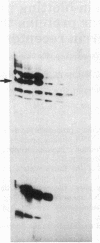
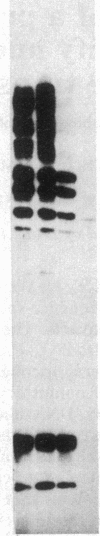
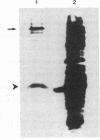
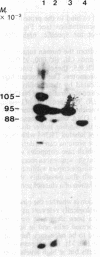
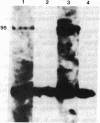
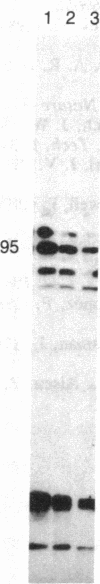
Abstract
We describe a procedure for detecting high-affinity, sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins from crude nuclear extracts. The technique utilizes electrophoretic transfer of NaDodSO4/PAGE-fractionated proteins onto nitrocellulose filters. Incubation of the filters with a 5% (wt/vol) solution of nonfat dry milk effectively blocks nonspecific and low-affinity DNA-binding sites. Incubation of the blocked filters with radiolabeled DNA under optimal binding conditions and subsequent autoradiography reveals high-affinity DNA-protein interactions. We have used this procedure to identify proteins that bind specifically to the promoter region of the transferrin receptor gene.
Full text
PDF
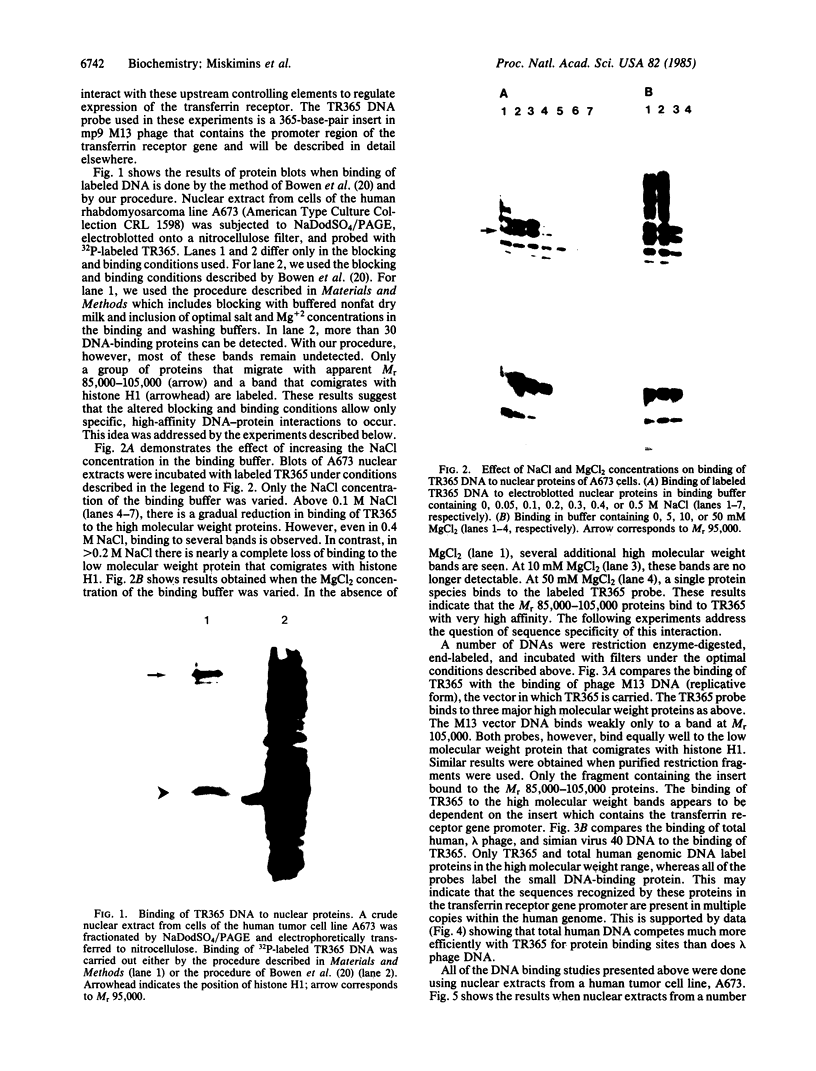
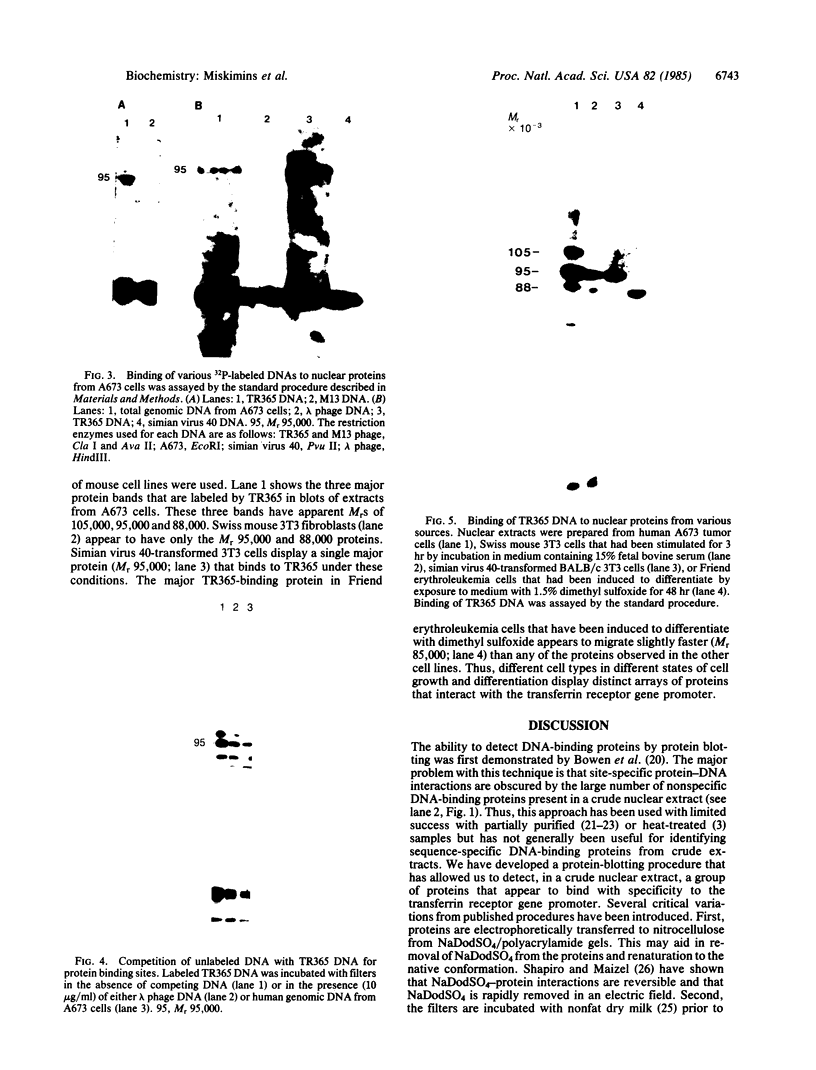

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anachkova B., Russev G. Differential binding of nonhistone chromosomal proteins to the putative mouse origin of replication. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 9;740(4):369–372. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Isolation of transcription factors that discriminate between different promoters recognized by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):669–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Anatomy of hypersensitive sites. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):213–214. doi: 10.1038/309213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. DNAase I-hypersensitive sites of chromatin. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90381-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson B. M., Felsenfeld G. Specific factor conferring nuclease hypersensitivity at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):95–99. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Roth E., Paule M. R. Ribosomal RNA transcription in vitro is species specific. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):173–174. doi: 10.1038/296173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. A. Regulation of transferrin receptor expression in concanavalin A stimulated and Gross virus transformed rat lymphoblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Oct;113(1):40–46. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T., Brutlag D. L. A protein that preferentially binds Drosophila satellite DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu H. Y., Gardner J., Aisen P. Inducibility of transferrin receptors on friend erythroleukemic cells. Science. 1977 Aug 5;197(4303):559–561. doi: 10.1126/science.267327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack R. S., Gehring W. J., Brack C. Protein component from Drosophila larval nuclei showing sequence specificity for a short region near a major heat-shock protein gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Cresswell P. Modulation of cell surface iron transferrin receptors by cellular density and state of activation. