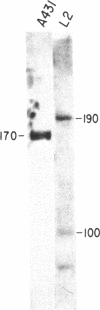Abstract
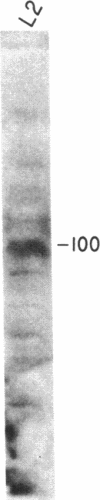
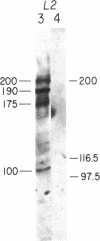
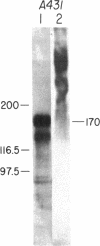
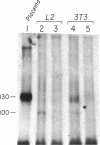
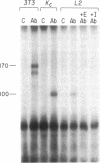
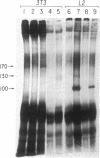
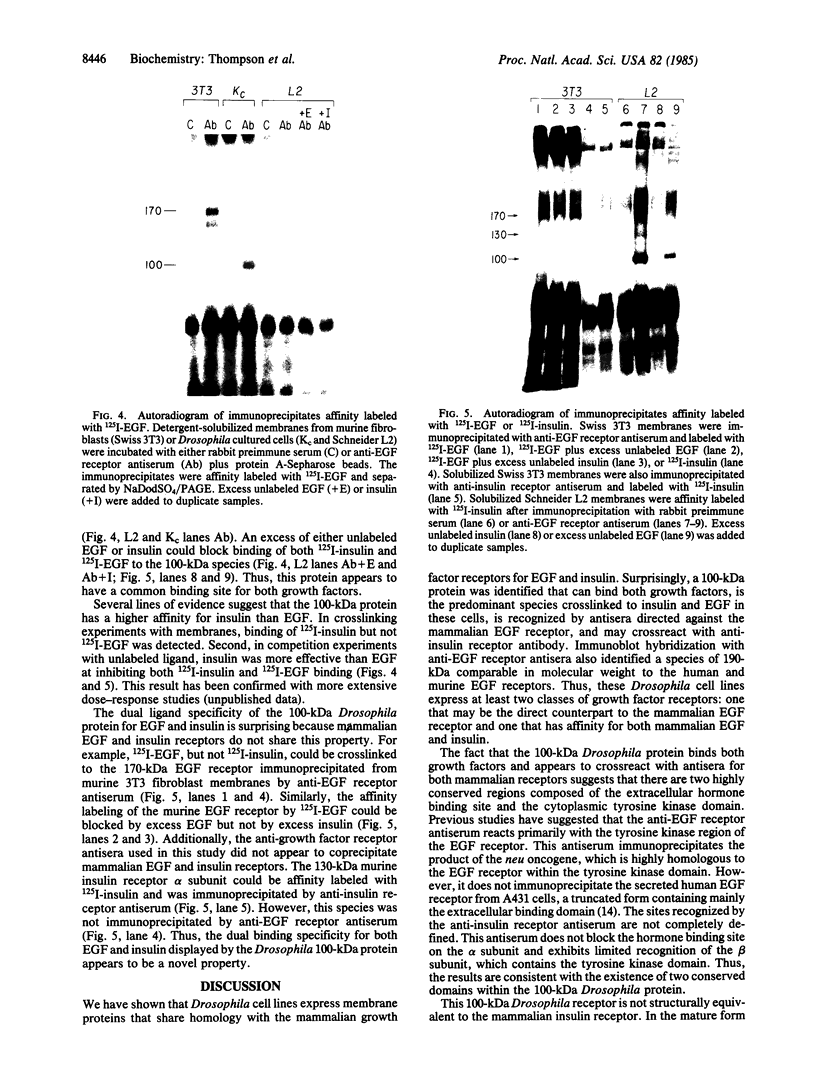
The notable amino acid homology among mammalian growth factor receptors with tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity has led to speculation that these receptors derived from a common evolutionary precursor. We report the identification of a novel growth factor receptor from Drosophila cell cultures that has dual binding specificity for both insulin and epidermal growth factor (EGF). This 100-kDa protein is also related antigenically to the mammalian receptors for EGF and possibly insulin but may not correspond to the mammalian counterpart of either receptor in Drosophila. The Drosophila protein is recognized by antisera directed against the mammalian receptor for EGF in immunoblot hybridizations. It can be affinity labeled with either 125I-labeled insulin or 125I-labeled EGF after immunoprecipitation with anti-EGF receptor antiserum. Excess unlabeled EGF or insulin will block the affinity labeling with either growth factor, suggesting that both EGF and insulin share a common binding site on the 100-kDa Drosophila receptor. This Drosophila protein, therefore, may be closely related to an evolutionary precursor of the mammalian receptors for insulin and EGF.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J. Phosphorylation of the erbB gene product from an avian erythroblastosis virus-transformed chick fibroblast cell line. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2003–2006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. Purification of denatured epidermal growth factor-receptor from A431 human epidermoid carcinoma cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 1;228(2):621–626. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Genes-in-pieces revisited. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):823–824. doi: 10.1126/science.4001923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann F. M., Fresco L. D., Hoffman-Falk H., Shilo B. Z. Nucleotide sequences of the Drosophila src and abl homologs: conservation and variability in the src family oncogenes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. The epidermal growth factor receptor gene and its product. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):414–416. doi: 10.1038/311414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Chang K. J., Cuatrecasas P. Antibodies to purified insulin receptor have insulin-like activity. Science. 1978 Jun 16;200(4347):1283–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.663609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Bar-Eli M., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Antibodies to two defined regions of the transforming protein pp60src interact specifically with the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):5911–5915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.5911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeRoith D., Lesniak M. A., Roth J. Insulin in insects and annelids. Diabetes. 1981 Jan;30(1):70–76. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.1.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Glazer L., Segal D., Schlessinger J., Shilo B. Z. The Drosophila EGF receptor gene homolog: conservation of both hormone binding and kinase domains. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):599–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90208-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrotti N., Taylor S. I., Richert N. D., Rapp U. R., Pastan I. H., Roth J. Immunoprecipitation of insulin receptors from cultured human lymphocytes (IM-9 cells) by antibodies to pp60src. Science. 1985 Feb 15;227(4688):761–763. doi: 10.1126/science.3918346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike L. J., Kuenzel E. A., Casnellie J. E., Krebs E. G. A comparison of the insulin- and epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinases from human placenta. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9913–9921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter A. L., Stern D. F., Vaidyanathan L., Decker S. J., Drebin J. A., Greene M. I., Weinberg R. A. The neu oncogene: an erb-B-related gene encoding a 185,000-Mr tumour antigen. Nature. 1984 Dec 6;312(5994):513–516. doi: 10.1038/312513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shia M. A., Rubin J. B., Pilch P. F. The insulin receptor protein kinase. Physicochemical requirements for activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14450–14455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Kornberg T. B., Bishop J. M. Three loci related to the src oncogene and tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity in Drosophila. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):837–839. doi: 10.1038/302837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S. C., Vincent W. S., 3rd, Bilodeau-Wentworth D. A Drosophila genomic sequence with homology to human epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):178–180. doi: 10.1038/314178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]