Abstract
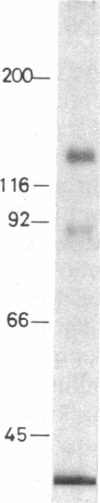
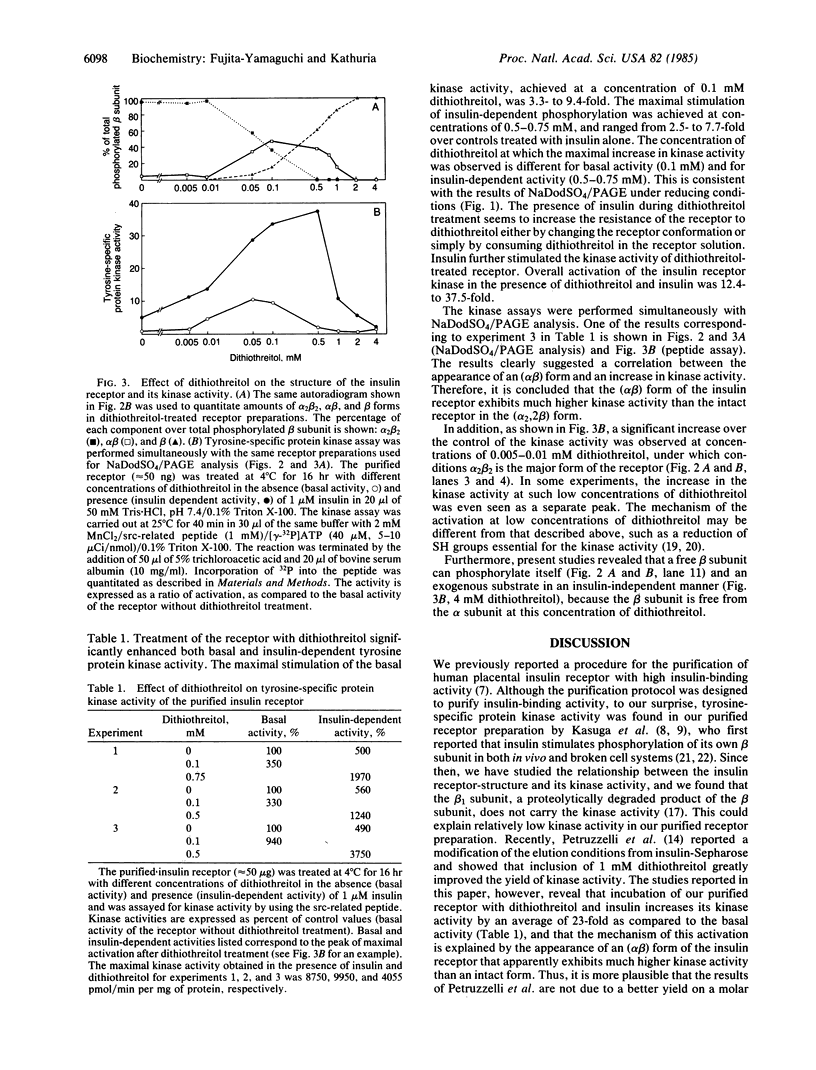
The relationship between the structure of the insulin receptor and its kinase activity was studied on the purified receptor treated with different concentrations of dithiothreitol. An enhanced autophosphorylation of the beta subunit (Mr, 90,000) was observed on NaDodSO4/PAGE under reducing conditions when the receptor was treated with 0.1-0.75 mM dithiothreitol in the presence of 1 microM insulin. Since we have previously observed (unpublished data) that incubation of the purified receptor with 1 mM dithiothreitol completely reduced an intact form of the receptor, alpha 2 beta 2, to free alpha subunit (Mr, 125,000) and beta subunit, the population of disulfide-linked complexes of the receptor after the dithiothreitol treatment was analyzed by NaDodSO4/PAGE under nonreducing conditions. The same receptor preparations were assayed for tyrosine kinase activity by using an exogenous substrate. Treatment of the receptor with dithiothreitol significantly enhanced both basal and insulin-dependent kinase activity. The kinase activity was enhanced 12- to 37-fold at concentrations of 0.5-0.75 mM dithiothreitol in the presence of 1 microM insulin. The amount of alpha 2 beta 2, alpha beta, and beta forms in each dithiothreitol-treated receptor preparation was quantified and compared with its kinase activity. These studies clearly indicate a correlation between the appearance of an alpha beta form and an increase in kinase activity. Therefore, we conclude that the alpha beta form of the insulin receptor exhibits much higher kinase activity than the intact receptor in the alpha 2 beta 2 form.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron M. D., Wisher M. H., Thamm P. M., Saunders D. J., Brandenburg D., Sönksen P. H. Hydrodynamic characterization of the photoaffinity-labeled insulin receptor solubilized in Triton X-100. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4156–4161. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Harrison M. L., Pike L. J., Hellström K. E., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation of synthetic peptides by a tyrosine protein kinase from the particulate fraction of a lymphoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):282–286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S., DeLuise M., Larkins R. G., Melick R. A., Harrison L. C. The effects of digestive enzymes on characteristics of placental insulin receptor. Comparison of particulate and soluble receptor preparations. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):37–43. doi: 10.1042/bj1740037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crettaz M., Jialal I., Kasuga M., Kahn C. R. Insulin receptor regulation and desensitization in rat hepatoma cells. The loss of the oligomeric forms of the receptor correlates with the change in receptor affinity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11543–11549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Heldin C. H. Characterization of a tyrosine-specific kinase activity in human fibroblast membranes stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10486–10492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita-Yamaguchi Y. Characterization of purified insulin receptor subunits. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):1206–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Choi S., Sakamoto Y., Itakura K. Purification of insulin receptor with full binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5045–5049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Sato Y., Kathuria S. Removal of sialic acids from the purified insulin receptor results in enhanced insulin-binding and kinase activities. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91954-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goko H., Takashima S., Kawamuro A., Matsuoka A. Insulin-like effects of dithiothreitol on isolated rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1981 Nov 15;200(2):425–428. doi: 10.1042/bj2000425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedo J. A., Kahn C. R., Hayashi M., Yamada K. M., Kasuga M. Biosynthesis and glycosylation of the insulin receptor. Evidence for a single polypeptide precursor of the two major subunits. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10020–10026. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Kull F. C., Jr, Earp H. S., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Somatomedin-C stimulates the phosphorylation of the beta-subunit of its own receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9581–9584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K. L., Flier J. S., Grunfeld C., Harmon J. T., Harrison L. C., Karlsson F. A., Kasuga M., King G. L., Lang U. C. Insulin receptors, receptor antibodies, and the mechanism of insulin action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1981;37:477–538. