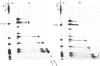Abstract
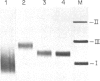
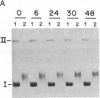
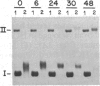
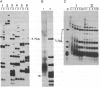
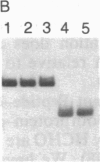
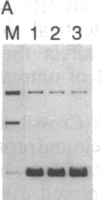
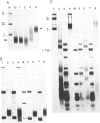
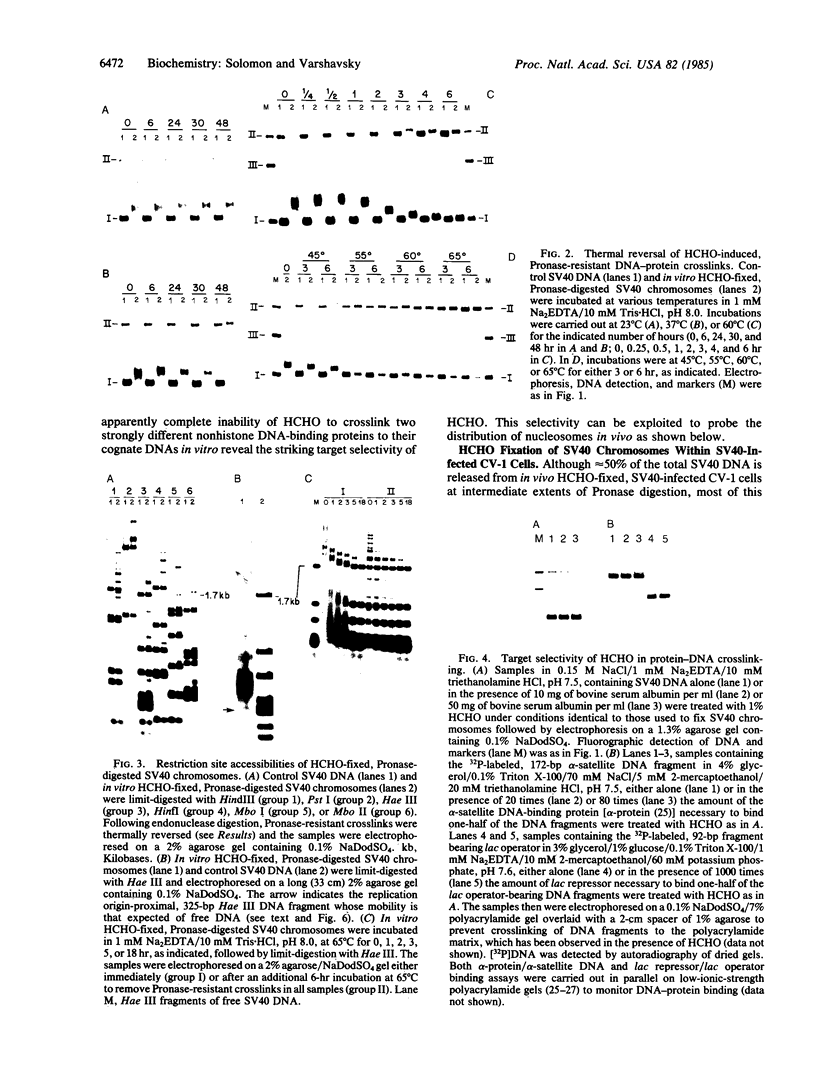
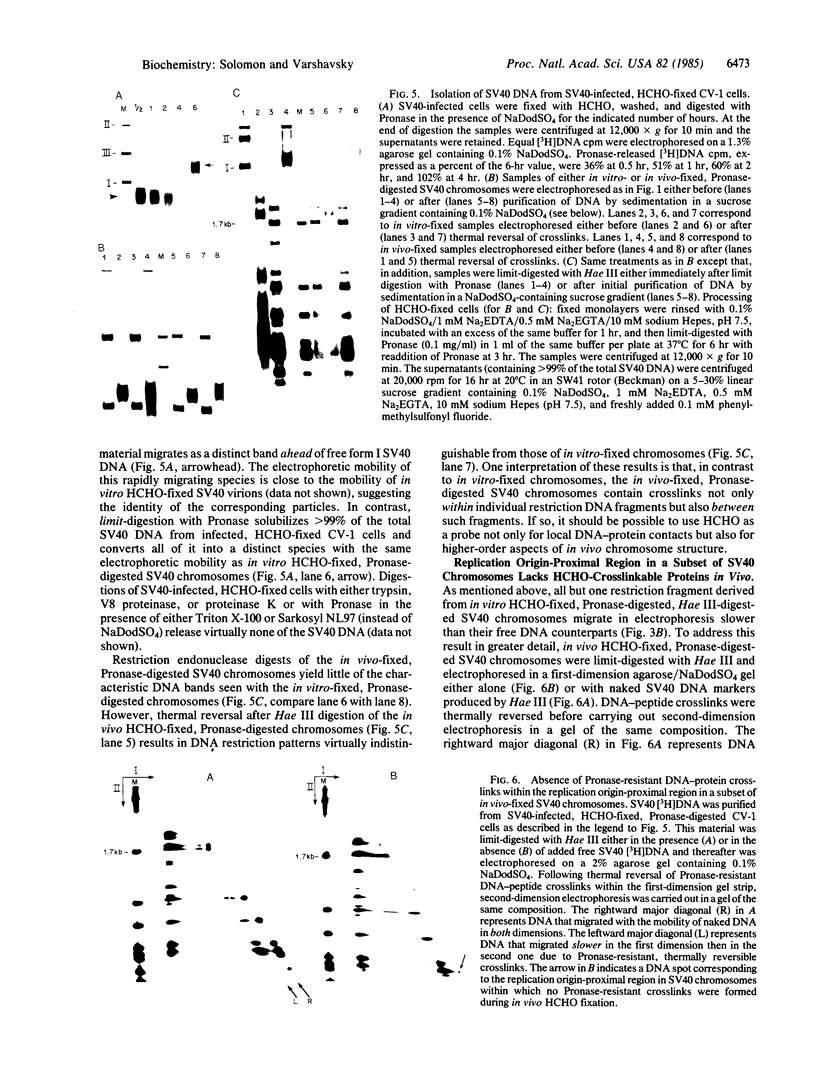
Formaldehyde (HCHO) produces DNA-protein crosslinks both in vitro and in vivo. Simian virus 40 (SV40) chromosomes that have been fixed by prolonged incubation with HCHO either in vitro or in vivo (within SV40-infected cells) can be converted to nearly protein-free DNA by limit-digestion with Pronase in the presence of NaDodSO4. The remaining Pronase-resistant DNA-peptide adducts retard the DNA upon gel electrophoresis, allowing resolution of free and crosslink-containing DNA. Though efficiently crosslinking histones to DNA within nucleosomes both in vitro and in vivo, HCHO does not crosslink either purified lac repressor to lac operator-containing DNA or an (A + T)-DNA-binding protein (alpha-protein) to its cognate DNA in vitro. Furthermore, a protein that does not bind to DNA, such as serum albumin, is not crosslinked to DNA by HCHO even at extremely high protein concentrations. These properties of HCHO as a DNA-protein crosslinker are used to probe the distribution of nucleosomes in vivo. We show that there are no HCHO-crosslinkable DNA-protein contacts in a subset of SV40 chromosomes in vivo within a 325-base-pair stretch that spans the "exposed" (nuclease-hypersensitive) region of the SV40 chromosome. This replication origin-proximal region has been found previously to lack nucleosomes in a subset of isolated SV40 chromosomes. We discuss other applications of the HCHO technique, including the possibility of obtaining base-resolution in vivo nucleosome "footprints."
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker M. M., Wang J. C. Use of light for footprinting DNA in vivo. Nature. 1984 Jun 21;309(5970):682–687. doi: 10.1038/309682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brutlag D., Schlehuber C., Bonner J. Properties of formaldehyde-treated nucleohistone. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3214–3218. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B., Elgin S. C. Cleavage of chromatin with methidiumpropyl-EDTA . iron(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doenecke D. Digestion of chromosomal proteins in formaldehyde treated chromatin. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Oct;359(10):1343–1352. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.1343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Anatomy of hypersensitive sites. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):213–214. doi: 10.1038/309213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ephrussi A., Church G. M., Tonegawa S., Gilbert W. B lineage--specific interactions of an immunoglobulin enhancer with cellular factors in vivo. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):134–140. doi: 10.1126/science.3917574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton A. B. How crowded is the cytoplasm? Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):345–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90231-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Lis J. T. Detecting protein-DNA interactions in vivo: distribution of RNA polymerase on specific bacterial genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilyin Y. V., Georgiev G. P. Heterogeneity of deoxynucleoprotein particles as evidencec by ultracentrifugation of cesium chloride density gradient. J Mol Biol. 1969 Apr;41(2):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Chalkley R. Use of whole-cell fixation to visualize replicating and maturing simian virus 40: identification of new viral gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6081–6085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V. Studies on histone organization in the nucleosome using formaldehyde as a reversible cross-linking agent. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):945–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Bratosin S., Aloni Y. A nucleosome-free region in SV40 minichromosomes. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):263–265. doi: 10.1038/285263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpov V. L., Preobrazhenskaya O. V., Mirzabekov A. D. Chromatin structure of hsp 70 genes, activated by heat shock: selective removal of histones from the coding region and their absence from the 5' region. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohwi-Shigematsu T., Gelinas R., Weintraub H. Detection of an altered DNA conformation at specific sites in chromatin and supercoiled DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4389–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews K. S. Tryptic core protein of lactose repressor binds operator DNA. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3348–3353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., von Hippel P. H. Formaldehyde as a probe of DNA structure. I. Reaction with exocyclic amino groups of DNA bases. Biochemistry. 1975 Mar 25;14(6):1281–1296. doi: 10.1021/bi00677a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller K., Rinke J., Ross A., Buddle G., Brimacombe R. The use of formaldehyde in RNA-protein cross-linking studies with ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jun 1;76(1):175–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11583.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Moyne G., Yaniv M. Absence of nucleosomes in a fraction of SV40 chromatin between the origin of replication and the region coding for the late leader RNA. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90235-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A., Wigmore D. J. Sites in simian virus 40 chromatin which are preferentially cleaved by endonucleases. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1511–1518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O. H., Bohn M. J. SV40 viral minichromosome: preferential exposure of the origin of replication as probed by restriction endonucleases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Oct;5(10):3469–3477. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.10.3469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Sundin O., Bohn M. A stretch of "late" SV40 viral DNA about 400 bp long which includes the origin of replication is specifically exposed in SV40 minichromosomes. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):453–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]