamics in experimental diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 1981 Mar;19(3):410–415. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I., Purkerson M. L., Klahr S., Troy J. L., Martinez-Maldonado M., Brenner B. M. Mechanism of reduced glomerular filtration rate in chronic malnutrition. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):982–988. doi: 10.1172/JCI109784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. K., Christiansen J. S., Steven K., Parving H. H. Renal function in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia. 1981 Oct;21(4):409–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy L., Baynes J. W. Non-enzymatic glycosylation and the chronic complications of diabetes: an overview. Diabetologia. 1984 Feb;26(2):93–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00281113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg J. I., Patel P. Y. The effects of insulin, glucose and diabetes on prostaglandin production by rat kidney glomeruli and cultured glomerular mesangial cells. Prostaglandins Leukot Med. 1983 Aug;11(4):431–442. doi: 10.1016/0262-1746(83)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Steffes M. W., Azar S., Sandberg S. K., Brown D. M. The effects of Goldblatt hypertension on development of the glomerular lesions of diabetes mellitus in the rat. Diabetes. 1978 Jul;27(7):738–744. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.7.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVerry B. A., Fisher C., Hopp A., Huehns E. R. Production of pseudodiabetic renal glomerular changes in mice after repeated injections of glucosylated proteins. Lancet. 1980 Apr 5;1(8171):738–740. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michels L. D., Davidman M., Keane W. F. Determinants of glomerular filtration and plasma flow in experimental diabetic rats. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Dec;98(6):869–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. Glomerular filtration rate and renal plasma flow in short-term and long-term juvenile diabetes mellitus. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971 Sep;28(1):91–100. doi: 10.3109/00365517109090667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. L., Hostetter T. H., Rennke H. G., Brenner B. M., Venkatachalam M. A. Altered glomerular permselectivity and progressive sclerosis following extreme ablation of renal mass. Kidney Int. 1982 Aug;22(2):112–126. doi: 10.1038/ki.1982.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasch R. Control of blood glucose levels in the streptozotocin diabetic rat using a long-acting heat-treated insulin. Diabetologia. 1979 Mar;16(3):185–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01219796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STALDER G., SCHMID R. Severe functional disorders of glomerular capillaries and renal hemodynamics in treated diabetes mellitus during childhood. Ann Paediatr. 1959 Sep;193:129–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schambelan M., Blake S., Sraer J., Bens M., Nivez M. P., Wahbe F. Increased prostaglandin production by glomeruli isolated from rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):404–412. doi: 10.1172/JCI111714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schober E., Pollak A., Coradello H., Lubec G. Glycosylation of glomerular basement membrane in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic children. Diabetologia. 1982 Dec;23(6):485–487. doi: 10.1007/BF00254295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolwerth A. C., Sandler R. S., Hoffman P. M., Klahr S. Effects of nephron reduction and dietary protein content on renal ammoniagenesis in the rat. Kidney Int. 1975 Jun;7(6):397–404. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyer-Hansen K. Renal hypertrophy in experimental diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 1983 Apr;23(4):643–646. doi: 10.1038/ki.1983.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura T., Morrison A. B. A progressive glomerulosclerosis occurring in partial five-sixths nephrectomized rats. Am J Pathol. 1975 Apr;79(1):95–106. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffes M. W., Brown D. M., Mauer S. M. Diabetic glomerulopathy following unilateral nephrectomy in the rat. Diabetes. 1978 Jan;27(1):35–41. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turlapaty P. D., Lum G., Altura B. M. Vascular responsiveness and serum biochemical parameters in alloxan diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol. 1980 Dec;239(6):E412–E421. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.6.E412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viets J. W., Deen W. M., Troy J. L., Brenner B. M. Determination of serum protein concentration in nanoliter blood samples using fluorescamine or 9-phthalaldehyde. Anal Biochem. 1978 Aug 1;88(2):513–521. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]