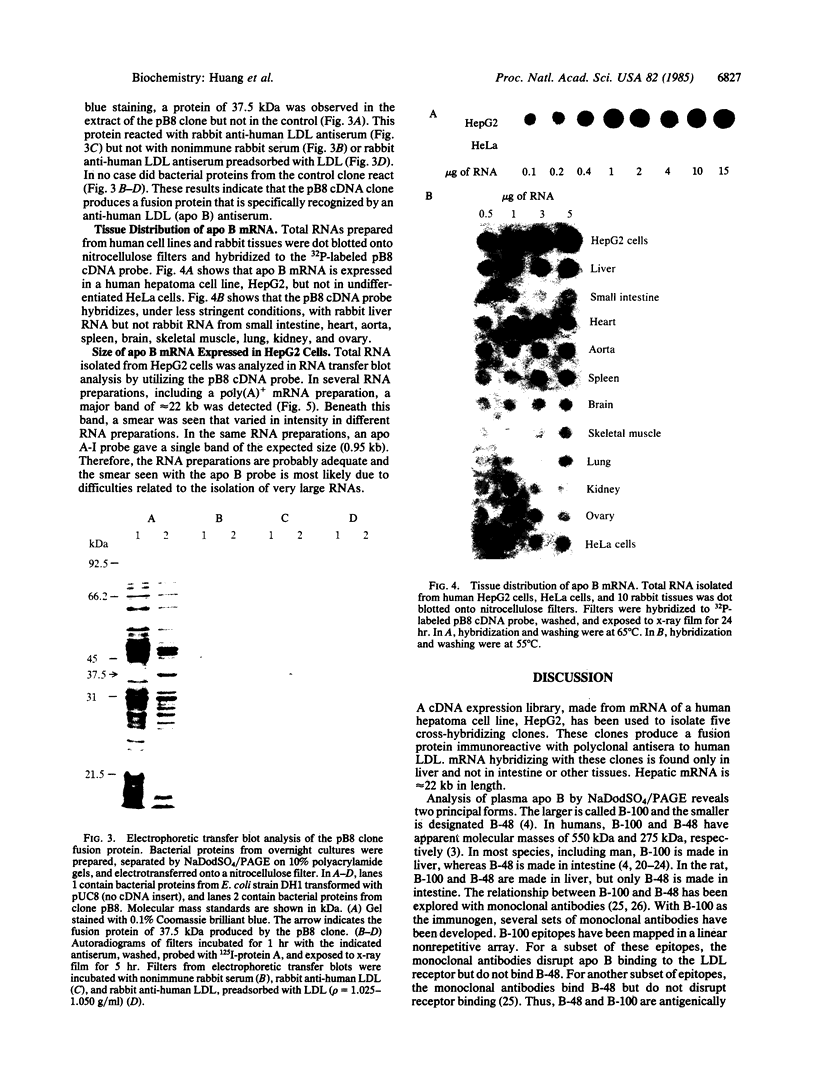
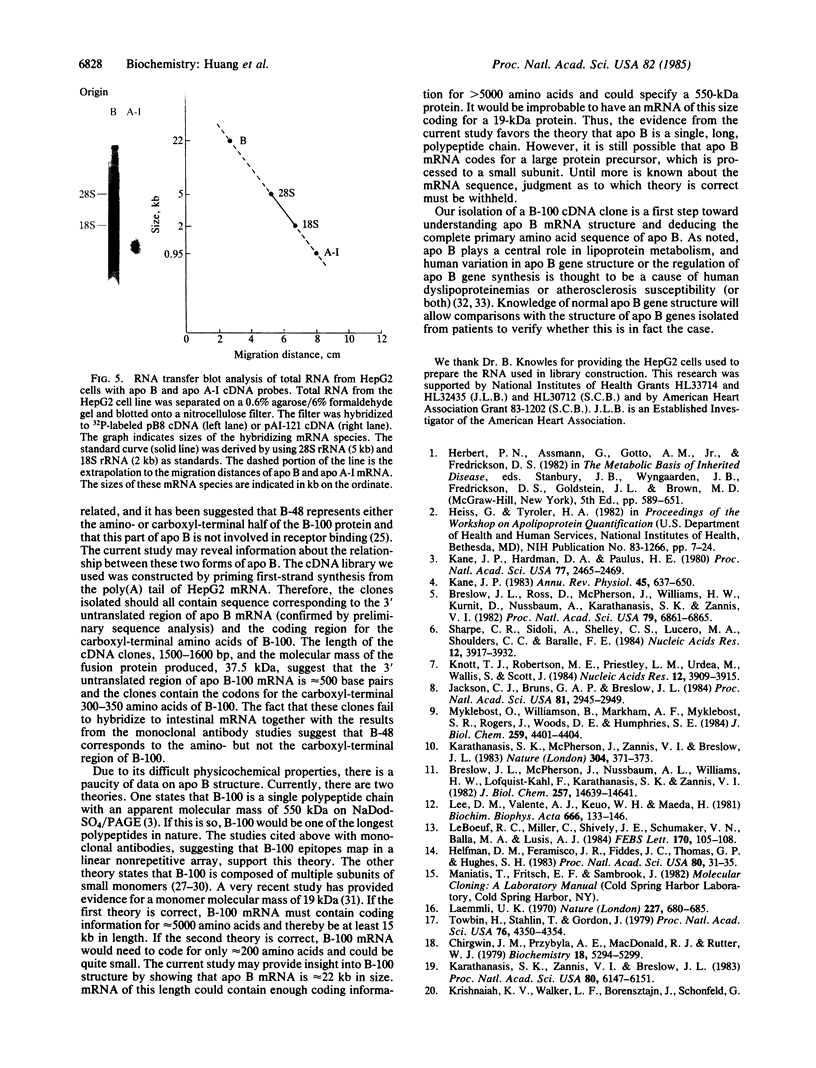
Abstract
An expression library made in plasmids pUC8 and pUC9 with mRNA derived from the human hepatoma cell line HepG2 was screened with a rabbit antiserum to human low density lipoprotein (LDL). Approximately 12,000 clones were screened and five positives were identified. The cDNA inserts were all 1500-1600 base pairs in length. The insert from one clone, pB8, was isolated, labeled by nicktranslation, and found to cross-hybridize strongly with the other four cDNA clones. The pB8 clone produces a fusion protein of approximately equal to 37.5 kDa that reacts in electrophoretic transfer blot analysis with rabbit anti-human LDL. This reactivity can be abolished by pretreatment of the antiserum with purified human LDL, p = 1.025 - 1.050 g/ml. A pB8-derived probe was used to demonstrate that apolipoprotein B (apo B) mRNA is present in HepG2 cells and liver extracts but not in HeLa cells or extracts from small intestine, heart, aorta, spleen, brain, skeletal muscle, lung, kidney, or ovary. RNA transfer blot analysis revealed that HepG2 cell apo B mRNA was approximately equal to 22 kilobases in length. These cDNA clones should allow the isolation of the apo B gene and ultimately the elucidation of the primary structure of this protein.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley W. A., Rohde M. F., Gotto A. M., Jr, Jackson R. L. The cyanogen bromide peptides of the apoprotein of low density lipoprotein (ApoB): its molecular weight from a chemical view. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Apr 14;81(3):928–935. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow J. L., McPherson J., Nussbaum A. L., Williams H. W., Lofquist-Kahl F., Karathanasis S. K., Zannis V. I. Identification and DNA sequence of a human apolipoprotein E cDNA clone. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14639–14641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow J. L., Ross D., McPherson J., Williams H., Kurnit D., Nussbaum A. L., Karathanasis S. K., Zannis V. I. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for human apolipoprotein A-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6861–6865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunzell J. D., Albers J. J., Chait A., Grundy S. M., Groszek E., McDonald G. B. Plasma lipoproteins in familial combined hyperlipidemia and monogenic familial hypertriglyceridemia. J Lipid Res. 1983 Feb;24(2):147–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. H., Aladjem F. Further studies on the subunit structure of human serum low density lipoproteins. Biochem Med. 1978 Apr;19(2):178–187. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(78)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss L. K., Edgington T. S. Immunochemical heterogeneity of human plasma apolipoprotein B. I. Apolipoprotein B binding of mouse hybridoma antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15213–15221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Heinrikson R. L., Foreman J., Scanu A. M. Studies of the cyanogen bromide fragments of the apoprotein of human serum low density lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 25;529(2):342–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(78)90077-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovson J., Huang Y. O., Baker N., Kannan R. Apolipoprotein B is structurally and metabolically heterogeneous in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):157–161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. L., Bruns G. A., Breslow J. L. Isolation and sequence of a human apolipoprotein CII cDNA clone and its use to isolate and map to human chromosome 19 the gene for apolipoprotein CII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2945–2949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P. Apolipoprotein B: structural and metabolic heterogeneity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1983;45:637–650. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.45.030183.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Hardman D. A., Paulus H. E. Heterogeneity of apolipoprotein B: isolation of a new species from human chylomicrons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2465–2469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., McPherson J., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Linkage of human apolipoproteins A-I and C-III genes. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):371–373. doi: 10.1038/304371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karathanasis S. K., Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Isolation and characterization of the human apolipoprotein A-I gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6147–6151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knott T. J., Robertson M. E., Priestley L. M., Urdea M., Wallis S., Scott J. Characterisation of mRNAs encoding the precursor for human apolipoprotein CI. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3909–3915. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnaiah K. V., Walker L. F., Borensztajn J., Schonfeld G., Getz G. S. Apolipoprotein B variant derived from rat intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3806–3810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBoeuf R. C., Miller C., Shively J. E., Schumaker V. N., Balla M. A., Lusis A. J. Human apolipoprotein B: partial amino acid sequence. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81378-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. M., Valente A. J., Kuo W. H., Maeda H. Properties of apolipoprotein B in urea and in aqueous buffers. The use of glutathione and nitrogen in its solubilization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 23;666(1):133–146. