Abstract
Pure bovine brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor is a very potent mitogen for vascular endothelial cells in culture and, in the presence of heparin, induces blood vessel growth in vivo. Partial amino acid sequence determinations confirm that this mitogen is a unique protein having amino acid sequence homology with human interleukin 1.
Full text
PDF


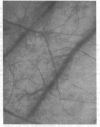
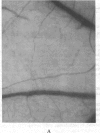
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausprunk D. H., Folkman J. Migration and proliferation of endothelial cells in preformed and newly formed blood vessels during tumor angiogenesis. Microvasc Res. 1977 Jul;14(1):53–65. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(77)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger P. C., Chandler D. B., Klintworth G. K. Corneal neovascularization as studied by scanning electron microscopy of vascular casts. Lab Invest. 1983 Feb;48(2):169–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Baird A., Esch F., Ling N., Gospodarowicz D. Isolation and partial molecular characterization of pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5364–5368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. C., Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Matsumoto-Kobayashi M., Kay R. M., Kaufman R. J., Brown E. L., Shoemaker C., Copeland T., Oroszlan S. Human T-cell growth factor: partial amino acid sequence, cDNA cloning, and organization and expression in normal and leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2543–2547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn G., Hatcher V. B. The isolation and purification of two anionic endothelial cell growth factors from human brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 15;124(1):262–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90946-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore P. A., Klagsbrun M. Endothelial cell mitogens derived from retina and hypothalamus: biochemical and biological similarities. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1545–1549. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B. E., Fitzharris T. P., Barnett B. D. Effects of varying chamber construction and embryo pre-incubation age on survival and growth of chick embryos in shell-less culture. Anat Rec. 1981 Jan;199(1):33–43. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091990105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenselau A., Mello R. J. Growth stimulation of cultured endothelial cells by tumor cell homogenates. Cancer Res. 1976 Sep;36(9 PT1):3269–3273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Cotran R. Relation of vascular proliferation to tumor growth. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1976;16:207–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Cotran R. Relation of vascular proliferation to tumor growth. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1976;16:207–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Taylor S., Spillberg C. The role of heparin in angiogenesis. Ciba Found Symp. 1983;100:132–149. doi: 10.1002/9780470720813.ch9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Bialecki H., Greenburg G. Purification of the fibroblast growth factor activity from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 25;253(10):3736–3743. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Localisation of a fibroblast growth factor and its effect alone and with hydrocortisone on 3T3 cell growth. Nature. 1974 May 10;249(453):123–127. doi: 10.1038/249123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D. Purification of a fibroblast growth factor from bovine pituitary. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2515–2520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Meredith S. C. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobson B., Denekamp J. Endothelial proliferation in tumours and normal tissues: continuous labelling studies. Br J Cancer. 1984 Apr;49(4):405–413. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R., Bradshaw R. A. Polypeptide growth factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:259–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon S. K., Bradshaw R. A. Purification and partial characterization of bovine pituitary fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biochem. 1983;21(3):195–208. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240210302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon S. K., Riley M. C., Thomas K. A., Hoover G. A., Maciag T., Bradshaw R. A. Bovine fibroblast growth factor: comparison of brain and pituitary preparations. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):162–169. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R. R., Fett J. W. Purification of two distinct growth factors from bovine neural tissue by heparin affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6295–6299. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Gubler U., Hellmann C. P., Dukovich M., Giri J. G., Pan Y. C., Collier K., Semionow R., Chua A. O., Mizel S. B. Cloning and expression of murine interleukin-1 cDNA in Escherichia coli. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):458–462. doi: 10.1038/312458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Mehlman T., Friesel R., Schreiber A. B. Heparin binds endothelial cell growth factor, the principal endothelial cell mitogen in bovine brain. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.6382607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Twardzik D. R., De Larco J. E., Stephenson J. R., Todaro G. J. Transforming growth factors produced by retrovirus-transformed rodent fibroblasts and human melanoma cells: amino acid sequence homology with epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4684–4688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa L. K., Jones D. B., Wright D. H. Mechanism of the induction of angiogenesis by human neoplastic lymphoid tissue: studies employing bovine aortic endothelial cells in vitro. J Pathol. 1980 Nov;132(3):207–216. doi: 10.1002/path.1711320303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olander J. V., Marasa J. C., Kimes R. C., Johnston G. M., Feder J. An assay measuring the stimulation of several types of bovine endothelial cells by growth factor(s) derived from cultured human tumor cells. In Vitro. 1982 Feb;18(2):99–107. doi: 10.1007/BF02796401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polverini P. J., Cotran P. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Unanue E. R. Activated macrophages induce vascular proliferation. Nature. 1977 Oct 27;269(5631):804–806. doi: 10.1038/269804a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Butterfield C., Murray J., Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1296–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.6199844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Riley M. C., Lemmon S. K., Baglan N. C., Bradshaw R. A. Brain fibroblast growth factor: nonidentity with myelin basic protein fragments. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5517–5520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Rios-Candelore M., Fitzpatrick S. Purification and characterization of acidic fibroblast growth factor from bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):357–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornton S. C., Mueller S. N., Levine E. M. Human endothelial cells: use of heparin in cloning and long-term serial cultivation. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):623–625. doi: 10.1126/science.6635659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Sasagawa T., Resing K., Walsh K. A. A simple and rapid purification of commercial trypsin and chymotrypsin by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jul 1;123(2):408–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90465-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]