Abstract
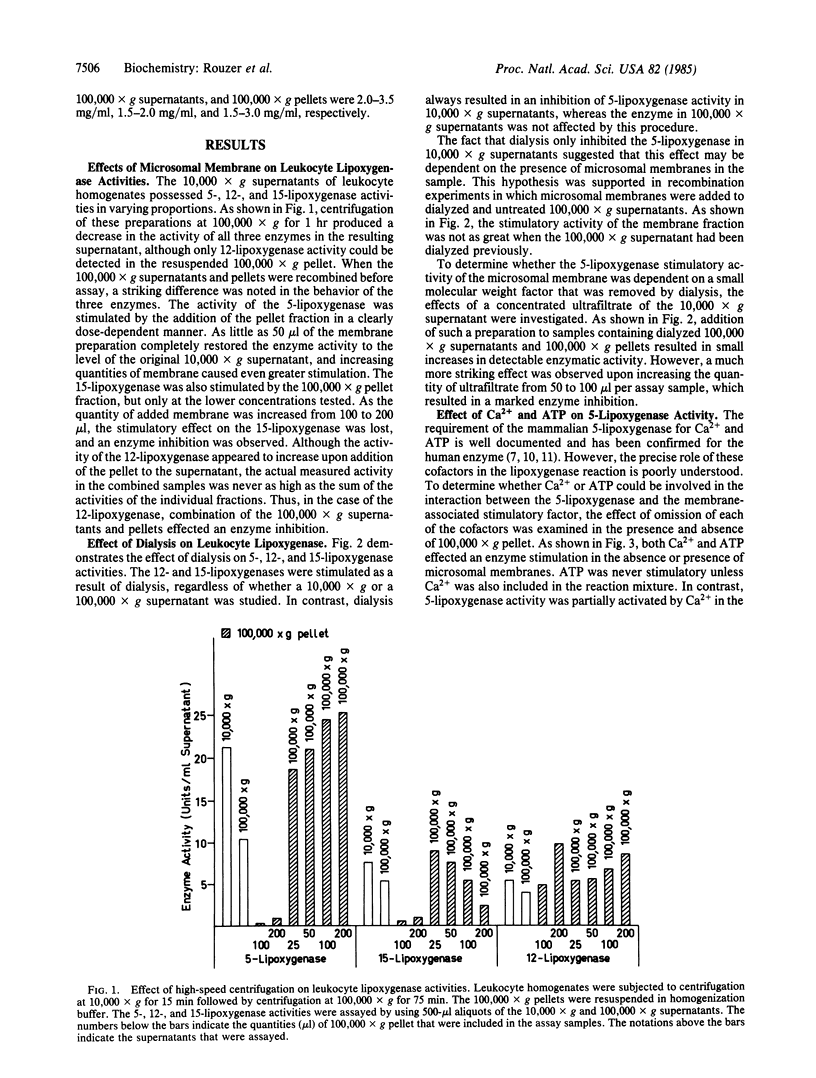
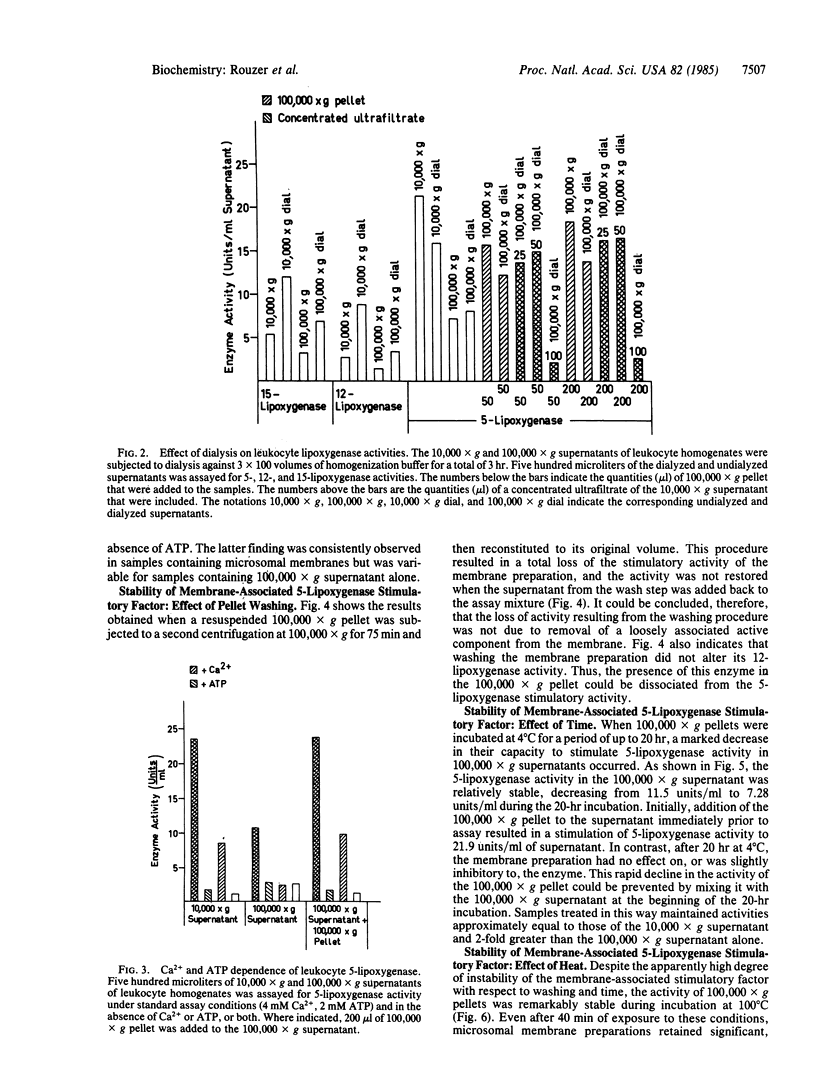
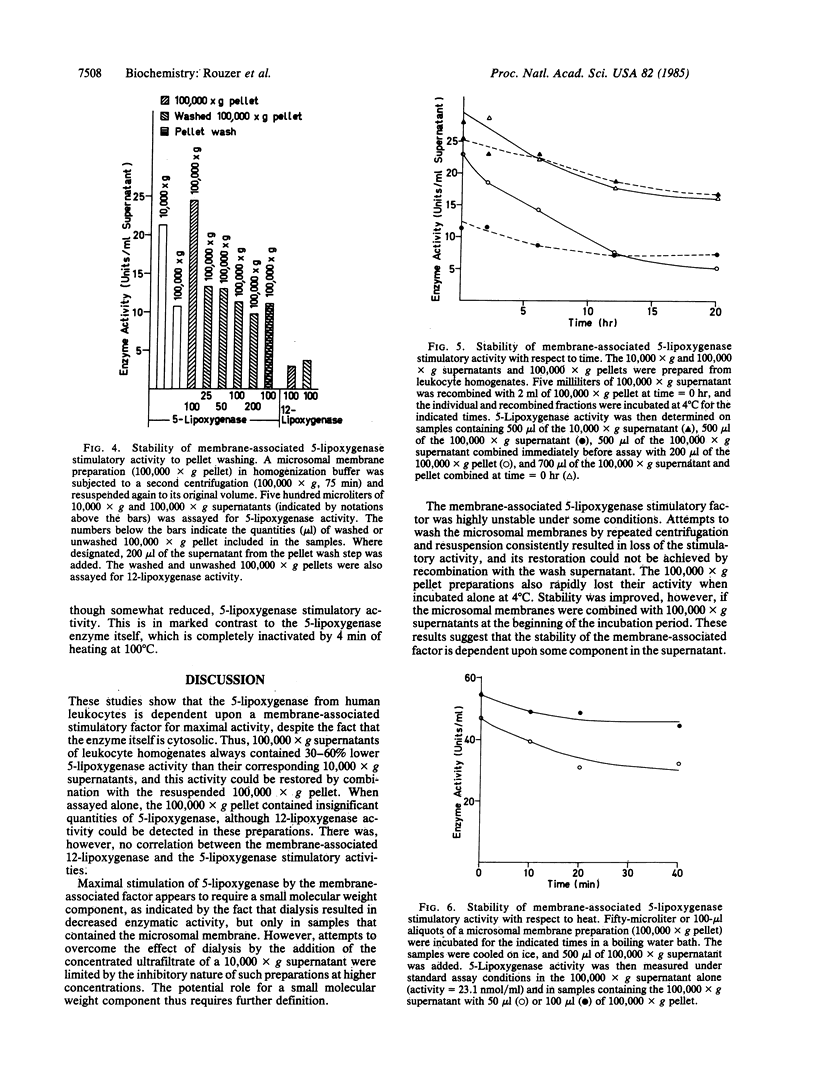
When 10,000 X g supernatants of human leukocyte homogenates were subjected to centrifugation at 100,000 X g for 75 min, the activity of 5-lipoxygenase decreased by 30-60%, even though no enzyme was detectable in the resuspended 100,000 X g pellet. Recombination of the 100,000 X g supernatant and pellet resulted in a restoration of the lost enzymatic activity, indicating the presence of a 5-lipoxygenase stimulatory factor in the microsomal membrane preparation. Dialysis of human leukocyte supernatants resulted in an apparent decrease in 5-lipoxygenase activity, but only in samples that contained the membrane-associated stimulatory factor, suggesting that the factor required a small molecular weight component for optimal function. The 5-lipoxygenase stimulatory activity was highly unstable to washing of the 100,000 X g pellet or to incubation (16-20 hr) at 4 degrees C. In contrast, the activity was remarkably stable to heat (100 degrees C for 40 min). The responses of the 12- and 15-lipoxygenases in human leukocyte homogenates to the membrane-associated factor and to dialysis were notably different from that of the 5-lipoxygenase. These results demonstrate, therefore, that the 5-lipoxygenase is unique among the human lipoxygenases, not only in its requirement for Ca2+ and ATP but also in its regulation by a membrane-associated stimulatory factor. The mechanism of action of this regulatory factor is of obvious interest for the understanding of the control of leukotriene and lipoxin biosynthesis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finazzi-Agrò A., Avigliano L., Veldink G. A., Vliegenthart J. F., Boldingh J. The influence of oxygen on the fluorescence of lipoxygenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):462–470. