Abstract
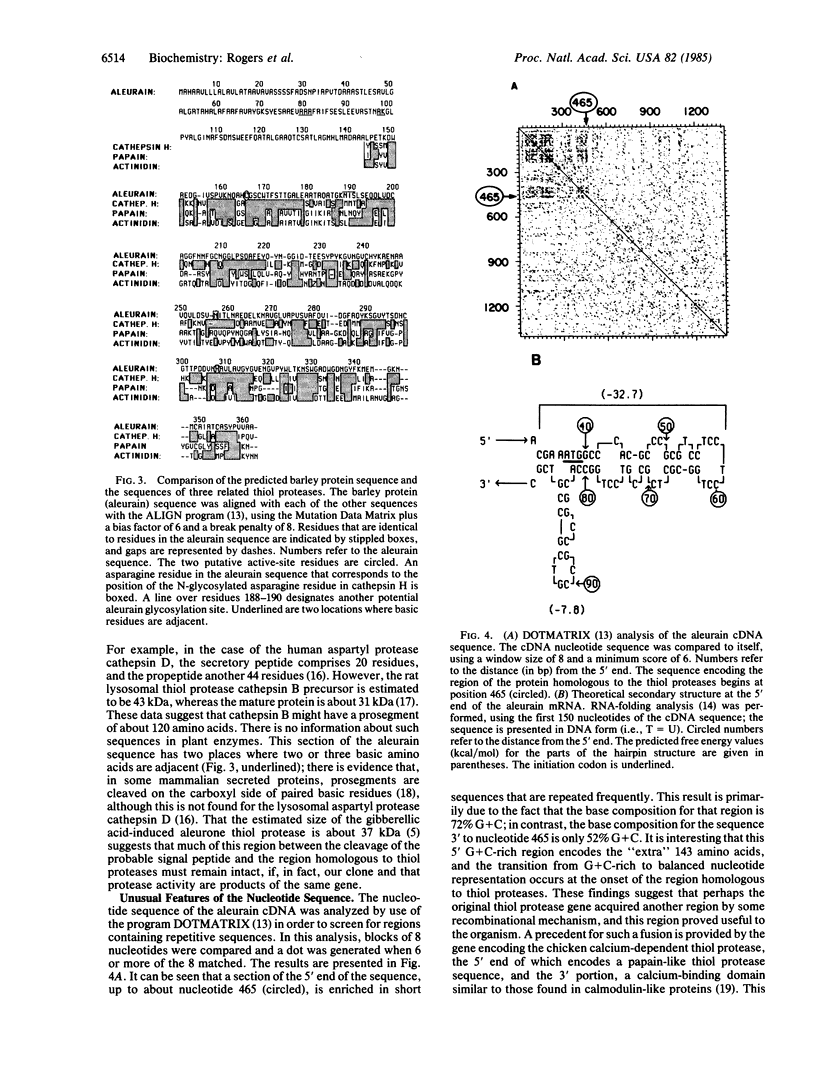
We have isolated and sequenced a 1400-base-pair cDNA derived from gibberellic acid-treated aleurone cell mRNA. This sequence contains an open reading frame that would code for a protein of 361 amino acids. The carboxyl-terminal two-thirds of the predicted amino acid sequence is closely related to that of the rat lysosomal thiol protease cathepsin H; the initial 143 amino acids may code for a secretory peptide plus a prosegment. The expression of this aleurone thiol protease mRNA is unusual in that, in aleurone cells, its abundance is regulated by the plant hormones gibberellic acid and abscisic acid, but it is also expressed at high levels in leaf and root tissue. This protease may represent the equivalent of a plant lysosomal thiol protease.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carne A., Moore C. H. The amino acid sequence of the tryptic peptides from actinidin, a proteolytic enzyme from the fruit of Actinidia chinensis. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 1;173(1):73–83. doi: 10.1042/bj1730073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Carroll R. J., Steiner D. F. Conversion of proinsulin to insulin: involvement of a 31,500 molecular weight thiol protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4613–4617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust P. L., Kornfeld S., Chirgwin J. M. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for human cathepsin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Sims H. F., Edelstein C., Scanu A. M., Strauss A. W. Human proapolipoprotein A-II is cleaved following secretion from Hep G2 cells by a thiol protease. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15556–15563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Sims H. F., Lentz S. R., Edelstein C., Scanu A. M., Strauss A. W. Proteolytic processing of human preproapolipoprotein A-I. A proposed defect in the conversion of pro A-I to A-I in Tangier's disease. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):4037–4044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsen J. V., Varner J. E. Gibberellic Acid-induced synthesis of protease by isolated aleurone layers of barley. Plant Physiol. 1967 Nov;42(11):1596–1600. doi: 10.1104/pp.42.11.1596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchel R. E., Chaiken I. M., Smith E. L. The complete amino acid sequence of papain. Additions and corrections. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3485–3492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mozer T. J. Control of protein synthesis in barley aleurone layers by the plant hormones gibberellic acid and abscisic acid. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S., Emori Y., Imajoh S., Kawasaki H., Kisaragi M., Suzuki K. Evolutionary origin of a calcium-dependent protease by fusion of genes for a thiol protease and a calcium-binding protein? Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):566–570. doi: 10.1038/312566a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C., Milliman C. Coordinate increase in major transcripts from the high pI alpha-amylase multigene family in barley aleurone cells stimulated with gibberellic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12234–12240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C., Milliman C. Isolation and sequence analysis of a barley alpha-amylase cDNA clone. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8169–8174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C. Two barley alpha-amylase gene families are regulated differently in aleurone cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3731–3738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder R. L., Burger W. C. Development and Localization of Carboxypeptidase Activity in Embryo-less Barley Half-kernels. Plant Physiol. 1978 Sep;62(3):458–462. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.3.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Docherty K., Carroll R. Golgi/granule processing of peptide hormone and neuropeptide precursors: a minireview. J Cell Biochem. 1984;24(2):121–130. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240240204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Dehdarani A. H., Schmidt P. G., Tang J. Cathepsins B and H from porcine spleen. Purification, polypeptide chain arrangements, and carbohydrate content. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9874–9882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Towatari T., Katunuma N., Teller D. C., Titani K. Homology of amino acid sequences of rat liver cathepsins B and H with that of papain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3666–3670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thayer S. S., Huffaker R. C. Vacuolar Localization of Endoproteinases EP(1) and EP(2) in Barley Mesophyll Cells. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):70–73. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]