Abstract
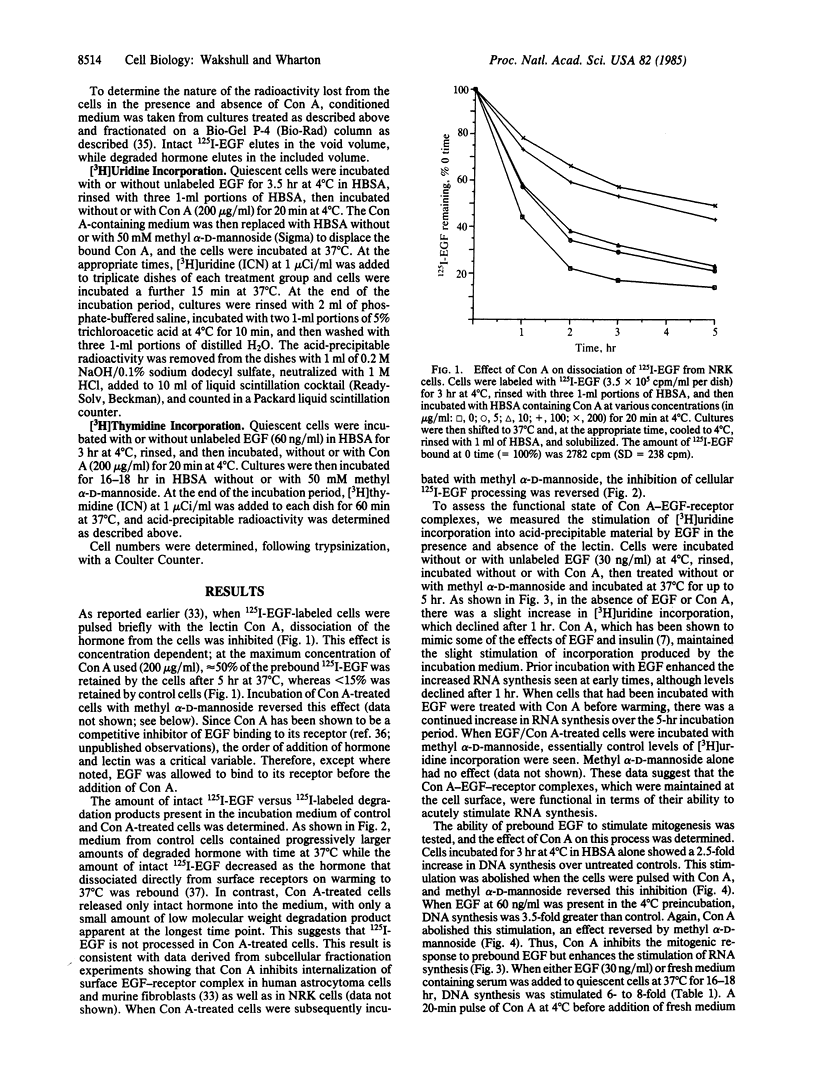
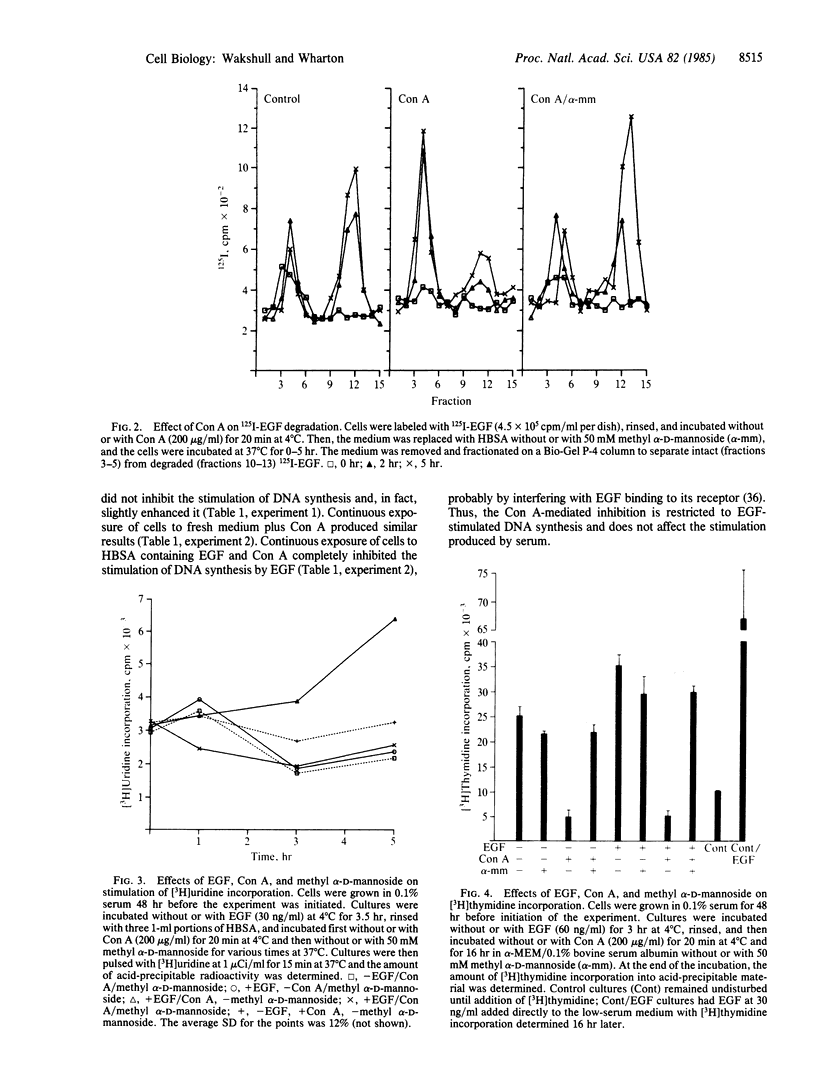
Treatment of mouse fibroblasts, prelabeled at 4 degrees C with 125I-labeled epidermal growth factor (EGF), with the lectin concanavalin A (Con A) stabilized the 125I-labeled EGF-receptor complex to dissociation and prevented receptor-mediated endocytosis; after 5 hr at 37 degrees C, approximately 50% of the 125I-labeled EGF initially bound at 4 degrees C remained cell associated, compared to less than 15% in control cells. The radioactivity lost from the Con A-treated cells was found as intact hormone in the medium, with almost no hormone degradation evident, whereas in control cells most of the medium radioactivity was in the form of low molecular weight degradation products. The trimolecular complex Con A-EGF-receptor was capable of stimulating RNA synthesis to levels greater than control (untreated) or EGF alone and maintained this stimulation for prolonged periods of time. However, there was no effect of Con A treatment on the stimulation of DNA synthesis induced by EGF prebound at 4 degrees C. Thus, maintaining the EGF-receptor complex at the cell surface allows enhanced stimulation of an acute biological response to EGF (RNA synthesis) but not stimulation of DNA synthesis. These data support the idea that processing subsequent to receptor binding is necessary to produce the mitogenic signal.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aharonov A., Pruss R. M., Herschman H. R. Epidermal growth factor. Relationship between receptor regulation and mitogenesis in 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3970–3977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum J. J., Conn P. M. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone stimulation of luteinizing hormone release: A ligand-receptor-effector model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7307–7311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradshaw R. A., Rubin J. S. Polypeptide growth factors: some structural and mechanistic considerations. J Supramol Struct. 1980;14(2):183–199. doi: 10.1002/jss.400140207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandenburg D., Diaconescu C., Saunders D., Thamm P. Covalent linking of photoreactive insulin to adipocytes produces a prolonged signal. Nature. 1980 Aug 21;286(5775):821–822. doi: 10.1038/286821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Chouvet C., Gill G. N. Comparison of protein phosphorylations in variant A431 cells with different growth responses to epidermal growth factor. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Jun;119(3):296–306. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041190307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:193–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Human epidermal growth factor and the proliferation of human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Jun;88(2):227–237. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Influence of lectins on the binding of 125I-labeled EGF to human fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Nov 21;79(2):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor stimulates phosphorylation in membrane preparations in vitro. Nature. 1978 Nov 23;276(5686):409–410. doi: 10.1038/276409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M. Epidermal growth factor: mechanisms of action. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;78:233–256. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das M., Fox C. F. Molecular mechanism of mitogen action: processing of receptor induced by epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2644–2648. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh-Dastidar P., Fox C. F. Epidermal growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent phosphorylation of a Mr = 34,000 protein substrate for pp60src. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2041–2044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory H., Taylor C. L., Hopkins C. R. Luteinizing hormone release from dissociated pituitary cells by dimerization of occupied LHRH receptors. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):269–271. doi: 10.1038/300269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazum E., Keinan D. Covalent linking of photoreactive gonadotropin-releasing hormone to gonadotropes produces a prolonged signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1902–1904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg M. D., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin and epidermal growth factor. Human fibroblast receptors related to deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and amino acid uptake. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):3845–3853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R., Bradshaw R. A. Polypeptide growth factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:259–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Baird K. L., Jarrett D. B., Flier J. S. Direct demonstration that receptor crosslinking or aggregation is important in insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4209–4213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Cuatrecasas P. Exposure of cells to an acidic environment reverses the inhibition by methylamine of the mitogenic response to epidermal growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 May 31;106(2):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Hernaez-Davis L., Cuatrecasas P. Lysosomotropic amines inhibit mitogenesis induced by growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):717–721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C. Monensin, like methylamine, prevents degradation of 125I-epidermal growth factor, causes intracellular accumulation of receptors and blocks the mitogenic response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):585–591. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91594-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauer D. J., Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. Relationship between epidermal growth factor receptor occupancy and mitogenic response. Quantitative analysis using a steady state model system. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5623–5631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leof E. B., Van Wyk J. J., O'Keefe E. J., Pledger W. J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is required only during the traverse of early G1 in PDGF stimulated density-arrested BALB/c-3T3 cells. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Aug;147(1):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren A., Westermark B. Subdivision of the G1 phase of human glia cells in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magun B. E., Planck S. R., Matrisian L. M., Finch J. S. Binding, internalization and intracellular processing of 125I-epidermal growth factor purified by isoelectric focusing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Sep 16;108(1):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91866-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Davies P. J., Klempner L., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. Epidermal growth factor stimulation of DNA synthesis is potentiated by compounds that inhibit its clustering in coated pits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5731–5735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael H. J., Bishayee S., Das M. Effect of methylamine on internalization, processing and biological activation of epidermal growth factor receptor. FEBS Lett. 1980 Aug 11;117(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80927-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olashaw N. E., Leof E. B., O'Keefe E. J., Pledger W. J. Differential sensitivity of fibroblasts to epidermal growth factor is related to cyclic AMP concentration. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Mar;118(3):291–297. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041180312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planck S. R., Finch J. S., Magun B. E. Intracellular processing of epidermal growth factor. II. Intracellular cleavage of the COOH-terminal region of 125I-epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3053–3057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podestá E. J., Solano A. R., Attar R., Sánchez M. L., Molina y Vedia L. Receptor aggregation induced by antilutropin receptor antibody and biological response in rat testis Leydig cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3986–3990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramachandran J., Hagman J., Muramoto K. Persistent activation of steroidogenesis in adrenocortical cells by photoaffinity labeling of corticotropin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11424–11427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg P., Glaser L., Schlesinger P., Cassel D. Epidermal growth factor stimulates amiloride-sensitive 22Na+ uptake in A431 cells. Evidence for Na+/H+ exchange. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4883–4889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter Y., Hernaez L., Schlessinger J., Cuatrecasas P. Local aggregation of hormone-receptor complexes is required for activation by epidermal growth factor. Nature. 1979 Apr 26;278(5707):835–838. doi: 10.1038/278835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Lax I., Yarden Y., Eshhar Z., Schlessinger J. Monoclonal antibodies against receptor for epidermal growth factor induce early and delayed effects of epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7535–7539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Libermann T. A., Lax I., Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Biological role of epidermal growth factor-receptor clustering. Investigation with monoclonal anti-receptor antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):846–853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Hernaez L., Cuatrecasas P. Epidermal growth factor: biological activity requires persistent occupation of high-affinity cell surface receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5788–5791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoscheck C. M., Carpenter G. Down regulation of epidermal growth factor receptors: direct demonstration of receptor degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1048–1053. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakshull E., Cooper J. L., Wharton W. Chloroquine allows the secretion of internalized 125I-epidermal growth factor from fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Nov;125(2):215–222. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041250207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakshull E., Kraemer P. M., Wharton W. Multistep change in epidermal growth factor receptors during spontaneous neoplastic progression in Chinese hamster embryo fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1985 May;45(5):2070–2075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton W., Leof E., Pledger W. J., O'Keefe E. J. Modulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by platelet-derived growth factor and choleragen: effects on mitogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5567–5571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graan P. N., Eberle A. N. Irreversible stimulation of Xenopus melanophores by photoaffinity labelling with p-azidophenylalanine13-alpha-melanotropin. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 11;116(1):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80540-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



