Abstract
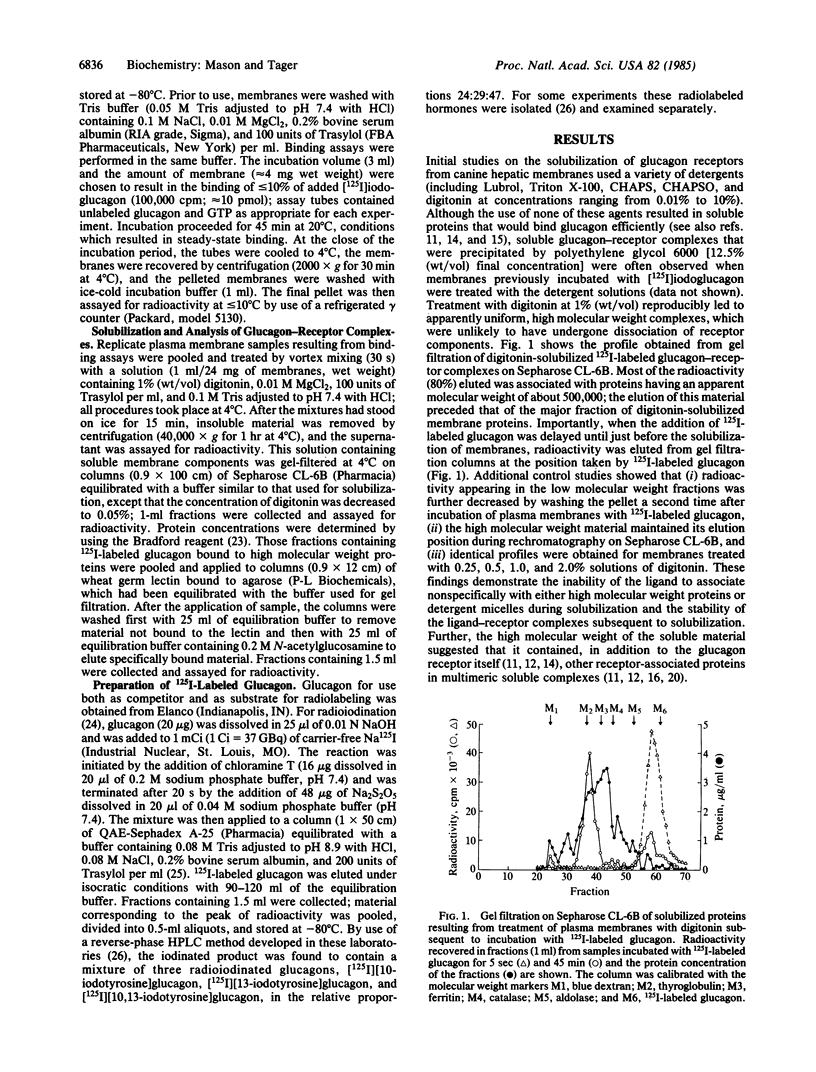
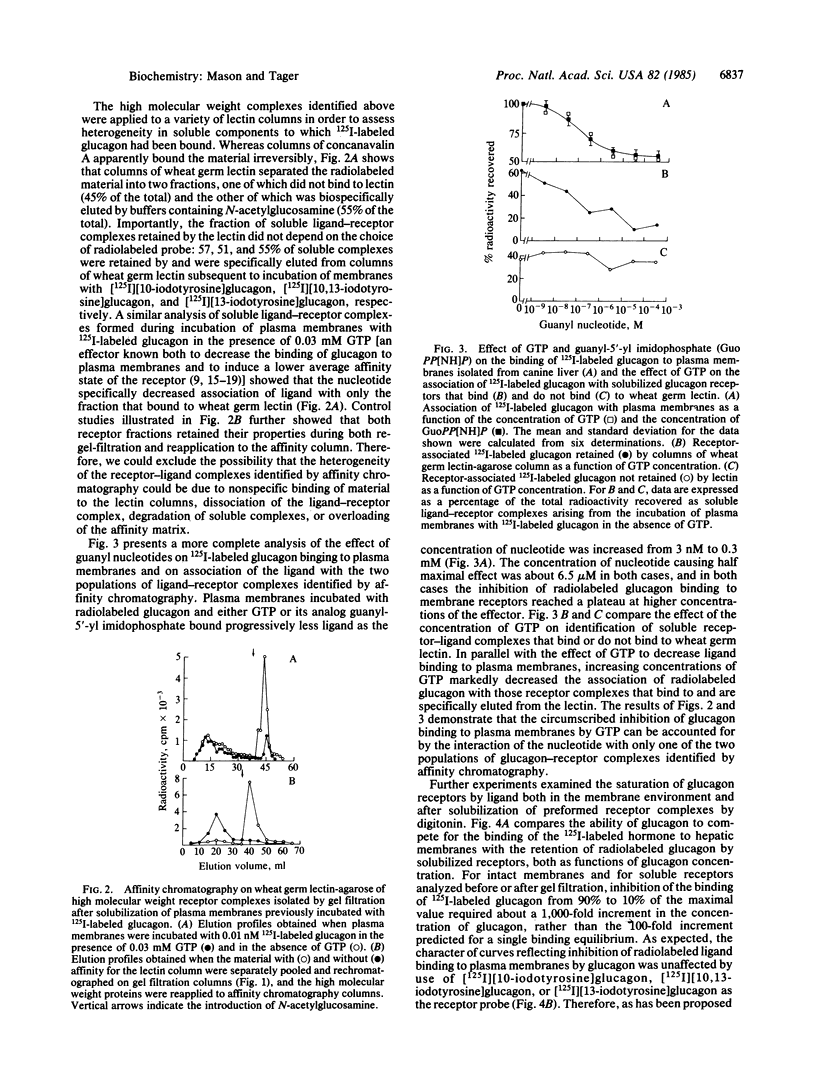
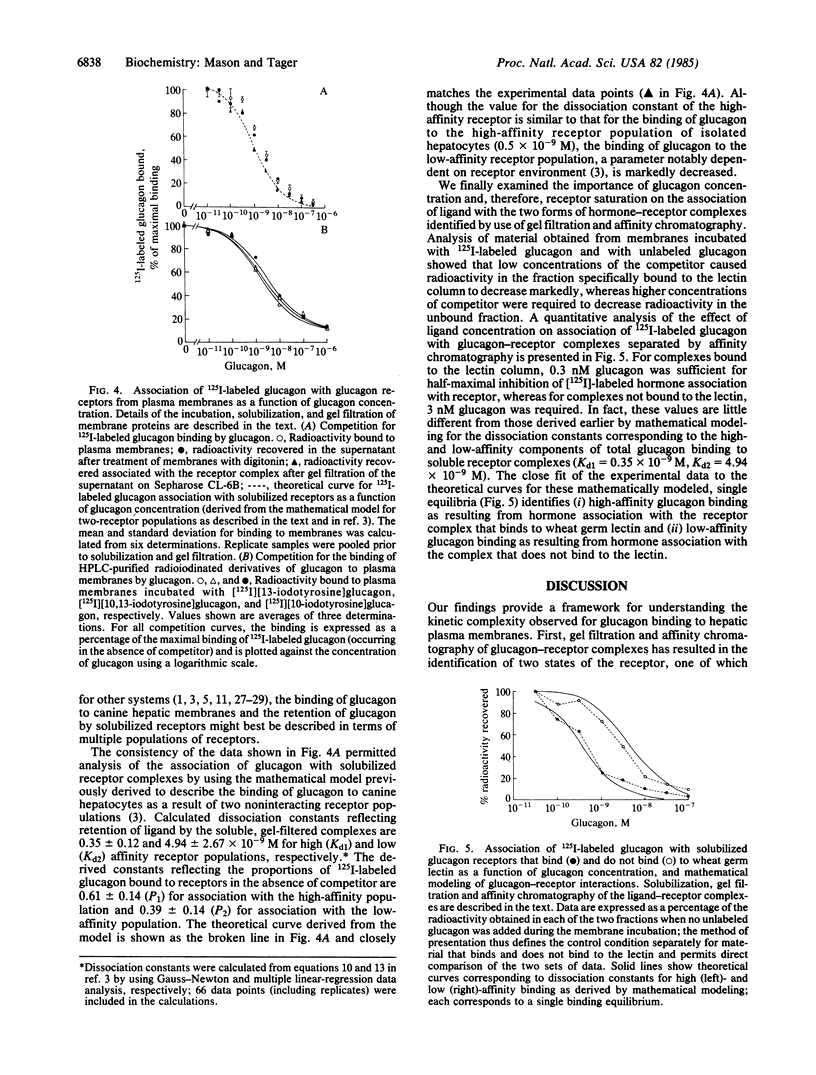
We have analyzed ligand-receptor complexes resulting from (i) the incubation of canine hepatic plasma membranes with [125I]iodoglucagon and (ii) subsequent gentle solubilization of receptor-bound ligand with digitonin. The complexes (molecular weight approximately equal to 500,000) retain the radiolabeled ligand during gel filtration and subsequent manipulation at 4 degrees C in the absence of covalent crosslinking. Affinity chromatography of the glucagon-receptor complexes on columns of wheat germ lectin linked to agarose resulted in two fractions, one of which was not bound by the column and the other of which was specifically eluted by N-acetylglucosamine. The presence of GTP during the incubation of plasma membranes with [125I]iodoglucagon caused about a 50% decrease in total ligand binding but affected only the ligand-receptor complexes that bound to wheat germ lectin. Moreover, it was found that the proportion of the two forms of ligand-receptor complexes identified by chromatography on wheat germ lectin depended on the degree of saturation of the membrane receptor. Thus, both the inhibition by glucagon of radiolabeled glucagon binding to membranes and the concomitantly decreased extent of association of the radiolabeled ligand with solubilized receptor complexes could be modeled in terms of two noninteracting receptor populations (having dissociation constants of about 0.35 and 4.94 X 10(-9) M). We conclude that (i) glucagon-receptor complexes formed on canine hepatic plasma membranes exist in two forms that differ after solubilization by digitonin in their avidities for wheat germ lectin, (ii) the high-and low-affinity binding of glucagon characteristic of hepatic plasma membranes arises from distinct receptor populations that probably differ in glycosylation, and (iii) the effect of GTP to decrease binding of glucagon to membranes arises from interactions of the nucleotide with the receptor complex that binds to wheat germ lectin.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Rodbell M., Sundby F. The glucagon-sensitive adenylate cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. VII. Hormonal stimulation: reversibility and dependence on concentration of free hormone. