Abstract
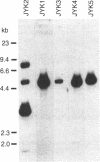
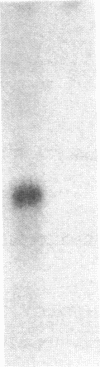
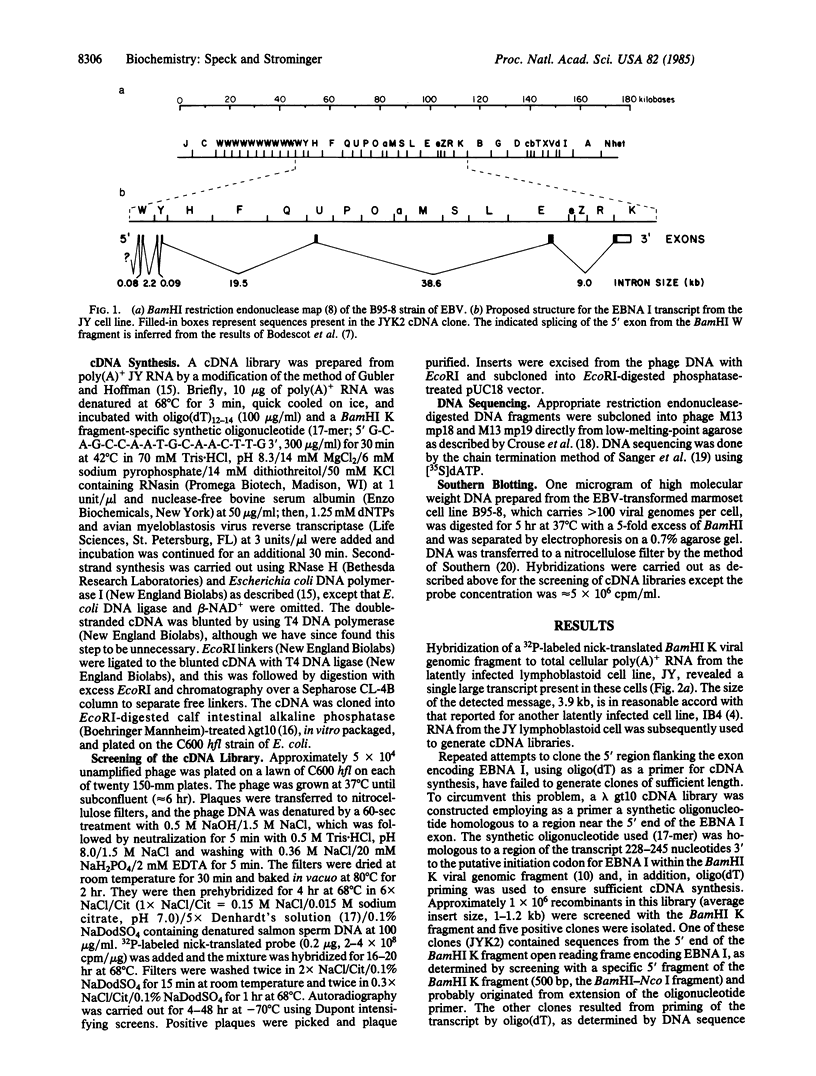
The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA I) present in latently infected cells is encoded in a 2-kilobase exon contained in the BamHI K viral genomic fragment. This exon is, however, found within a 3.7-kilobase mRNA transcript. The origin of the remaining 1.7 kilobases is unknown, although it is not derived from adjacent Epstein-Barr virus DNA sequences. A 1.1-kilobase cDNA clone generated by primer extension using an oligonucleotide complimentary to a sequence 245 base pairs 3' to the putative initiation codon for EBNA I in the BamHI K fragment has been isolated. This clone contains seven exons (from the BamHI W, Y, U, E, and K viral genomic fragments), which are spread over approximately 70 kilobases of the viral genome. However, this clone does not appear to contain the complete 5' end of the transcript. In addition to the open reading frame in the exon encoding EBNA I, three other open reading frames are found in this transcript that potentially encode other viral antigens present in latently infected cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Akam M., Karch F., Beachy P. A., Peifer M., Spierer P., Lewis E. B., Hogness D. S. Molecular Genetics of the Bithorax Complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):23–29. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4605.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Chambraud B., Farrell P., Perricaudet M. Spliced RNA from the IR1-U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus: presence of an open reading frame for a repetitive polypeptide. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1913–1917. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen L. K., Speck S. H., Roberts B. E., Strominger J. L. Identification and mapping of polypeptides encoded by the P3HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4183–4187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouse G. F., Frischauf A., Lehrach H. An integrated and simplified approach to cloning into plasmids and single-stranded phages. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:78–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennewald S., van Santen V., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequence of an mRNA transcribed in latent growth-transforming virus infection indicates that it may encode a membrane protein. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.411-419.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber R. L., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. Genomic and cDNA clones of the homeotic locus Antennapedia in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2027–2036. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01696.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E. A., Summers W. P., Dowling S., Shedd D., Gradoville L., Miller G. Two Epstein-Barr viral nuclear neoantigens distinguished by gene transfer, serology, and chromosome binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7650–7653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyaux M., Cornelissen A. W., Pays E., Steinert M., Borst P. Trypanosoma brucei: a surface antigen mRNA is discontinuously transcribed from two distinct chromosomes. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):995–998. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03729.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA encodes part of the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1396–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.6304878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medford R. M., Nguyen H. T., Destree A. T., Summers E., Nadal-Ginard B. A novel mechanism of alternative RNA splicing for the developmentally regulated generation of troponin T isoforms from a single gene. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):409–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90496-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Robinson J., Heston L., Lipman M. Differences between laboratory strains of Epstein-Barr virus based on immortalization, abortive infection, and interference. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4006–4010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons M., Nelson R. G., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Trypanosome mRNAs share a common 5' spliced leader sequence. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90552-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Grogan E. A., Shedd D., Robert M., Liu C. R., Miller G. Stable expression in mouse cells of nuclear neoantigen after transfer of a 3.4-megadalton cloned fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terhorst C., Parham P., Mann D. L., Strominger J. L. Structure of HLA antigens: amino-acid and carbohydrate compositions and NH2-terminal sequences of four antigen preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):910–914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel R., Miller G. Major EB virus-specific cytoplasmic transcripts in a cellular clone of the HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma line during latency and after induction of viral replicative cycle by phorbol esters. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):287–298. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90202-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V., Cheung A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus RNA VII: size and direction of transcription of virus-specified cytoplasmic RNAs in a transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1930–1934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]