Abstract
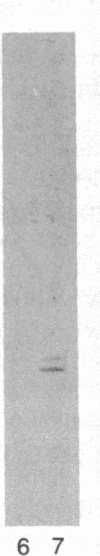
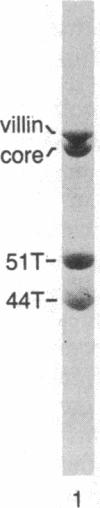
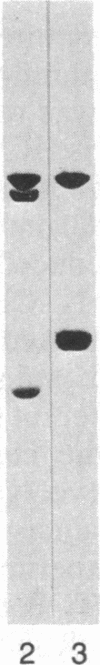
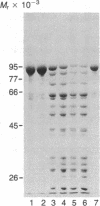
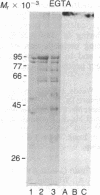
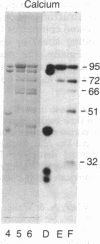
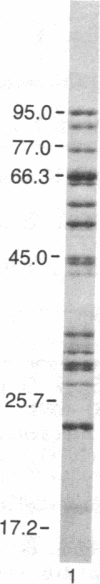
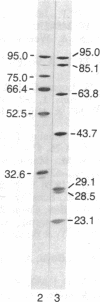
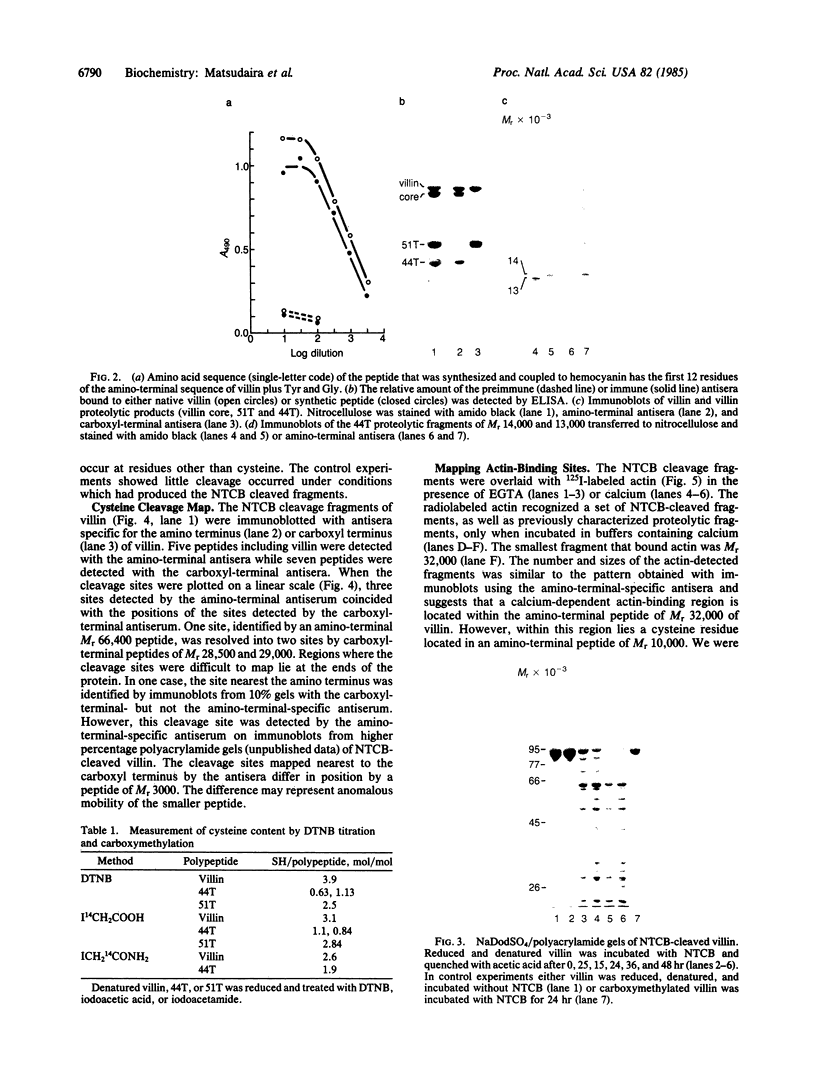
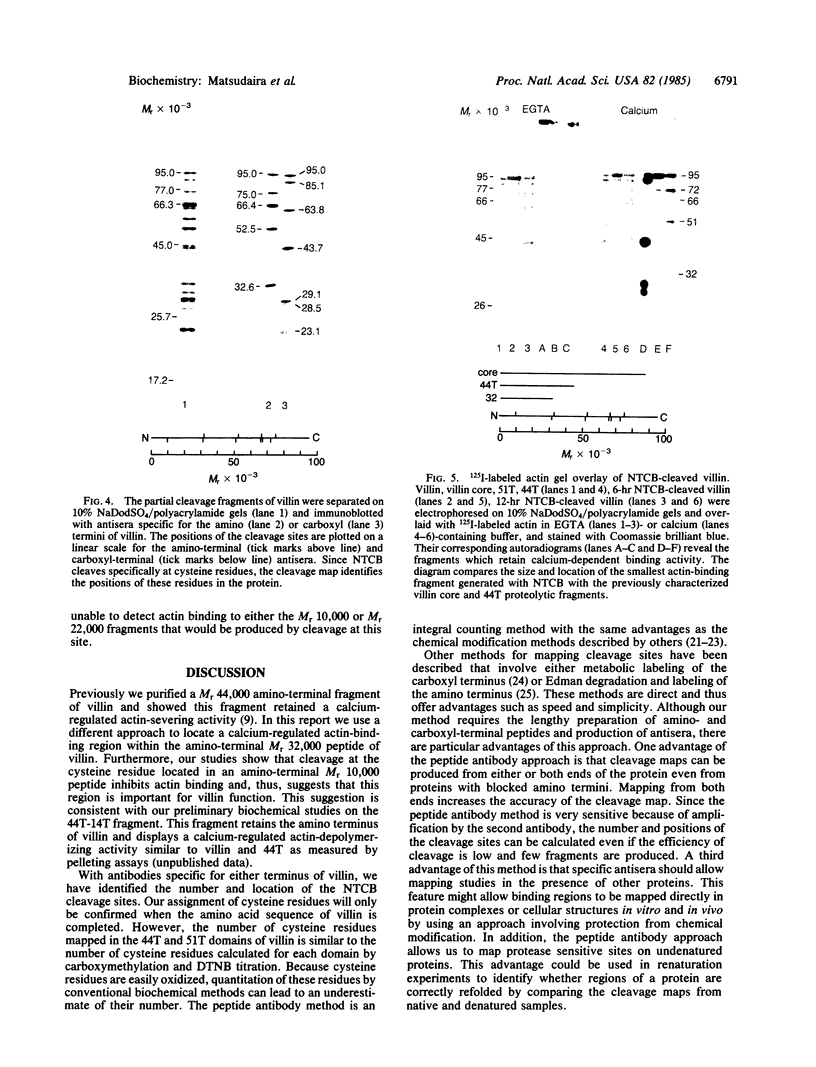
Peptide antisera specific for either the amino- or carboxyl-terminal regions of villin were used to locate the position of cysteine residues in immunoblots of villin cleaved with 2-nitro-5-thiocyanobenzoic acid. Maps constructed from the cleavage pattern suggest that villin contains six cysteine residues, two located in its amino-terminal peptide of Mr 44,000, and four located in the carboxyl-terminal peptide of Mr 51,000. Gel overlays of the partial cleavage fragments with 125I-labeled actin identified a calcium-dependent actin-binding region located within the amino-terminal peptide of Mr 32,000 of villin. The peptide antibody method used, called cleavage mapping, should be a convenient technique for mapping residues and ligand binding sites in proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassiri R. M., Utiger R. D. The preparation and specificity of antibody to thyrotropin releasing hormone. Endocrinology. 1972 Mar;90(3):722–727. doi: 10.1210/endo-90-3-722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin is a major protein of the microvillus cytoskeleton which binds both G and F actin in a calcium-dependent manner. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Counting integral numbers of amino acid residues per polypeptide chain. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):487–489. doi: 10.1038/284487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degani Y., Patchornik A. Cyanylation of sulfhydryl groups by 2-nitro-5-thiocyanobenzoic acid. High-yield modification and cleavage of peptides at cysteine residues. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 1;13(1):1–11. doi: 10.1021/bi00698a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L. Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 May;82(1):70–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein A. Use of charged thiol reagents in interpreting the electrophoretic patterns of immune globulin chains and fragments. Nature. 1966 Apr 9;210(5032):135–137. doi: 10.1038/210135a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Weber K. Isolation and characterization of mammalian villin and fimbrin, the two bundling proteins of the intestinal microvilli. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;31(2):249–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Geisler N., Kaulfus P., Weber K. Demonstration of at least two different actin-binding sites in villin, a calcium-regulated modulator of F-actin organization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8156–8161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Weber K. Calcium control of microfilaments: uncoupling of the F-actin-severing and -bundling activity of villin by limited proteolysis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2810–2814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesterberg L. K., Weber K. Demonstration of three distinct calcium-binding sites in villin, a modulator of actin assembly. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):365–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesterberg L. K., Weber K. Ligand-induced conformational changes in villin, a calcium-controlled actin-modulating protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Schaffer M. H., Stark G. R., Vanaman T. C. Specific chemical cleavage in high yield at the amino peptide bonds of cysteine and cystine residues. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6583–6591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay D. G. A general procedure for the end labeling of proteins and positioning of amino acids in the sequence. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15572–15578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. T., Burgess D. R. Partial reconstruction of the microvillus core bundle: characterization of villin as a Ca++-dependent, actin-bundling/depolymerizing protein. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):648–656. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P., Jakes R., Walker J. E. A gelsolin-like Ca2+-dependent actin-binding domain in villin. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):248–250. doi: 10.1038/315248a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Graves T. A., Wharton K. A., Falco N., Howe C. L. Regulation of microvillus structure: calcium-dependent solation and cross-linking of actin filaments in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):809–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runswick M. J., Walker J. E. The amino acid sequence of the beta-subunit of ATP synthase from bovine heart mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3081–3089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snabes M. C., Boyd A. E., 3rd, Bryan J. Detection of actin-binding proteins in human platelets by 125I-actin overlay of polyacrylamide gels. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):809–812. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A. Mapping endpoints of partial proteolysis fragments from regulatory subunit of type I cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;141(1):220–231. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90449-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott D. I., Feinstein A. Biosynthesis and assembly of IgM. Free thiol groups present on the intracellular subunits. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Apr;3(4):229–235. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830030410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. S., Weeds A. G. The magnesium-ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase of bovine cardiac Myosin and its subfragment-1. Biochem J. 1976 Nov;159(2):301–315. doi: 10.1042/bj1590301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]