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571137-1.50015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Blithe D. L., Kahn C. R. Tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity is associated with the purified insulin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2137–2141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Blithe D. L., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Characterization of the insulin receptor kinase purified from human placental membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):10973–10980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Karlsson F. A., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates the phosphorylation of the 95,000-dalton subunit of its own receptor. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):185–187. doi: 10.1126/science.7031900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blithe D. L., Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in a cell-free system. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):667–669. doi: 10.1038/298667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon G. L., Reed G. H. Creatine kinase: structure-activity relationships. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983;54:367–426. doi: 10.1002/9780470122990.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavis V. R., Williams R. H. Studies of the insulin-like actions of thiols upon isolated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 10;245(1):23–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massague J., Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Electrophoretic resolution of three major insulin receptor structures with unique subunit stoichiometries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7137–7141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maturo J. M., 3rd, Hollenberg M. D., Aglio L. S. Insulin receptor: insulin-modulated interconversion between distinct molecular forms involving disulfide-sulfhydryl exchange. Biochemistry. 1983 May 10;22(10):2579–2586. doi: 10.1021/bi00279a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petruzzelli L., Herrera R., Rosen O. M. Insulin receptor is an insulin-dependent tyrosine protein kinase: copurification of insulin-binding activity and protein kinase activity to homogeneity from human placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3327–3331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollet R. J., Kempner E. S., Standaert M. L., Haase B. A. Structure of the insulin receptor of the cultured human lymphoblastoid cell IM-9. Evidence suggesting that two subunits are required for insulin binding. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 25;257(2):894–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronnett G. V., Knutson V. P., Kohanski R. A., Simpson T. L., Lane M. D. Role of glycosylation in the processing of newly translated insulin proreceptor in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4566–4575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Cassell D. J. Insulin receptor: evidence that it is a protein kinase. Science. 1983 Jan 21;219(4582):299–301. doi: 10.1126/science.6849137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shia M. A., Pilch P. F. The beta subunit of the insulin receptor is an insulin-activated protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1983 Feb 15;22(4):717–721. doi: 10.1021/bi00273a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shia M. A., Rubin J. B., Pilch P. F. The insulin receptor protein kinase. Physicochemical requirements for activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14450–14455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Hedo J. A. Insulin receptor phosphorylation may not be a prerequisite for acute insulin action. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1301–1304. doi: 10.1126/science.6367041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Brown T. A., Whipple J. H., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Dubler R. E., Cheng K., Larner J. A novel mechanism for the insulin-like effect of vanadate on glycogen synthase in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6650–6658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Larner J. Insulin-like effect of trypsin on the phosphorylation of rat adipocyte insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14749–14752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Togashi C. T., Reisler E. 5'-p-Fluorosulfonylbenzoyladenosine. Inactivation of myosin subfragment 1 and a model reaction with cysteine. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10112–10118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velicelebi G., Aiyer R. A. Identification of the alpha beta monomer of the adipocyte insulin receptor by insulin binding and autophosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7693–7697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Haring H. U., Kasuga M., Kahn C. R. Kinetic properties and sites of autophosphorylation of the partially purified insulin receptor from hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):255–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zick Y., Rees-Jones R. W., Taylor S. I., Gorden P., Roth J. The role of antireceptor antibodies in stimulating phosphorylation of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4396–4400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]