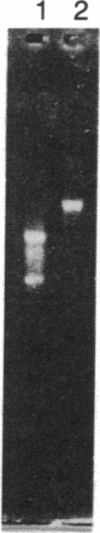
Abstract
The molecular cloning of double-stranded cDNA synthesized from the single-stranded RNA genome of the cardiotropic Coxsackie B3 virus (Nancy strain) is reported. Full-length reverse-transcribed cloned viral cDNA of approximately equal to 7500 nucleotides generated infectious antigenically identical Coxsackie B3 virus upon transfection of recombinant plasmid DNA into mammalian cells, demonstrating the molecular cloning of a biologically active viral cDNA copy. Furthermore, the cloned cDNA is characterized by restriction enzyme analysis and partial nucleotide sequencing of the 5' end. The Coxsackie B3 virus cDNA described can now be used to study the molecular basis of human enteroviral heart disease, and it provides a valuable diagnostic means for patients with suspected viral heart disease.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cann A. J., Stanway G., Hauptmann R., Minor P. D., Schild G. C., Clarke L. D., Mountford R. C., Almond J. W. Poliovirus type 3: molecular cloning of the genome and nucleotide sequence of the region encoding the protease and polymerase proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1267–1281. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee N. K., Samsonoff W. A., Tuchowski C. Isolation and characterization of a membrane-bound population of group B coxsackieviruses. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):832–841. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.832-841.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewlett M. J., Florkiewicz R. Z. Sequence of picornavirus RNAs containing a radioiodinated 5'-linked peptide reveals a conserved 5' sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):303–307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyypiä T., Stålhandske P., Vainionpä R., Pettersson U. Detection of enteroviruses by spot hybridization. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Mar;19(3):436–438. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.3.436-438.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Palacios I. Dilated cardiomyopathies of the adult (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1982 Oct 28;307(18):1119–1126. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198210283071804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandolf R., Canu A., Hofschneider P. H. Coxsackie B3 virus can replicate in cultured human foetal heart cells and is inhibited by interferon. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1985 Feb;17(2):167–181. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(85)80019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küpper H., Keller W., Kurz C., Forss S., Schaller H., Franze R., Strohmaier K., Marquardt O., Zaslavsky V. G., Hofschneider P. H. Cloning of cDNA of major antigen of foot and mouth disease virus and expression in E. coli. Nature. 1981 Feb 12;289(5798):555–559. doi: 10.1038/289555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L. Portraits of viruses: the picornaviruses. Intervirology. 1983;20(2-3):61–100. doi: 10.1159/000149376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabhakar B. S., Haspel M. V., McClintock P. R., Notkins A. L. High frequency of antigenic variants among naturally occurring human Coxsackie B4 virus isolates identified by monoclonal antibodies. Nature. 1982 Nov 25;300(5890):374–376. doi: 10.1038/300374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putnak J. R., Phillips B. A. Picornaviral structure and assembly. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):287–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.287-315.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Cloned poliovirus complementary DNA is infectious in mammalian cells. Science. 1981 Nov 20;214(4523):916–919. doi: 10.1126/science.6272391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Wilkie N. M. An improved technique for obtaining enhanced infectivity with herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Gen Virol. 1976 Dec;33(3):447–458. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-33-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålhandske P. O., Lindberg M., Pettersson U. Replicase gene of coxsackievirus B3. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):742–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.742-746.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ticehurst J. R., Racaniello V. R., Baroudy B. M., Baltimore D., Purcell R. H., Feinstone S. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of hepatitis A virus cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5885–5889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bregegere F., Kopecka H., Kitamura N., Rothberg P. G., Kourilsky P., Wimmer E., Girard M. Molecular cloning of the genome of poliovirus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):5983–5987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.5983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]