Abstract
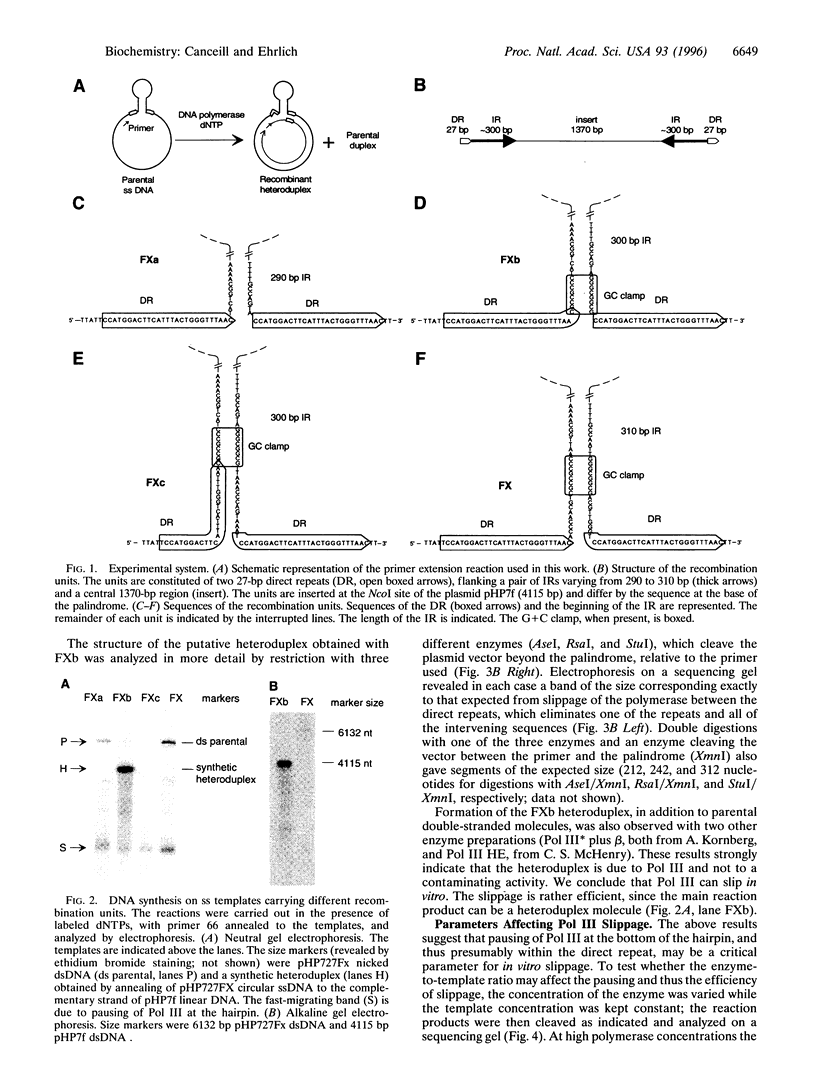
Formation of deletions by recombination between short direct repeats is thought to involve either a break-join or a copy-choice process. The key step of the latter is slippage of the replication machinery between the repeats. We report that the main replicase of Escherichia coli, DNA polymerase III holoenzyme, slips between two direct repeats of 27 bp that flank an inverted repeat of approximately equal 300bp. Slippage was detected in vitro, on a single-stranded DNA template, in a primer extension assay. It requires the presence of a short (8 bp) G+C-rich sequence at the base of a hairpin that can form by annealing of the inverted repeats. It is stimulated by (i) high salt concentration, which might stabilize the hairpin, and (ii) two proteins that ensure the processivity of the DNA polymerase III holoenzyme: the single-stranded DNA binding protein and the beta subunit of the polymerase. Slippage is rather efficient under optimal reaction conditions because it can take place on >50% of template molecules. This observation supports the copy-choice model for recombination between short direct repeats.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertini A. M., Hofer M., Calos M. P., Miller J. H. On the formation of spontaneous deletions: the importance of short sequence homologies in the generation of large deletions. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashkirov V. I., Stoilova-Disheva M. M., Prozorov A. A. Interplasmidic illegitimate recombination in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Aug;213(2-3):465–470. doi: 10.1007/BF00339617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chédin F., Dervyn E., Dervyn R., Ehrlich S. D., Noirot P. Frequency of deletion formation decreases exponentially with distance between short direct repeats. Mol Microbiol. 1994 May;12(4):561–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01042.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley E. C., Saunders V. A., Jackson V., Saunders J. R. Mechanism of intramolecular recyclization and deletion formation following transformation of Escherichia coli with linearized plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8919–8932. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta U., Weston-Hafer K., Berg D. E. Local DNA sequence control of deletion formation in Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Genetics. 1987 Jan;115(1):41–49. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Normark S. Recombination between short DNA homologies causes tandem duplication. Nature. 1981 Jul 16;292(5820):269–271. doi: 10.1038/292269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egner C., Berg D. E. Excision of transposon Tn5 is dependent on the inverted repeats but not on the transposase function of Tn5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich S. D., Bierne H., d'Alençon E., Vilette D., Petranovic M., Noirot P., Michel B. Mechanisms of illegitimate recombination. Gene. 1993 Dec 15;135(1-2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escarceller M., Hicks J., Gudmundsson G., Trump G., Touati D., Lovett S., Foster P. L., McEntee K., Goodman M. F. Involvement of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase II in response to oxidative damage and adaptive mutation. J Bacteriol. 1994 Oct;176(20):6221–6228. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.20.6221-6228.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J., Johanson K. O., McHenry C. S., Bambara R. A. Size classes of products synthesized processively by DNA polymerase III and DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):976–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay P. J., Johanson K. O., McHenry C. S., Bambara R. A. Size classes of products synthesized processively by two subassemblies of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5692–5699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordenin D. A., Malkova A. L., Peterzen A., Kulikov V. N., Pavlov Y. I., Perkins E., Resnick M. A. Transposon Tn5 excision in yeast: influence of DNA polymerases alpha, delta, and epsilon and repair genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3785–3789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenstein D., Horiuchi K. Interaction between the replication origin and the initiator protein of the filamentous phage f1. Binding occurs in two steps. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 20;197(2):157–174. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelman Z., O'Donnell M. DNA polymerase III holoenzyme: structure and function of a chromosomal replicating machine. Annu Rev Biochem. 1995;64:171–200. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.64.070195.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelman Z., O'Donnell M. DNA replication: enzymology and mechanisms. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Apr;4(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong X. P., Onrust R., O'Donnell M., Kuriyan J. Three-dimensional structure of the beta subunit of E. coli DNA polymerase III holoenzyme: a sliding DNA clamp. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):425–437. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90445-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyan J., O'Donnell M. Sliding clamps of DNA polymerases. