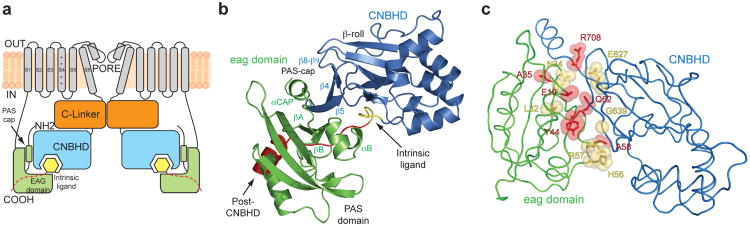
Figure 1. Structure of the eag domain-CNBHD complex of mEAG1.
a, Cartoon of a cross section of a KCNH channel. Transmembrane domains are in grey, the amino-terminal eag domains are in green, the C-linkers are in orange and the CNBHD domains in blue. The intrinsic ligand motifs are highlighted in yellow, and the post-CNBHD in red. b, Structure of the eag domain-CNBHD complex. Color corresponds to panel a. c, Disease-causing mutations at the interface of eag domain and CNBHD. LQT2 mutations are shown in yellow. Cancer-associated mutations are shown in red. Y44 is involved in both LQT2 and cancer and is shown in red.