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2038–2043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnevie-Nielsen V., Polonsky K. S., Jaspan J. J., Rubenstein A. H., Schwartz T. W., Tager H. S. Surface receptors for pancreatic hormones in dog and rat hepatocytes: qualitative and quantitative differences in hormone-target cell interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnevie-Nielsen V., Tager H. S. Glucagon receptors on isolated hepatocytes and hepatocyte membrane vesicles. Discrete populations with ligand- and environment-dependent affinities. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11313–11320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crettaz M., Jialal I., Kasuga M., Kahn C. R. Insulin receptor regulation and desensitization in rat hepatoma cells. The loss of the oligomeric forms of the receptor correlates with the change in receptor affinity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11543–11549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demoliou-Mason C., Epand R. M. Binding of a glucagon photoaffinity label to rat liver plasma membranes and its effect on adenylate cyclase activity before and after photolysis. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 27;21(9):1989–1996. doi: 10.1021/bi00538a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England R. D., Jenkins W. T., Flanders K. C., Gurd R. S. Noncooperative receptor interactions of glucagon and eleven analogues: inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1722–1728. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunther S. Characterization of angiotensin II receptor subtypes in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7622–7629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagopian W. A., Tager H. S. Receptor binding and cell-mediated metabolism of [125I]monoiodoglucagon by isolated canine hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):8986–8993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberg J. T., Codina J., Rich K. A., Rojas F. J., Iyengar R. The hepatic glucagon receptor. Solubilization, characterization, and development of an affinity adsorption assay for the soluble receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9285–9294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horuk R., Wright D. E. Partial purification and characterization of the glucagon receptor. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 8;155(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80605-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R., Herberg J. T. Structural analysis of the hepatic glucagon receptor. Identification of a guanine nucleotide-sensitive hormone-binding region. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5222–5229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen K. H., Larsen U. D. Purification of 125 I-glucagon by anion exchange chromatography. Horm Metab Res. 1972 May;4(3):223–224. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1097092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick B. F., Caron M. G. Agonist binding promotes a guanine nucleotide reversible increase in the apparent size of the bovine anterior pituitary dopamine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13528–13534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Welton A. F., Rodbell M. Evidence for distinct guanine nucleotide sites in the regulation of the glucagon receptor and of adenylate cyclase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5942–5946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafuse W., Edidin M. Influence of the mouse major histocompatibility complex, H-2, on liver adenylate cyclase activity and on glucagon binding to liver cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1980 Jan 8;19(1):49–54. doi: 10.1021/bi00542a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. C., Nicosia S., Lad P. M., Rodbell M. Effects of GTP on binding of (3H) glucagon to receptors in rat hepatic plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2790–2792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musso G. F., Assoian R. K., Kaiser E. T., Kézdy F. J., Tager H. S. Heterogeneity of glucagon receptors of rat hepatocytes: a synthetic peptide probe for the high affinity site. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Mar 15;119(2):713–719. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80309-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Isolation of an organ specific protein antigen from cell-surface membrane of rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 9;154(3):540–552. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pingoud V. A., Peters F., Haas T. D., Trautschold I. A quantitative analysis of glucagon binding to isolated intact neonatal and adult rat hepatocytes on the basis of two different binding models. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 25;714(3):448–455. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Krans H. M., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. Inactivation of glucagon by plasma membranes of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 25;247(8):2295–2301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. K. A modified method for the isolation of the plasma membrane from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 6;196(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. 