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 20;234(4):915–925. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Recombination mechanisms in bacteria. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1955 May;45(Suppl 2):75–107. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030450506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaDuca R. J., Fay P. J., Chuang C., McHenry C. S., Bambara R. A. Site-specific pausing of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis catalyzed by four forms of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase III. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 25;22(22):5177–5188. doi: 10.1021/bi00291a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen C. S., Ghivizzani S. C., Hauswirth W. W. In vivo and in vitro evidence for slipped mispairing in mammalian mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7671–7675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry C. S. DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. Components, structure, and mechanism of a true replicative complex. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 15;266(29):19127–19130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHenry C., Kornberg A. DNA polymerase III holoenzyme of Escherichia coli. Purification and resolution into subunits. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6478–6484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer T. F., Geider K. Bacteriophage fd gene II-protein. II. Specific cleavage and relaxation of supercoiled RF from filamentous phages. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12642–12646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris T., Thacker J. Formation of large deletions by illegitimate recombination in the HPRT gene of primary human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1392–1396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papanicolaou C., Ripley L. S. Polymerase-specific differences in the DNA intermediates of frameshift mutagenesis. In vitro synthesis errors of Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I and its large fragment derivative. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):335–353. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90258-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters B. P., de Boer J. H., Bron S., Venema G. Structural plasmid instability in Bacillus subtilis: effect of direct and inverted repeats. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jun;212(3):450–458. doi: 10.1007/BF00330849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinden R. R., Zheng G. X., Brankamp R. G., Allen K. N. On the deletion of inverted repeated DNA in Escherichia coli: effects of length, thermal stability, and cruciform formation in vivo. Genetics. 1991 Dec;129(4):991–1005. doi: 10.1093/genetics/129.4.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer B. S., Westlye J. Deletion formation in bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90454-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand M., Prolla T. A., Liskay R. M., Petes T. D. Destabilization of tracts of simple repetitive DNA in yeast by mutations affecting DNA mismatch repair. Nature. 1993 Sep 16;365(6443):274–276. doi: 10.1038/365274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streisinger G., Okada Y., Emrich J., Newton J., Tsugita A., Terzaghi E., Inouye M. Frameshift mutations and the genetic code. This paper is dedicated to Professor Theodosius Dobzhansky on the occasion of his 66th birthday. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stukenberg P. T., Studwell-Vaughan P. S., O'Donnell M. Mechanism of the sliding beta-clamp of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11328–11334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stukenberg P. T., Turner J., O'Donnell M. An explanation for lagging strand replication: polymerase hopping among DNA sliding clamps. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):877–887. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90662-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang R. S. The return of copy-choice in DNA recombination. Bioessays. 1994 Nov;16(11):785–788. doi: 10.1002/bies.950161102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinh T. Q., Sinden R. R. Preferential DNA secondary structure mutagenesis in the lagging strand of replication in E. coli. Nature. 1991 Aug 8;352(6335):544–547. doi: 10.1038/352544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. C. Diseases of the mitochondrial DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:1175–1212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.005523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston-Hafer K., Berg D. E. Palindromy and the location of deletion endpoints in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1989 Apr;121(4):651–658. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.4.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Alençon E., Petranovic M., Michel B., Noirot P., Aucouturier A., Uzest M., Ehrlich S. D. Copy-choice illegitimate DNA recombination revisited. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 1;13(11):2725–2734. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







