Abstract
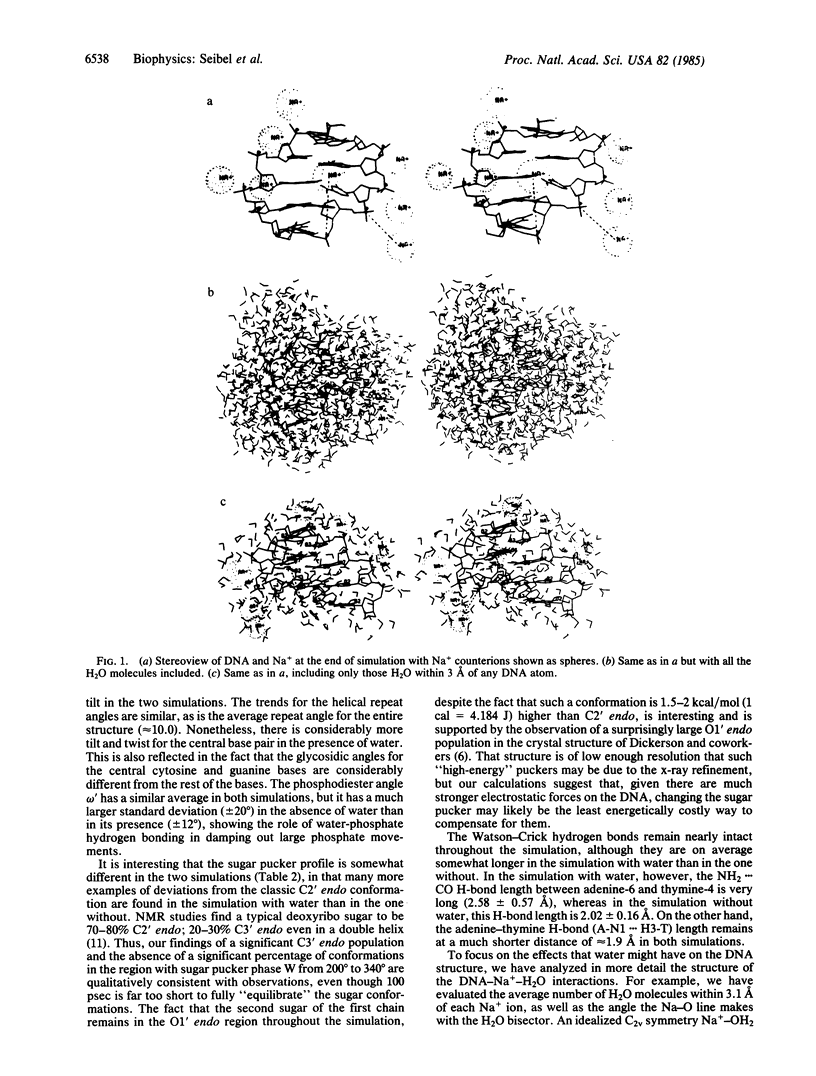
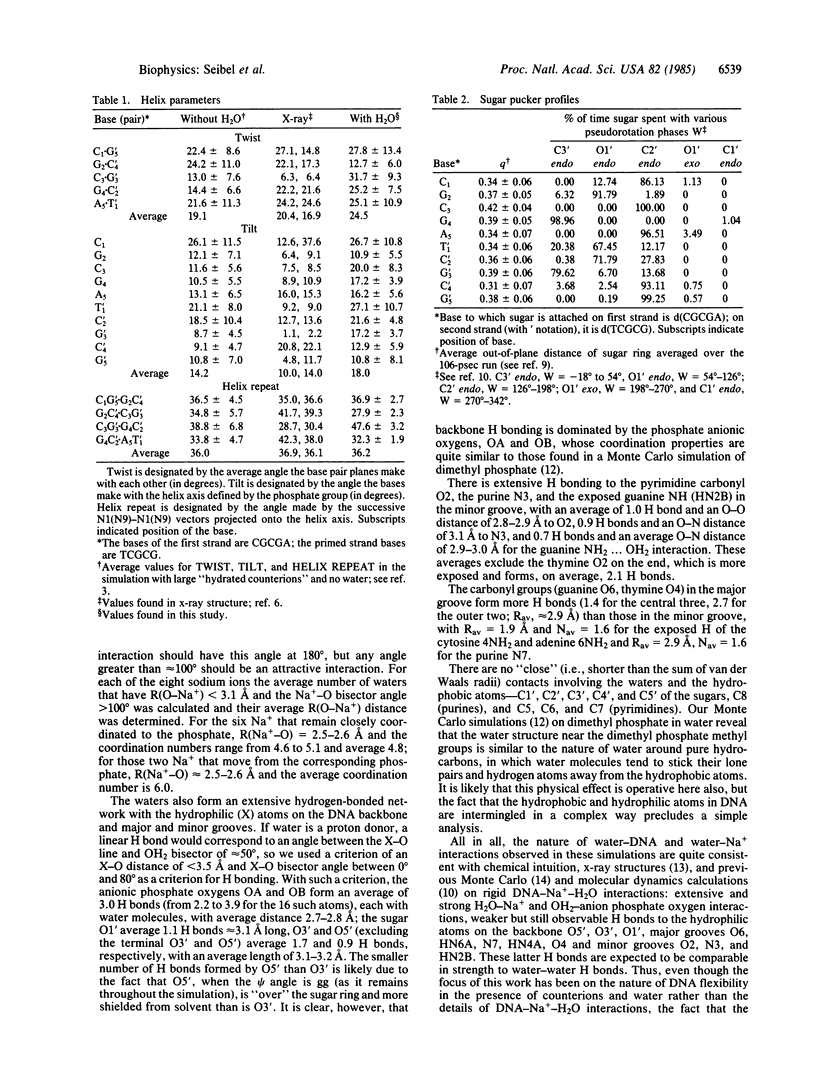
We present the results of an atomic level molecular dynamical simulation of a 5-base-pair fragment of double-helical DNA with inclusion of water and sodium counterions and a complete description of their electrostatic interactions. The shape of the double helix is preserved throughout the simulation, and the helix repeat is calculated to be 10.0, in reasonable agreement with experimental results. The most flexible conformational angles in the structure are the glycosidic angle and the sugar pucker.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Drew H. R., Wing R. M., Takano T., Broka C., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer: conformation and dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2179–2183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Fratini A. V., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Ordered water structure around a B-DNA dodecamer. A quantitative study. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 5;163(1):129–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. K., Gao Y., Prohofsky E. W. Structure of hydrated Na+ ions around a region of A- or B-DNA helix. Biopolymers. 1984 Feb;23(2):257–270. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellema J. R., Haasnoot C. A., van der Marel G. A., Wille G., van Boeckel C. A., van Boom J. H., Altona C. Proton NMR studies on the covalently linked RNA-DNA hybrid r(GCG)d(TATACGC). Assignment of proton resonances by application of the nuclear Overhauser effect. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5717–5738. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh U. C., Weiner S. J., Kollman P. Molecular dynamics simulations of d(C-G-C-G-A) X d(T-C-G-C-G) with and without "hydrated" counterions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tidor B., Irikura K. K., Brooks B. R., Karplus M. Dynamics of DNA oligomers. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(1):231–252. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trifonov E. N. Sequence-dependent variations of B-DNA structure and protein-DNA recognition. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):271–278. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



