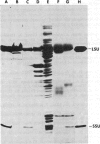
Abstract
We have placed the genes encoding ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from the Anabaena 7120 operon under transcriptional control of the lac promoter carried on the Escherichia coli plasmid pUC19. The genes encoding both the large and small subunit polypeptides (rbcL and rbcS) are transcribed and translated so that ≈0.6% of the soluble protein in E. coli extracts is a fully functional holoenzyme with a sedimentation coefficient of approximately 18S, which contains stoichiometric amounts of the two subunits. However, expression of the large subunit polypeptide vastly exceeds that of the small subunit because the majority of transcripts terminate in the intergenic region between the rbcL and rbcS genes. As a result, excess large subunit is synthesized and accumulates in E. coli as an insoluble and catalytically inactive form. Because small subunit is found only in the high molecular weight soluble form of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, we propose that the small subunit promotes assembly of the hexadecameric form of the enzyme via heterodimers of large and small subunits.
Keywords: enzyme assembly
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews T. J., Abel K. M. Kinetics and subunit interactions of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase from the cyanobacterium, Synechococcus sp. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8445–8451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews T. J., Ballment B. The function of the small subunits of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7514–7518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews T. J., Greenwood D. M., Yellowlees D. Catalytically active hybrids formed in vitro between large and small subunits of different procaryotic ribulose bisphosphate carboxylases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Oct;234(1):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90354-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger M. R. Kinetic properties of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Anabaena variabilis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Apr 15;201(1):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90509-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barcena J. A., Pickersgill R. W., Adams M. J., Phillips D. C., Whatley F. R. Crystallisation and preliminary X-ray data of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from spinach. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2363–2367. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01747.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barraclough R., Ellis R. J. Protein synthesis in chloroplasts. IX. Assembly of newly-synthesized large subunits into ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in isolated intact pea chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 27;608(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. V., Milos P., Roy H. Light-dependent assembly of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):1013–1017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelm B. K., Hallick R. B. Changes in the expression of the chloroplast genome of Euglena gracilis during chloroplast development. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):593–599. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis S. E., Haselkorn R. Isolation and sequence of the gene for the large subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from the cyanobacterium Anabaena 7120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1835–1839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R., Tuli R., Haselkorn R. A cloned cyanobacterial gene for glutamine synthetase functions in Escherichia coli, but the enzyme is not adenylylated. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3393–3397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatenby A. A. The properties of the large subunit of maize ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase synthesised in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):361–366. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W., Maxam A. The nucleotide sequence of the lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3581–3584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M., Lorimer G. H. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:507–535. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miziorko H. M. Ribulose-1,5-biphosphate carboxylase. Evidence in support of the existence of distinct CO2 activator and CO2 substrate sites. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):270–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierzwicki-Bauer S. A., Curtis S. E., Haselkorn R. Cotranscription of genes encoding the small and large subunits of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in the cyanobacterium Anabaena 7120. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5961–5965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce J. W., McCurry S. D., Mulligan R. M., Tolbert N. E. Activation and assay of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):47–55. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy H., Bloom M., Milos P., Monroe M. Studies on the assembly of large subunits of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in isolated pea chloroplasts. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):20–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. The gene for the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase is located close to the gene for the large subunit in the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans 6301. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 25;11(20):6957–6964. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.20.6957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhoff P., Zetsche K. Regulation of the synthesis of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and its subunits in the flagellate Chlorogonium elongatum. Different levels of translatable messenger RNAs for the large and the small subunits in autotrophic and heterotrophic cells as determined by immunological techniques. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May 15;116(2):261–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05328.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]