Abstract
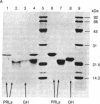
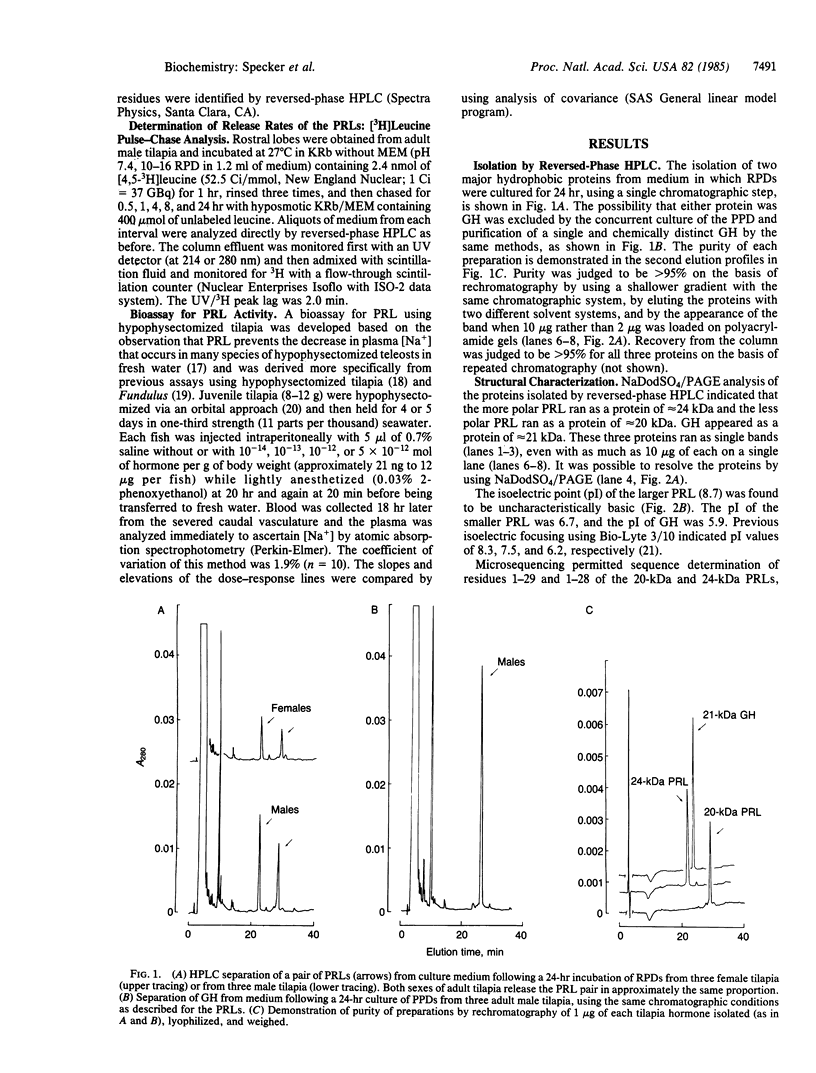
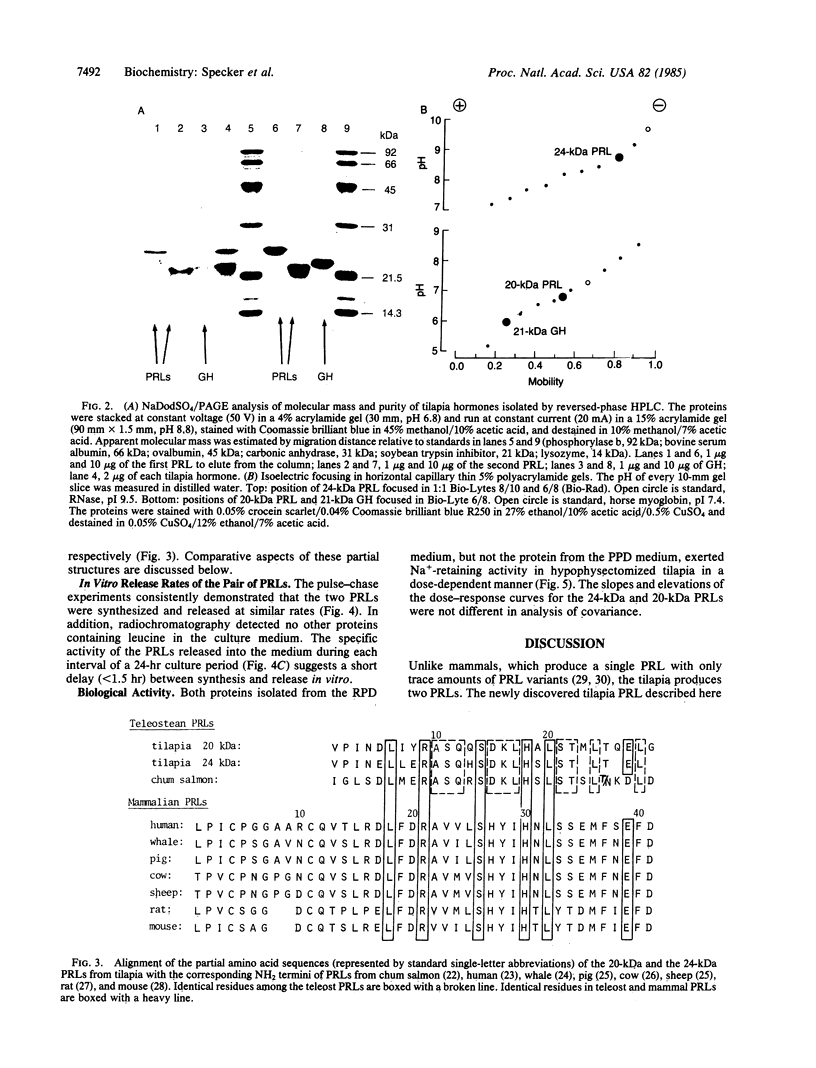
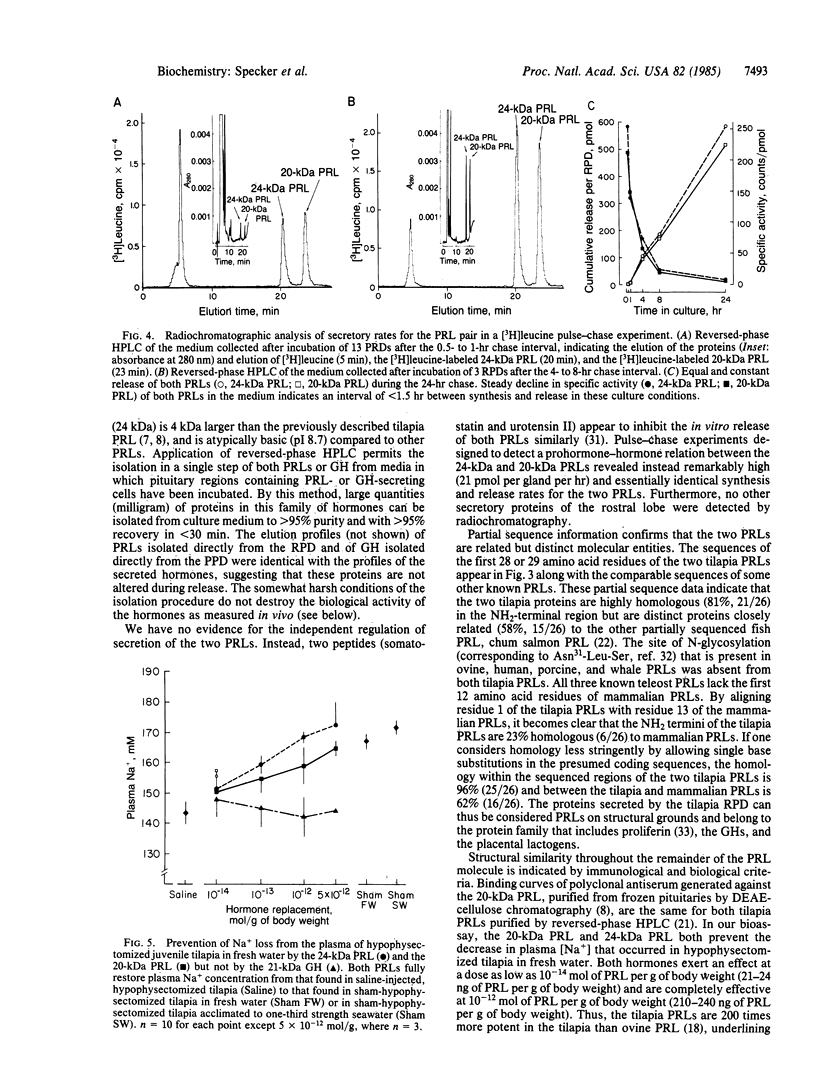
The pituitary of the cichlid fish tilapia secretes two prolactins (PRLs) of molecular masses 20 kDa and 24 kDa. The 20-kDa PRL has an isoelectric point in the range of those of mammalian PRLs (pI 6.7), but the 24-kDa PRL is unusually basic (pI 8.7). Partial sequence information indicates that the PRLs are homologous but distinct proteins, differing by five amino acids within the first 29 NH2-terminal residues. Homology in the known region is higher with chum salmon PRL than with known mammalian PRLs. Reversed-phase HPLC permits isolation of these two PRLs and a single tilapia growth hormone from culture medium or from the pituitary in a single step. HPLC and radio-HPLC analysis of [3H]leucine pulse-chase experiments reveal that each PRL is secreted in vitro at remarkably high rates (21 pmol per gland per hr) and that the two PRLs are released in approximately equimolar amounts, suggesting the coordinate regulation of the secretion. Both PRLs exert characteristic PRL activity in that they prevent the loss of Na+ from the plasma of hypophysectomized tilapia in fresh water.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asawaroengchai H. Metabolism of purified and secreted rat prolactin in vitro. Horm Res. 1978;9(3):151–160. doi: 10.1159/000178908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asawaroengchai H., Nicoll C. S. Relationships among bioassay, radioimmunoassay and disc electrophoretic assay methods of measuring rat prolactin in pituitary tissue and incubation medium. J Endocrinol. 1977 May;73(2):301–308. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0730301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asawaroengchai H., Russell S. M., Nicoll C. S. Electrophoretically separable forms of rat prolactin with different bioassay and radioimmunoassay activities. Endocrinology. 1978 Feb;102(2):407–414. doi: 10.1210/endo-102-2-407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett H. P. Isolation of pituitary peptides by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Expansion of the resolving power of reversed-phase columns by manipulating pH and the nature of the ion-pairing reagent. J Chromatogr. 1983 Aug 26;266:501–510. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)90921-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke N. E., Coit D., Shine J., Baxter J. D., Martial J. A. Human prolactin. cDNA structural analysis and evolutionary comparisons. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):4007–4016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmamba M., Nishioka R. S. Response of "prolactin-secreting" cells of Tilapia mossambica to environmental salinity. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1968 Jun;1(3):409–420. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(68)90051-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmamba M. Studies of the effects of hypophysectomy and prolactin on plasma osmolarity and plasma sodium in Tilapia mossambica. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1970 Apr;14(2):256–269. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(70)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. W., Clarke W. C., Papkoff H., Nishioka R. S., Bern H. A., Li C. H. Studies on the purification and properties of teleost prolactin. Life Sci. 1975 Jan 1;16(1):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. W., Papkoff H., Bewley T. A., Hayashida T., Nishioka R. S., Bern H. A., Li C. H. Isolation and properties of teleost prolactin. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1977 Jan;31(1):60–71. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(77)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grau E. G., Prunet P., Gross T., Nishioka R. S., Bern H. A. Bioassay for salmon prolactin using hypophysectomized Fundulus heteroclitus. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1984 Jan;53(1):78–85. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(84)90226-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubbins E. J., Maurer R. A., Lagrimini M., Erwin C. R., Donelson J. E. Structure of the rat prolactin gene. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8655–8662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawauchi H., Abe K., Takahashi A., Hirano T., Hasegawa S., Naito N., Nakai Y. Isolation and properties of chum salmon prolactin. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1983 Mar;49(3):446–458. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(83)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawauchi H., Tubokawa M. Isolation and characterization of fin whale prolactin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1979 Feb;13(2):229–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1979.tb01873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohmoto K., Tsunasawa S., Sakiyama F. Complete amino acid sequence of mouse prolactin. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):227–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis U. J., Singh R. N., Lewis L. J., Seavey B. K., Sinha Y. N. Glycosylated ovine prolactin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):385–389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis U. J. Variants of growth hormone and prolactin and their posttranslational modifications. Annu Rev Physiol. 1984;46:33–42. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.46.030184.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H. Studies on pituitary lactogenic hormone. The primary structure of the porcine hormone. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1976;8(2):205–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1976.tb02497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Nucleotide sequence of a growth-related mRNA encoding a member of the prolactin-growth hormone family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4255–4259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loretz C. A., Bern H. A. Prolactin and osmoregulation in vertebrates. An update. Neuroendocrinology. 