Abstract
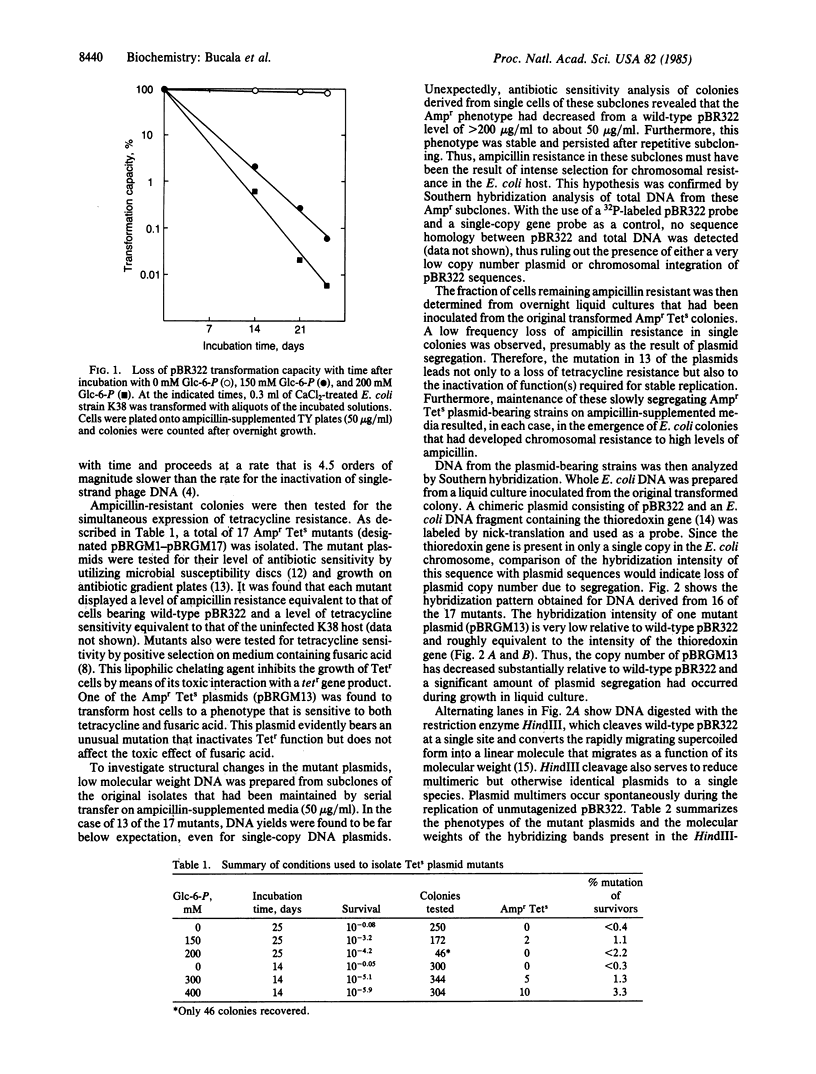
Reducing sugars such as glucose or glucose 6-phosphate (Glc-6-P) have been shown previously to modify the amino groups of nucleotides and single-stranded DNA. We have examined the mutagenic effect of Glc-6-P-induced lesions in the double-stranded DNA plasmid pBR322. Seventeen mutants of the Ampr Tets phenotype were isolated from plasmid preparations whose transforming capacity had been decreased by incubation with Glc-6-P. A number of the mutant plasmids were found to have undergone gross DNA alterations, including insertions and deletions, as well as the development of multiple species originating from a single cell. The ability of an endogenous reducing sugar to induce extensive DNA rearrangements suggests that these lesions may be significant contributors to cellular mutation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer A. W., Kirby W. M., Sherris J. C., Turck M. Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Am J Clin Pathol. 1966 Apr;45(4):493–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucala R., Model P., Cerami A. Modification of DNA by reducing sugars: a possible mechanism for nucleic acid aging and age-related dysfunction in gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):105–109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helling R. B., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Analysis of endonuclease R-EcoRI fragments of DNA from lambdoid bacteriophages and other viruses by agarose-gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1235–1244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1235-1244.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Nunn W. D. Selection for loss of tetracycline resistance by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1110–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1110-1111.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauron J. The Maillard reaction in food; a critical review from the nutritional standpoint. Prog Food Nutr Sci. 1981;5(1-6):5–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo H., Ohtsubo E. Nucleotide sequence of an insertion element, IS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolleston F. S., Newsholme E. A. Control of glycolysis in cerebral cortex slices. Biochem J. 1967 Aug;104(2):524–533. doi: 10.1042/bj1040524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russel M., Model P. Characterization of the cloned fip gene and its product. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):526–532. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.526-532.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Rupp W. D. A novel repair enzyme: UVRABC excision nuclease of Escherichia coli cuts a DNA strand on both sides of the damaged region. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):249–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung A. T., Mattes W. B., Oh E. Y., Grossman L. Enzymatic properties of purified Escherichia coli uvrABC proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6157–6161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]