Abstract
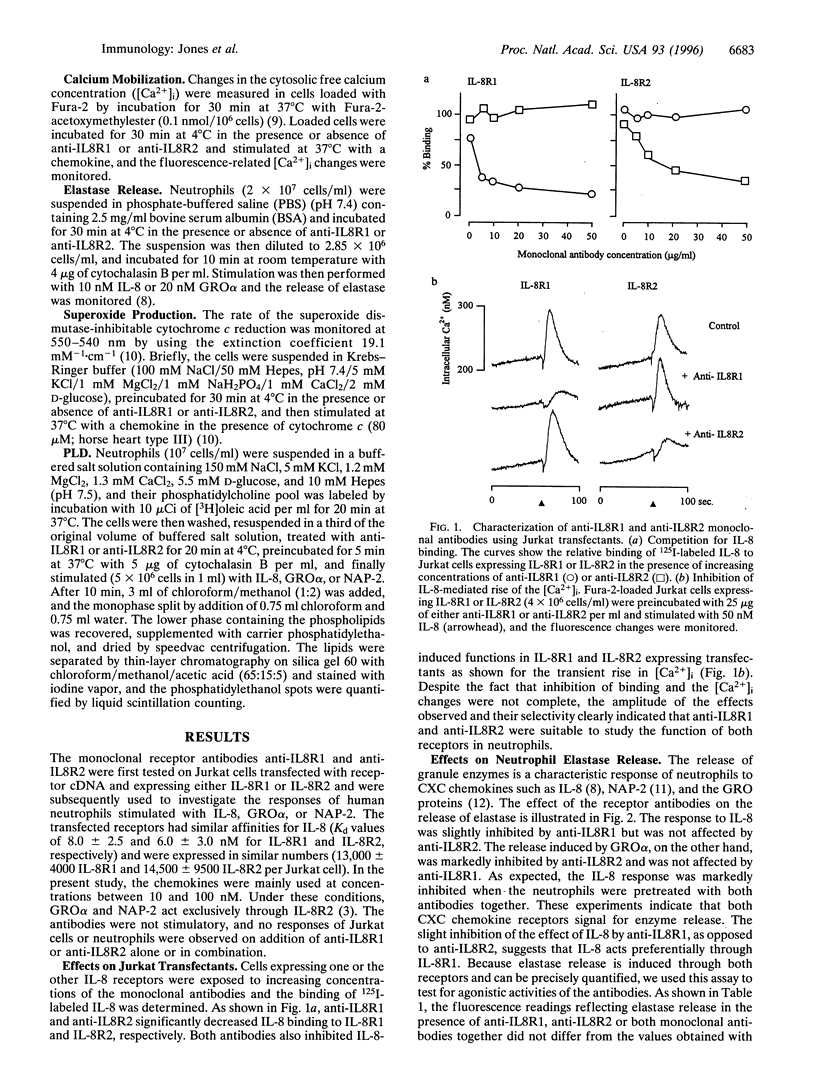
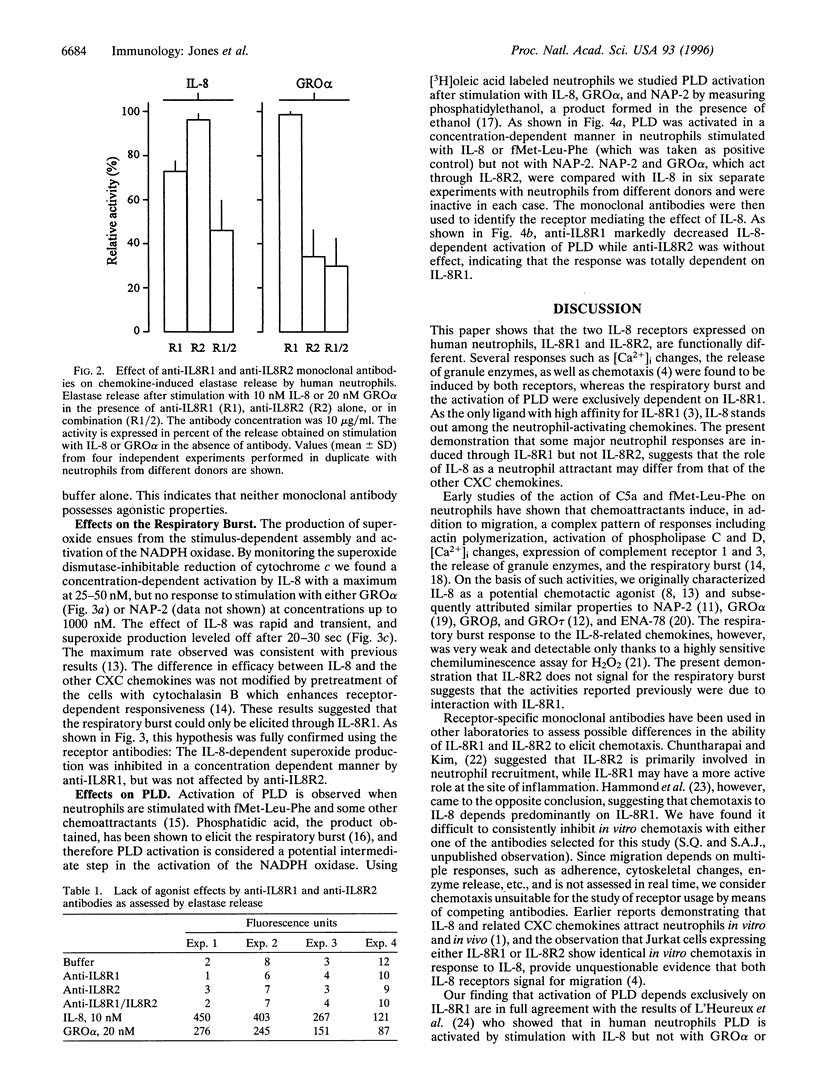
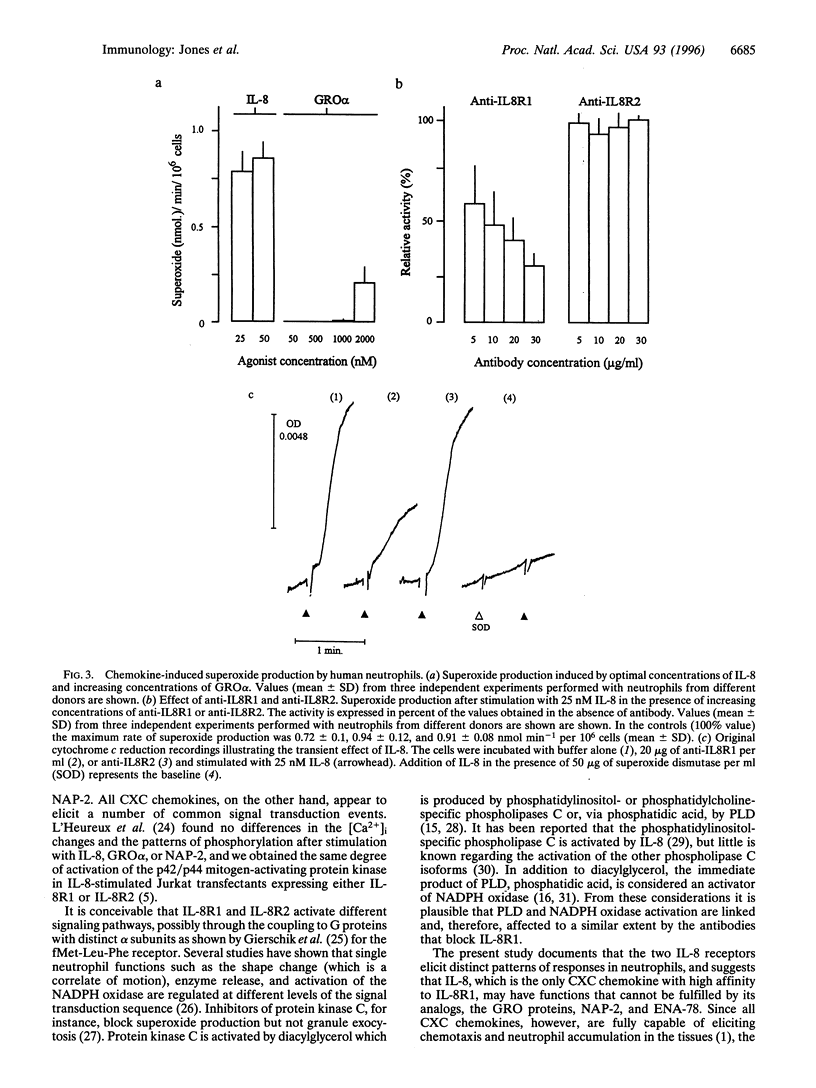
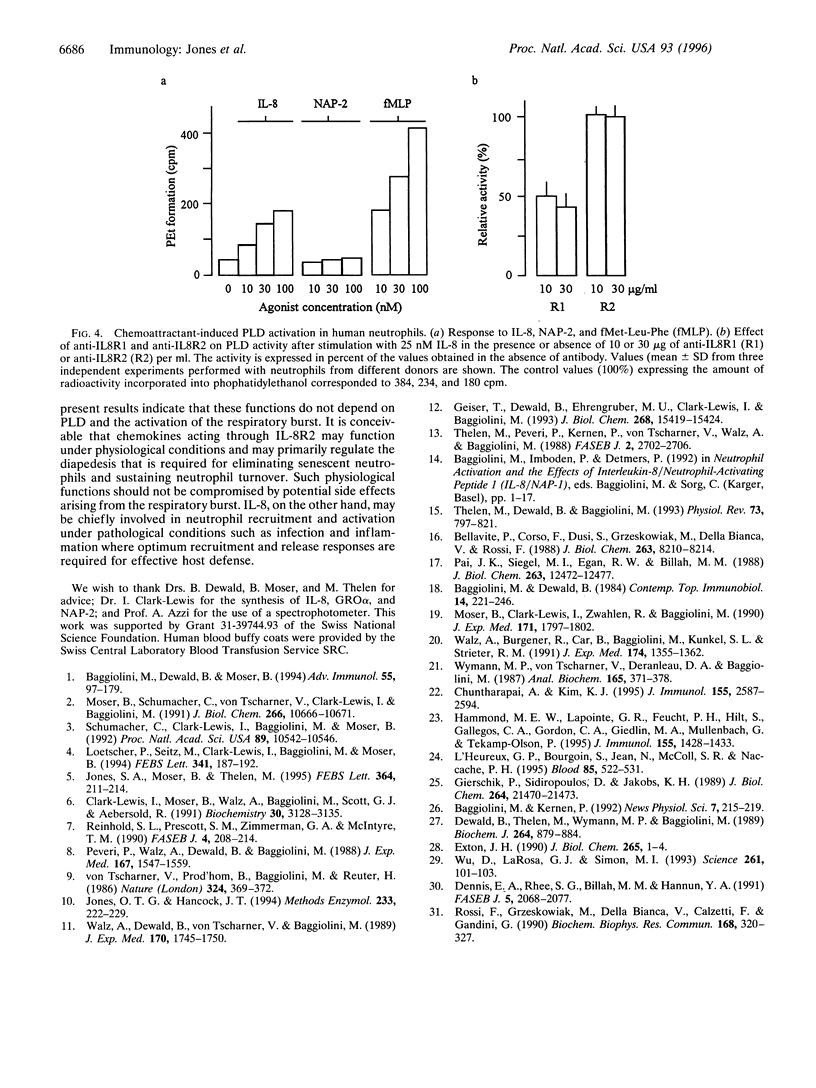
Two monoclonal antibodies, anti-IL8R1 and anti-IL8R2, raised against both interleukin 8 receptors (IL-8R) of human neutrophils, IL-8R1 and IL-8R2, were used to study individual receptor functions after stimulation with IL-8, GRO alpha, or NAP-2. Efficacy and selectivity of the antibodies were tested in Jurkat cells transfected with cDNA coding for one or the other receptor. The binding of 125 I labeled IL-8 and IL-8-induced changes of the cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration were inhibited by anti-IL8RI in cells expressing IL-8R1 and by anti-IL8R2 in cells expressing IL-8R2. In human neutrophils, release of elastase was observed after stimulation with IL-8 or GRO alpha. The response to IL-8 was inhibited slightly by anti-IL8R1 and more substantially when both monoclonal antibodies were present, while the response to GRO alpha was inhibited by anti-IL8R2 but was not affected by anti-IL8R1. These results indicate that both IL-8 receptors can signal independently for granule enzyme release. Superoxide production, a measure of the respiratory burst, was obtained with increasing concentrations of IL-8 with maximum effects at 25 to 50 nM, but no response was observed upon challenge with GRO alpha or NAP-2 up to 1000 nM. The superoxide production induced by IL-8 was inhibited by anti-IL8R1, but was not affected by anti-IL8R2. Stimulation of neutrophils with IL-8, in contrast to GRO alpha or NAP-2, also elicited phospholipase D activity. The effect of IL-8 was again inhibited by anti-IL-8R1 but not by anti-IL8R2, indicating that this response, like the respiratory burst, was mediated by IL-8R1. Taken together, our results show that IL-8R1 and IL-8R2 are functionally different. Responses, such as cytosolic free Ca2+ changes and the release of granule enzymes, are mediated through both receptors, whereas the respiratory burst and the activation of phospholipase D depend exclusively on stimulation through IL-8R1.