Abstract
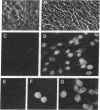
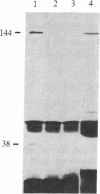
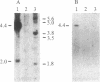
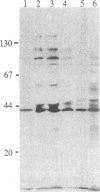
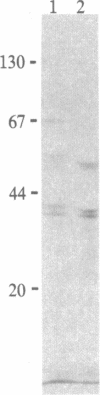
Diploid Syrian hamster embryo cells transfected with Bgl II C fragment of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA acquired a neoplastic phenotype. Cultures transfected with its left-hand 64% subclone EcoRI/HindIII fragment AE (0.419-0.525 map unit) grew into established but nontumorigenic lines. Transfection of EcoRI/HindIII AE-immortalized cells with a 4.4-kilobase Sac I/BamHI subfragment within BamHI E (0.554-0.584 map unit; overlaps the right-hand 16% of Bgl II C) converted them to tumorigenicity. The 4.4-kilobase subfragment encodes a 144-kDa protein immunologically and structurally similar to an infected cell protein designated ICP 10. DNA extracted from cells transformed with the 4.4-kilobase subfragment exhibited discrete hybridizing bands homologous to BamHI E fragment. Monoclonal antibody to ICP 10 precipitated a 144-kDa protein from the transformed cells and stained them in immunofluorescence. A tumor derivative established with the transformed cells did not stain with this antibody, but approximately equal to 25% of the cells stained with a monoclonal antibody to c-myc protooncogene products.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacchetti S., Evelegh M. J., Muirhead B., Sartori C. S., Huszar D. Immunological characterization of herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 polypeptide(s) involved in viral ribonucleotide reductase activity. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):591–593. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.591-593.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Bacchetti S., Rawls W. E. Protection against lethal challenge of BALB/c mice by passive transfer of monoclonal antibodies to five glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2. Infect Immun. 1982 Sep;37(3):1132–1137. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.3.1132-1137.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron I. R., Park M., Dutia B. M., Orr A., Macnab J. C. Herpes simplex virus sequences involved in the initiation of oncogenic morphological transformation of rat cells are not required for maintenance of the transformed state. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):517–527. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudry F., Harvey R., Smith A. E. Structure and biochemical functions of four simian virus 40 truncated large-T antigens. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):54–66. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.54-66.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. W., Chen E. Y., Smith D. H., Levinson A. D. Identification and nucleotide sequence of a human locus homologous to the v-myc oncogene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):722–725. doi: 10.1038/301722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Goldstein L. C., Lewis J. B. Identification of proteins encoded by a fragment of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA that has transforming activity. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):530–537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.530-537.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., McDougall J. K. Transformation of rodent cells by a cloned DNA fragment of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):749–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.749-760.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Swain M. A. Organization of the left-hand end of the herpes simplex virus type 2 BglII N fragment. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):724–730. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.724-730.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Thompson C. B., Eisenman R. N. c-myc oncogene protein synthesis is independent of the cell cycle in human and avian cells. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):366–369. doi: 10.1038/314366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huszar D., Bacchetti S. Is ribonucleotide reductase the transforming function of herpes simplex virus 2? Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):76–79. doi: 10.1038/302076a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jariwalla R. J., Aurelian L., Ts'o P. O. Immortalization and neoplastic transformation of normal diploid cells by defined cloned DNA fragments of herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5902–5906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jariwalla R. J., Aurelian L., Ts'o P. O. Tumorigenic transformation induced by a specific fragment of DNA from herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2279–2283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manak M. M., Aurelian L., Ts'o P. O. Focus formation and neoplastic transformation by herpes simplex virus type 2 inactivated intracellularly by 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine and near UV light. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):289–300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.289-300.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. DNA sequence homology between two co-linear loci on the HSV genome which have different transforming abilities. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):1953–1961. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Wolff M. H., Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. V. Properties of alpha polypeptides made in HSV-1 and HSV-2 infected cells. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):733–749. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Foulkes J. G., Rosenberg N., Baltimore D. Sequences of the A-MuLV protein needed for fibroblast and lymphoid cell transformation. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90389-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Evan G. I., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the human proto-oncogene c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7742–7746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Cowie A., Carr A., Glaichenhaus N., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The roles of individual polyoma virus early proteins in oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):713–718. doi: 10.1038/300713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Aurelian L. Proteins of herpesvirus type 2. III. Isolation and immunologic characterization of a large molecular weight viral protein. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):401–415. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90144-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Elsen P., Houweling A., Van der Eb A. Expression of region E1b of human adenoviruses in the absence of region E1a is not sufficient for complete transformation. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):377–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg G., Ullman B., Martin D. W., Jr Mutator phenotypes in mammalian cell mutants with distinct biochemical defects and abnormal deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate pools. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2447–2451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]