1982 Oct;35(4):292–304. doi: 10.1159/000123397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittra I. A novel "cleaved prolactin" in the rat pituitary: Part II. In vivo mammary mitogenic activity of its N-terminal 16K moiety. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 29;95(4):1760–1767. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahama Y., Nishioka R. S., Bern H. A., Gunther R. L. Control of prolactin secretion in teleosts, with special reference to Gillichthys mirabilis and Tilapia mossambica. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1975 Feb;25(2):166–188. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(75)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahama Y., Olivereau M., Farmer S. W., Nishioka R. S., Bern H. A. Immunocytochemical identification of the prolactin- and growth hormone-secreting cells in the teleost pituitary with antisera to tilapia prolactin and growth hormone. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1981 Jul;44(3):389–395. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(81)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll C. S., Wilson S. W., Nishioka R., Bern H. A. Blood and pituitary prolactin levels in tilapia (Sarotherodon mossambicus; Teleostei) from different salinities as measured by a homologous radioimmunoassay. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1981 Jul;44(3):365–373. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(81)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka R. S. Hypophysectomy of tilapia (Sarotherodon mossambicus) through the orbit. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1980 Mar;40(3):377–378. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(80)90281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha Y. N., Gilligan T. A. A cleaved form of prolactin in the mouse pituitary gland: identification and comparison of in vitro synthesis and release in strains with high and low incidences of mammary tumors. Endocrinology. 1984 Jun;114(6):2046–2053. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-6-2046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis M. The primary structure of bovine prolactin. FEBS Lett. 1974 Aug 25;44(2):205–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80726-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendelaar Bonga S. E., Flik G., Löwik C. W., van Eys G. J. Environmental control of prolactin synthesis in the teleost fish Oreochromis (formerly Sarotherodon) mossambicus. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1985 Mar;57(3):352–359. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(85)90214-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigham T., Nishioka R. S., Bern H. A. Factors affecting in vitro activity of prolactin cells in the euryhaline teleost Sarotherodon mossambicus (Tilapia mossambica). Gen Comp Endocrinol. 1977 Jun;32(2):120–131. doi: 10.1016/0016-6480(77)90142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]