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baggiolini M., Dewald B. Exocytosis by neutrophils. Contemp Top Immunobiol. 1984;14:221–246. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4862-8_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Dewald B., Moser B. Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines--CXC and CC chemokines. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:97–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggiolini M., Imboden P., Detmers P. Neutrophil activation and the effects of interleukin-8/neutrophil-activating peptide 1 (IL-8/NAP-1). Cytokines. 1992;4:1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellavite P., Corso F., Dusi S., Grzeskowiak M., Della-Bianca V., Rossi F. Activation of NADPH-dependent superoxide production in plasma membrane extracts of pig neutrophils by phosphatidic acid. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8210–8214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuntharapai A., Kim K. J. Regulation of the expression of IL-8 receptor A/B by IL-8: possible functions of each receptor. J Immunol. 1995 Sep 1;155(5):2587–2594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Moser B., Walz A., Baggiolini M., Scott G. J., Aebersold R. Chemical synthesis, purification, and characterization of two inflammatory proteins, neutrophil activating peptide 1 (interleukin-8) and neutrophil activating peptide. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 26;30(12):3128–3135. doi: 10.1021/bi00226a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis E. A., Rhee S. G., Billah M. M., Hannun Y. A. Role of phospholipase in generating lipid second messengers in signal transduction. FASEB J. 1991 Apr;5(7):2068–2077. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.7.1901288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewald B., Thelen M., Wymann M. P., Baggiolini M. Staurosporine inhibits the respiratory burst and induces exocytosis in human neutrophils. Biochem J. 1989 Dec 15;264(3):879–884. doi: 