Abstract
The Streptococcus faecalis plasmid pCF-10 is representative of a class of plasmids that enables its host cells to respond to sex pheromones produced by other S. faecalis cells. The pheromone response has been previously shown to result in increased conjugal plasmid transfer, cell clumping, and multiple cell-surface antigenic changes. To test for other effects of pheromone induction, cells carrying pCF-10 were used as recipients in matings with an isogenic donor strain carrying a derivative of pCF-10, tagged with a transposon to provide an additional selective marker. Pheromone induction of the "male recipients" decreased their recipient ability by a factor of 10-300 in comparison to uninduced cells or plasmid-free recipients. These results indicate that an entry exclusion (surface exclusion) function, similar to that described in studies of plasmids in Gram-negative bacteria, is induced during the S. faecalis pheromone response process. The exclusion operates only against homologous plasmids. Immunological, biochemical, and genetic experiments using monoclonal antibodies reactive with C130, the predominant protein antigen associated with the pheromone response of cells carrying pCF-10, indicate that this antigen is involved in surface exclusion. The data also support the notion that synthesis of C130 involves a posttranslational modification of a precursor of C130 to a final product of higher molecular weight form.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clewell D. B., Brown B. L. Sex pheromone cAD1 in Streptococcus faecalis: induction of a function related to plasmid transfer. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):1063–1065. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.1063-1065.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Brown B. L., Clewell D. B. Induced cell aggregation and mating in Streptococcus faecalis: evidence for a bacterial sex pheromone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3479–3483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Clewell D. B. Transmissible toxin (hemolysin) plasmid in Streptococcus faecalis and its mobilization of a noninfectious drug resistance plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):784–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.784-790.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G. M., Craig R. A., Carron R. L., Clewell D. B. Plasmid transfer in Streptococcus faecalis: production of multiple sex pheromones by recipients. Plasmid. 1979 Jul;2(3):454–465. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(79)90029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G., Funk C., Adsit J. Direct stimulation of the transfer of antibiotic resistance by sex pheromones in Streptococcus faecalis. Plasmid. 1981 Nov;6(3):270–278. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunny G., Yuhasz M., Ehrenfeld E. Genetic and physiological analysis of conjugation in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Aug;151(2):855–859. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.2.855-859.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler R. E., Yagi Y. Identification and partial characterization of a pheromone-induced adhesive surface antigen of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):714–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.714-721.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minkley E. G., Jr, Willetts N. S. Overproduction, purification and characterization of the F traT protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(2):225–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00328054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori M., Sakagami Y., Narita M., Isogai A., Fujino M., Kitada C., Craig R. A., Clewell D. B., Suzuki A. Isolation and structure of the bacterial sex pheromone, cAD1, that induces plasmid transfer in Streptococcus faecalis. FEBS Lett. 1984 Dec 3;178(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81248-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perumal N. B., Minkley E. G., Jr The product of the F sex factor traT surface exclusion gene is a lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5357–5360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomich P. K., An F. Y., Clewell D. B. Properties of erythromycin-inducible transposon Tn917 in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1366–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1366-1374.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomich P. K., An F. Y., Damle S. P., Clewell D. B. Plasmid-related transmissibility and multiple drug resistance in Streptococcus faecalis subsp. zymogenes strain DS16. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Jun;15(6):828–830. doi: 10.1128/aac.15.6.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
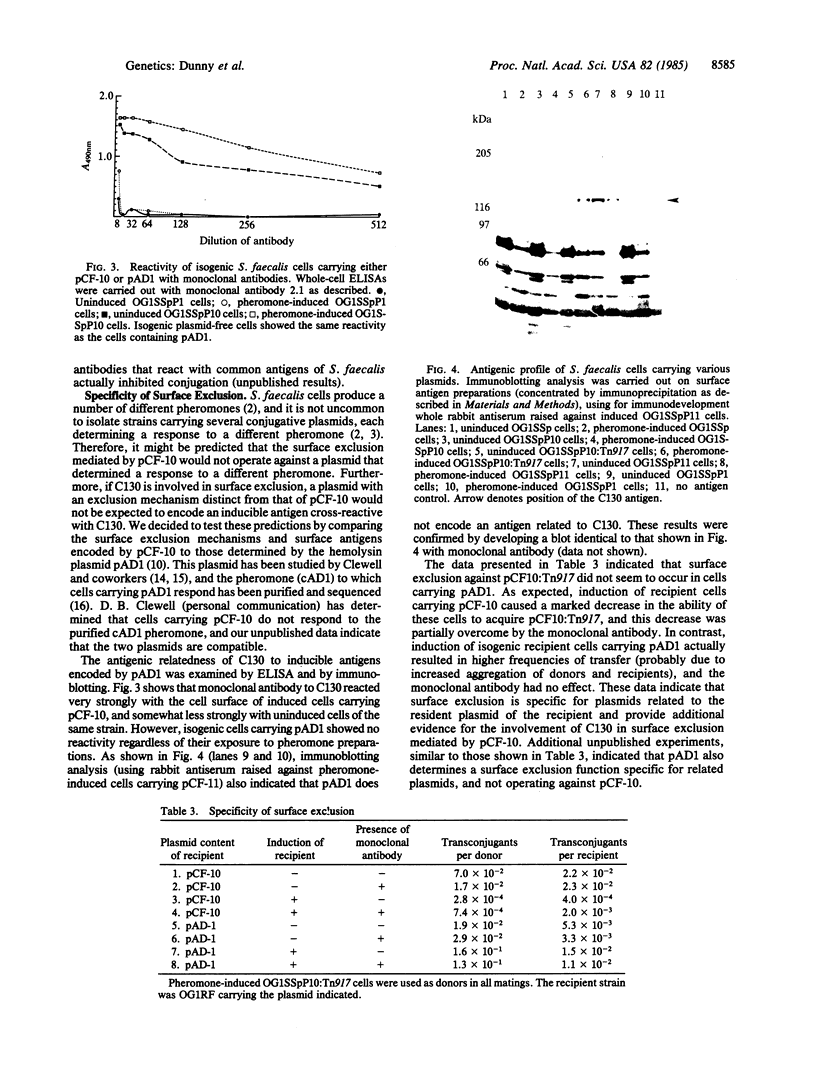
- Tortorello M. L., Dunny G. M. Identification of multiple cell surface antigens associated with the sex pheromone response of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):131–137. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.131-137.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi Y., Kessler R. E., Shaw J. H., Lopatin D. E., An F., Clewell D. B. Plasmid content of Streptococcus faecalis strain 39-5 and identification of a pheromone (cPD1)-induced surface antigen. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Apr;129(4):1207–1215. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-4-1207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]