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakschik B. A., Sun F. F., Lee L., Steinhoff M. M. Calcium stimulation of a novel lipoxygenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 16;95(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90710-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narumiya S., Salmon J. A., Cottee F. H., Weatherley B. C., Flower R. J. Arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase from rabbit peritoneal polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Partial purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9583–9592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochi K., Yoshimoto T., Yamamoto S., Taniguchi K., Miyamoto T. Arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase of guinea pig peritoneal polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Activation by adenosine 5'-triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5754–5758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport S. M., Schewe T., Wiesner R., Halangk W., Ludwig P., Janicke-Höhne M., Tannert C., Hiebsch C., Klatt D. The lipoxygenase of reticulocytes. Purification, characterization and biological dynamics of the lipoxygenase; its identity with the respiratory inhibitors of the reticulocyte. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun 1;96(3):545–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13068.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouzer C. A., Samuelsson B. On the nature of the 5-lipoxygenase reaction in human leukocytes: enzyme purification and requirement for multiple stimulatory factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6040–6044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rådmark O., Shimizu T., Jörnvall H., Samuelsson B. Leukotriene A4 hydrolase in human leukocytes. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12339–12345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B. Leukotrienes: mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions and inflammation. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):568–575. doi: 10.1126/science.6301011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serhan C. N., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Lipoxins: novel series of biologically active compounds formed from arachidonic acid in human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5335–5339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Rådmark O., Samuelsson B. Enzyme with dual lipoxygenase activities catalyzes leukotriene A4 synthesis from arachidonic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):689–693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberman R. J., Harper T. W., Betteridge D., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Characterization and separation of the arachidonic acid 5-lipoxygenase and linoleic acid omega-6 lipoxygenase (arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase) of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4508–4515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