3. Binding of glucagon: method of assay and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1861–1871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. IV. Effects of guanylnucleotides on binding of 125I-glucagon. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1872–1876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Lin M. C., Salomon Y. Evidence for interdependent action of glucagon and nucleotides on the hepatic adenylate cyclase system. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 10;249(1):59–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M. The role of hormone receptors and GTP-regulatory proteins in membrane transduction. Nature. 1980 Mar 6;284(5751):17–22. doi: 10.1038/284017a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel W., Kempner E. S., Rodbell M. Activation of adenylate cyclase in hepatic membranes involves interactions of the catalytic unit with multimeric complexes of regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5168–5176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonne O., Berg T., Christoffersen T. Binding of 125I-labeled glucagon and glucagon-stimulated accumulation of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in isolated intact rat hepatocytes. Evidence for receptor heterogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1978 May 10;253(9):3203–3210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling M. A., Ganguli S., Voina S., Kaptein E., Nicoloff J. T. Modulation by thyroid status of the glucagon receptor-adenyl cyclase system in rat liver plasma membranes. Endocrinology. 1980 Sep;107(3):684–690. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-3-684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toews M. L., Waldo G. L., Harden T. K., Perkins J. P. Relationship between an altered membrane form and a low affinity form of the beta-adrenergic receptor occurring during catecholamine-induced desensitization. Evidence for receptor internalization. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11844–11850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welton A. F., Lad P. M., Newby A. C., Yamamura H., Nicosia S., Rodbell M. Solubilization and separation of the glucagon receptor and adenylate cyclase in guanine nucleotide-sensitive states. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 10;252(17):5947–5950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. E., Rodbell M. Preparation of 2-thioltryptophan-glucagon and (tryptophan-S-glucagon)2. Differences in binding to the glucagon receptor in the hepatic adenylate cyclase system. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10884–10887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