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90099-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcel Y. L., Hogue M., Theolis R., Jr, Milne R. W. Mapping of antigenic determinants of human apolipoprotein B using monoclonal antibodies against low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13165–13168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith S. C. The determination of molecular weight of proteins by gel permeation chromatography in organic solvents. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11682–11685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myklebost O., Williamson B., Markham A. F., Myklebost S. R., Rogers J., Woods D. E., Humphries S. E. The isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for human apolipoprotein CII. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4401–4404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson S. O., Boström K., Svanberg U., Bondjers G. Isolation and partial characterization of a polypeptide belonging to apolipoprotein B from low-density lipoproteins of human plasma. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 18;19(6):1059–1064. doi: 10.1021/bi00547a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe C. R., Sidoli A., Shelley C. S., Lucero M. A., Shoulders C. C., Baralle F. E. Human apolipoproteins AI, AII, CII and CIII. cDNA sequences and mRNA abundance. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3917–3932. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sniderman A., Shapiro S., Marpole D., Skinner B., Teng B., Kwiterovich P. O., Jr Association of coronary atherosclerosis with hyperapobetalipoproteinemia [increased protein but normal cholesterol levels in human plasma low density (beta) lipoproteins]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):604–608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks C. E., Hnatiuk O., Marsh J. B. Hepatic and intestinal contribution of two forms of apolipoprotein B to plasma lipoprotein fractions in the rat. Can J Biochem. 1981 Aug;59(8):693–699. doi: 10.1139/o81-096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van't Hooft F. M., Hardman D. A., Kane J. P., Havel R. J. Apolipoprotein B (B-48) of rat chylomicrons is not a precursor of the apolipoprotein of low density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):179–182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. L., Windmueller H. G. Variant forms of plasma apolipoprotein B. Hepatic and intestinal biosynthesis and heterogeneous metabolism in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3615–3618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]











