Abstract
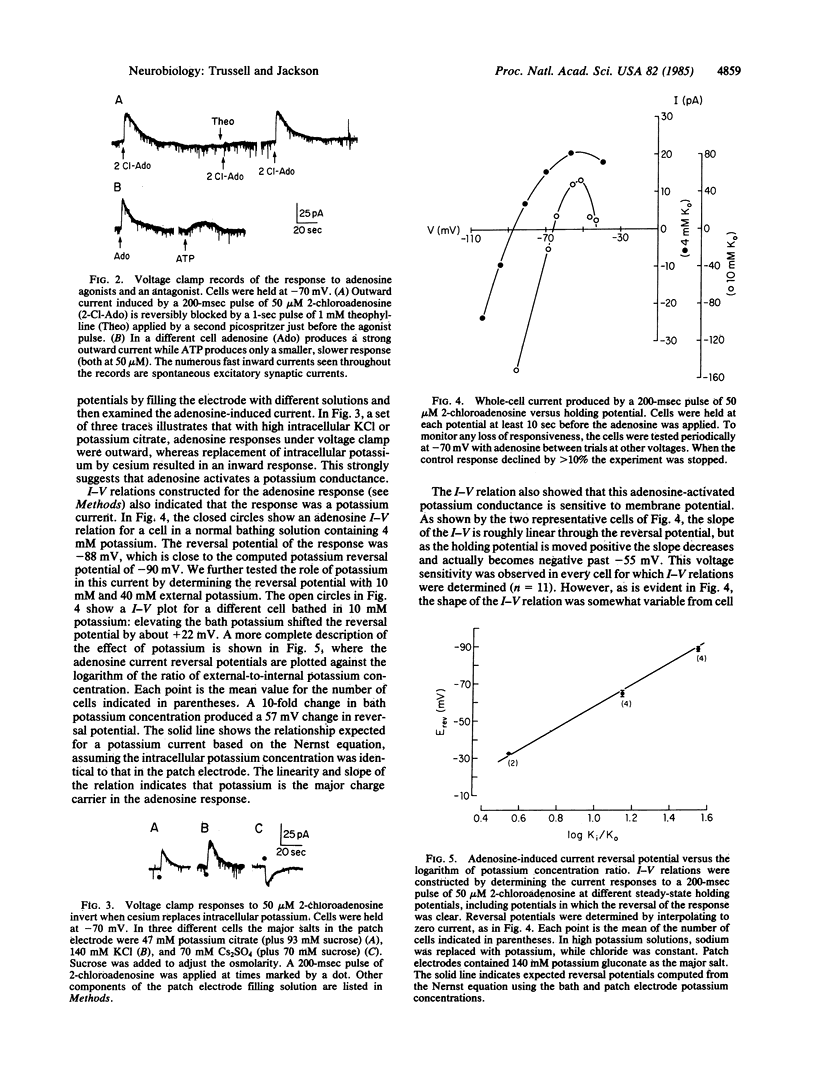
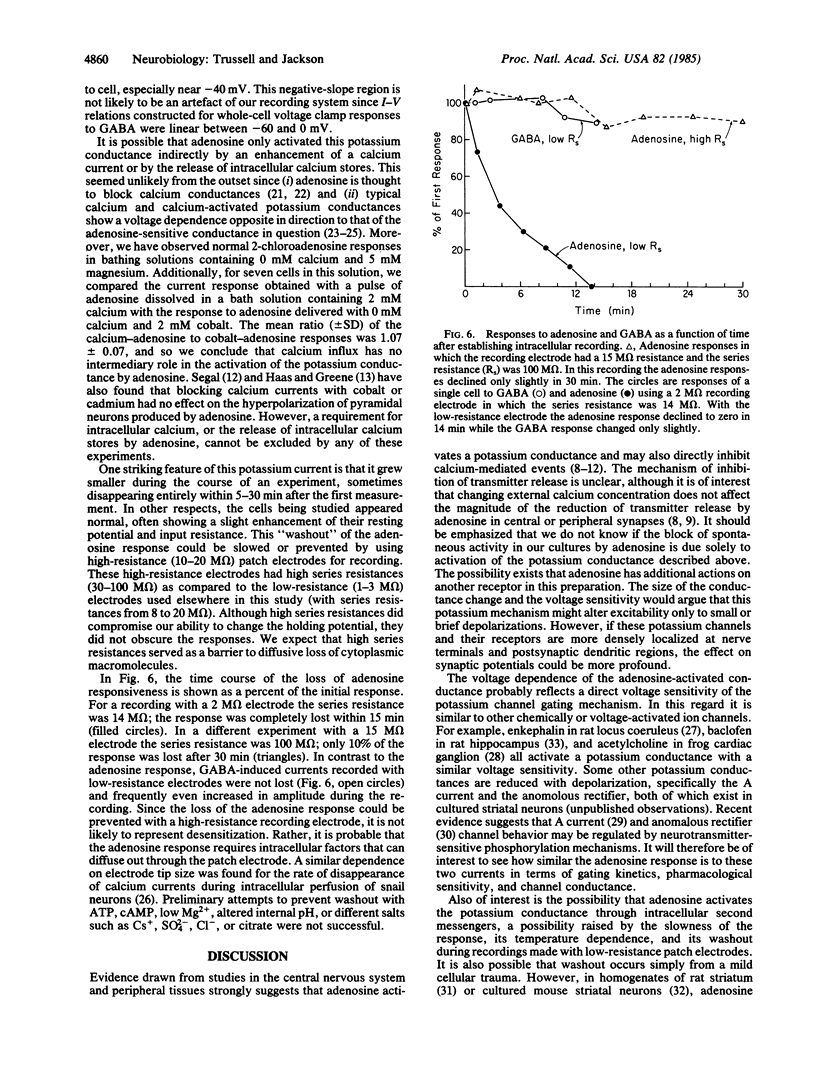
We have examined the effect of adenosine on the membrane properties of cultured embryonic mouse striatal neurons using patch electrode techniques. Adenosine at 50 microM effectively blocked spontaneous action potential activity. Adenosine or 2-chloroadenosine caused a slow hyperpolarization of the membrane potential and, under voltage clamp, an outward current that was blocked by 1 mM theophylline. ATP also caused a hyperpolarization that was slower and weaker than the adenosine response and could be blocked by 1 mM theophylline. The current induced by adenosine appears to be carried by potassium since (i) an inward current was generated by adenosine when the cells were internally perfused with cesium salts and (ii) the reversal potential of the outward current shifted 57 mV with a 10-fold change in extracellular potassium concentration. The adenosine response is voltage dependent in that the current evoked by adenosine is reduced at holding potentials more positive than -55 mV, despite a larger driving force. Though calcium influx is not required for adenosine to activate the potassium conductance, some components of the cytosol may be essential, since the response is lost during intracellular perfusion.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akasu T., Shinnick-Gallagher P., Gallagher J. P. Adenosine mediates a slow hyperpolarizing synaptic potential in autonomic neurones. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):62–65. doi: 10.1038/311062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Review lecture. Neurotransmitters and trophic factors in the autonomic nervous system. J Physiol. 1981;313:1–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerly L., Hagiwara S. Calcium currents in internally perfused nerve cell bodies of Limnea stagnalis. J Physiol. 1982 Jan;322:503–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie T. V. Interactions between the effects of adenosine and calcium on synaptic responses in rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:545–559. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas H. L., Greene R. W. Adenosine enhances afterhyperpolarization and accommodation in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Nov;402(3):244–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00585506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C. Adenosine receptors in frog sinus venosus: slow inhibitory potentials produced by adenine compounds and acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:23–49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell H. C., Kuffler S. W., Stickgold R., Yoshikami D. Synaptic excitation and inhibition resulting from direct action of acetylcholine on two types of chemoreceptors on individual amphibian parasympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Oct;271(3):817–846. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp012027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henon B. K., McAfee D. A. The ionic basis of adenosine receptor actions on post-ganglionic neurones in the rat. J Physiol. 1983 Mar;336:607–620. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostopoulos G. K., Phillis J. W. Purinergic depression of neurons in different areas of the rat brain. Exp Neurol. 1977 Jun;55(3 Pt 1):719–724. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(77)90296-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan I. B., Adams W. B. Cyclic AMP modulation of a specific ion channel in an identified nerve cell: possible role for protein phosphorylation. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;14:647–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson W. B., Kuruvilla A., Watlington T., Goehl K., Paul S. M., Skolnick P. Sedative and electroencephalographic actions of erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl)-adenine (EHNA): relationship to inhibition of brain adenosine deaminase. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983;79(2-3):126–129. doi: 10.1007/BF00427798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy J. I., LaBella L. A., Buss M., Daddona P. E. Immunohistochemistry of adenosine deaminase: implications for adenosine neurotransmission. Science. 1984 Apr 13;224(4645):166–168. doi: 10.1126/science.6142530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newberry N. R., Nicoll R. A. Comparison of the action of baclofen with gamma-aminobutyric acid on rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:161–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillis J. W., Wu P. H. The role of adenosine and its nucleotides in central synaptic transmission. Prog Neurobiol. 1981;16(3-4):187–239. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(81)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Premont J., Daguet-de Montety M. C., Herbet A., Glowinski J., Bockaert J., Prochiantz A. Biogenic amines and adenosine-sensitive adenylate cyclases in primary cultures of striatal neurons. Brain Res. 1983 Jul;285(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prémont J., Perez M., Blanc G., Tassin J. P., Thierry A. M., Hervé D., Bockaert J. Adenosine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in rat brain homogenates: kinetic characteristics, specificity, topographical, subcellular and cellular distribution. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Nov;16(3):790–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Intracellular analysis of a postsynaptic action of adenosine in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Apr 23;79(3-4):193–199. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90625-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silinsky E. M. On the mechanism by which adenosine receptor activation inhibits the release of acetylcholine from motor nerve endings. J Physiol. 1984 Jan;346:243–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Physiological roles for adenosine and adenosine 5'-triphosphate in the nervous system. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):523–555. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90145-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong J. A. Modulation of potassium current kinetics in bag cell neurons of Aplysia by an activator of adenylate cyclase. J Neurosci. 1984 Nov;4(11):2772–2783. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-11-02772.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su C. Purinergic neurotransmission and neuromodulation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:397–411. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaiman K. F., Neale E. A., Fitzgerald S. C., Nelson P. G. A method for large-scale production of mouse brain cortical cultures. Brain Res. 1982 Mar;255(3):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(82)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. T., Egan T. M., North R. A. Enkephalin opens potassium channels on mammalian central neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):74–77. doi: 10.1038/299074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M., Risley E. A. Biochemical characterization of putative central purinergic receptors by using 2-chloro[3H]adenosine, a stable analog of adenosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6892–6896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. S., Lecar H., Adler M. Single calcium-dependent potassium channels in clonal anterior pituitary cells. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):313–317. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84522-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu P. H., Phillis J. W., Thierry D. L. Adenosine receptor agonists inhibit K+-evoked Ca2+ uptake by rat brain cortical synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1982 Sep;39(3):700–708. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