10.1042/bj2640879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiser T., Dewald B., Ehrengruber M. U., Clark-Lewis I., Baggiolini M. The interleukin-8-related chemotactic cytokines GRO alpha, GRO beta, and GRO gamma activate human neutrophil and basophil leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15419–15424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Sidiropoulos D., Jakobs K. H. Two distinct Gi-proteins mediate formyl peptide receptor signal transduction in human leukemia (HL-60) cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21470–21473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond M. E., Lapointe G. R., Feucht P. H., Hilt S., Gallegos C. A., Gordon C. A., Giedlin M. A., Mullenbach G., Tekamp-Olson P. IL-8 induces neutrophil chemotaxis predominantly via type I IL-8 receptors. J Immunol. 1995 Aug 1;155(3):1428–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones O. T., Hancock J. T. Assays of plasma membrane NADPH oxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1994;233:222–229. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(94)33025-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. A., Moser B., Thelen M. A comparison of post-receptor signal transduction events in Jurkat cells transfected with either IL-8R1 or IL-8R2. Chemokine mediated activation of p42/p44 MAP-kinase (ERK-2). FEBS Lett. 1995 May 8;364(2):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00397-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- L'Heureux G. P., Bourgoin S., Jean N., McColl S. R., Naccache P. H. Diverging signal transduction pathways activated by interleukin-8 and related chemokines in human neutrophils: interleukin-8, but not NAP-2 or GRO alpha, stimulates phospholipase D activity. Blood. 1995 Jan 15;85(2):522–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loetscher P., Seitz M., Clark-Lewis I., Baggiolini M., Moser B. Both interleukin-8 receptors independently mediate chemotaxis. Jurkat cells transfected with IL-8R1 or IL-8R2 migrate in response to IL-8, GRO alpha and NAP-2. FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 21;341(2-3):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80454-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser B., Clark-Lewis I., Zwahlen R., Baggiolini M. Neutrophil-activating properties of the melanoma growth-stimulatory activity. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1797–1802. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser B., Schumacher C., von Tscharner V., Clark-Lewis I., Baggiolini M. Neutrophil-activating peptide 2 and gro/melanoma growth-stimulatory activity interact with neutrophil-activating peptide 1/interleukin 8 receptors on human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10666–10671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai J. K., Siegel M. I., Egan R. W., Billah M. M. Phospholipase D catalyzes phospholipid metabolism in chemotactic peptide-stimulated HL-60 granulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12472–12477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peveri P., Walz A., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. A novel neutrophil-activating factor produced by human mononuclear phagocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1547–1559. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhold S. L., Prescott S. M., Zimmerman G. A., McIntyre T. M. Activation of human neutrophil phospholipase D by three separable mechanisms. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):208–214. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2105252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Grzeskowiak M., Della Bianca V., Calzetti F., Gandini G. Phosphatidic acid and not diacylglycerol generated by phospholipase D is functionally linked to the activation of the NADPH oxidase by FMLP in human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 16;168(1):320–327. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91711-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher C., Clark-Lewis I., Baggiolini M., Moser B. High- and low-affinity binding of GRO alpha and neutrophil-activating peptide 2 to interleukin 8 receptors on human neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10542–10546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Dewald B., Baggiolini M. Neutrophil signal transduction and activation of the respiratory burst. Physiol Rev. 1993 Oct;73(4):797–821. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.4.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelen M., Peveri P., Kernen P., von Tscharner V., Walz A., Baggiolini M. Mechanism of neutrophil activation by NAF, a novel monocyte-derived peptide agonist. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2702–2706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Burgener R., Car B., Baggiolini M., Kunkel S. L., Strieter R. M. Structure and neutrophil-activating properties of a novel inflammatory peptide (ENA-78) with homology to interleukin 8. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1355–1362. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Dewald B., von Tscharner V., Baggiolini M. Effects of the neutrophil-activating peptide NAP-2, platelet basic protein, connective tissue-activating peptide III and platelet factor 4 on human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1745–1750. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D., LaRosa G. J., Simon M. I. G protein-coupled signal transduction pathways for interleukin-8. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):101–103. doi: 10.1126/science.8316840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wymann M. P., von Tscharner V., Deranleau D. A., Baggiolini M. Chemiluminescence detection of H2O2 produced by human neutrophils during the respiratory burst. Anal Biochem. 1987 Sep;165(2):371–378. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90284-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Tscharner V., Prod'hom B., Baggiolini M., Reuter H. Ion channels in human neutrophils activated by a rise in free cytosolic calcium concentration. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):369–372. doi: 10.1038/324369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



