Abstract
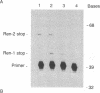
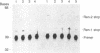
Inbred strains of mice can be categorized into two groups based on the absence or presence of a duplicated copy of the renin structural gene; one-gene strains carry a single renin gene (Ren-1), whereas two-gene strains carry two renin genes (Ren-1 and Ren-2). To investigate the contribution that each locus makes to the composite levels of renin mRNA observed to accumulate in different tissues of two-gene strains, we have developed two assays capable of distinguishing the highly homologous Ren-1 and Ren-2 transcripts. Both methods take advantage of established base sequence differences between Ren-1 and Ren-2 coding regions by using reverse transcriptase-mediated primer extension of oligonucleotide primer/mRNA hybrids in the presence of appropriate deoxy-and dideoxynucleotide phosphates. Using these techniques we found that Ren-1 and Ren-2 mRNAs accumulate in the kidney of two-gene strains to approximately equal levels. These observations are discussed in light of potential mechanisms regulating the tissue-specific expression of the Ren-1 and Ren-2 loci.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell B., Diamond D., Smith S., Pünter J., Schöne H. H., Goodman H. M. Disproportionate expression of the two nonallelic rat insulin genes in a pancreatic tumor is due to translational control. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90309-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson D. P., Gross K. W., Piccini N., Wilson C. M. Evolution and variation of renin genes in mice. Genetics. 1984 Nov;108(3):651–667. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. J., McGowan R. A., Dickinson D. P., Gross K. W. Tissue and gene specificity of mouse renin expression. Hypertension. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):597–603. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.6.4.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. J., Philbrick W. M., Howles P. N., Dickinson D. P., McGowan R. A., Gross K. W. Expression of tissue-specific Ren-1 and Ren-2 genes of mice: comparative analysis of 5'-proximal flanking regions. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2321–2331. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresik E. W., van der Noen H., Barka T. Hypertrophic and hyperplastic effects of thyroxine on the submandibular gland of the mouse. Anat Rec. 1981 Aug;200(4):443–446. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092000407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm I., Ollo R., Panthier J. J., Rougeon F. Evolution of aspartyl proteases by gene duplication: the mouse renin gene is organized in two homologous clusters of four exons. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):557–562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01846.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. J., Burt D. W., Windass J. D., McTurk P., George H., Brammar W. J. Molecular cloning of two distinct renin genes from the DBA/2 mouse. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1461–1466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Dreyfus M., Roux T. L., Rougeon F. Mouse kidney and submaxillary gland renin genes differ in their 5' putative regulatory sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5489–5493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Foote S., Chambraud B., Strosberg A. D., Corvol P., Rougeon F. Complete amino acid sequence and maturation of the mouse submaxillary gland renin precursor. Nature. 1982 Jul 1;298(5869):90–92. doi: 10.1038/298090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Holm I., Rougeon F. The mouse Rn locus: S allele of the renin regulator gene results from a single structural gene duplication. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1417–1421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Rougeon F. Kidney and submaxillary gland renins are encoded by two non-allelic genes in Swiss mice. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):675–678. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccini N., Knopf J. L., Gross K. W. A DNA polymorphism, consistent with gene duplication, correlates with high renin levels in the mouse submaxillary gland. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner R., Bührle C. P., Nobiling R. Ultrastructural changes associated with renin secretion from the juxtaglomerular apparatus of mice. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;237(3):459–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00228430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Cherry M., Taylor B. A., Wilson J. D. Genetic and endocrine control of renin activity in the submaxillary gland of the mouse. Biochem Genet. 1981 Jun;19(5-6):509–523. doi: 10.1007/BF00484623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M., Taylor B. A. Genetic regulation of thermostability of mouse submaxillary gland renin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):217–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]