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(4):579–586. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishima Y., Financsek I., Kominami R., Muramatsu M. Fractionation and reconstitution of factors required for accurate transcription of mammalian ribosomal RNA genes: identification of a species-dependent initiation factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6659–6670. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckers L. M., Cossman J. Transferrin receptor induction in mitogen-stimulated human T lymphocytes is required for DNA synthesis and cell division and is regulated by interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3494–3498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Bourgeois S., Newby R. F., Cohn M. DNA binding of the lac repressor. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):365–368. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90261-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanzo M., Stevens B., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Isolation of a protein fraction that binds preferentially to chicken middle repetitive DNA. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6491–6498. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptides by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: further data concerning resolving power and general considerations. Anal Biochem. 1969 Jun;29(3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Hennighausen L., Battey J., Leder P. Chromatin structure and protein binding in the putative regulatory region of the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triadou P., Crepin M., Gros F., Lelong J. C. Tissue-specific binding of total and beta-globin genomic deoxyribonucleic acid to non-histone chromosomal proteins from mouse erythropoietic cells. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6060–6065. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S., Lopez F. Monoclonal antibody to transferrin receptor blocks transferrin binding and inhibits human tumor cell growth in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1175–1179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S., Omary M. B. Human cell surface glycoprotein related to cell proliferation is the receptor for transferrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3039–3043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R. A., Shatzman A. R., Rosenberg M. Expression and characterization of the human c-myc DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):448–456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weideli H., Gehring W. J. A new method for the purification of DNA-binding proteins with sequence specificity. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Feb;104(1):5–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. Activating protein factor binds in vitro to upstream control sequences in heat shock gene chromatin. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):81–84. doi: 10.1038/311081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]