Abstract
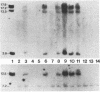
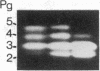
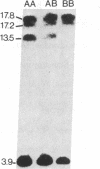
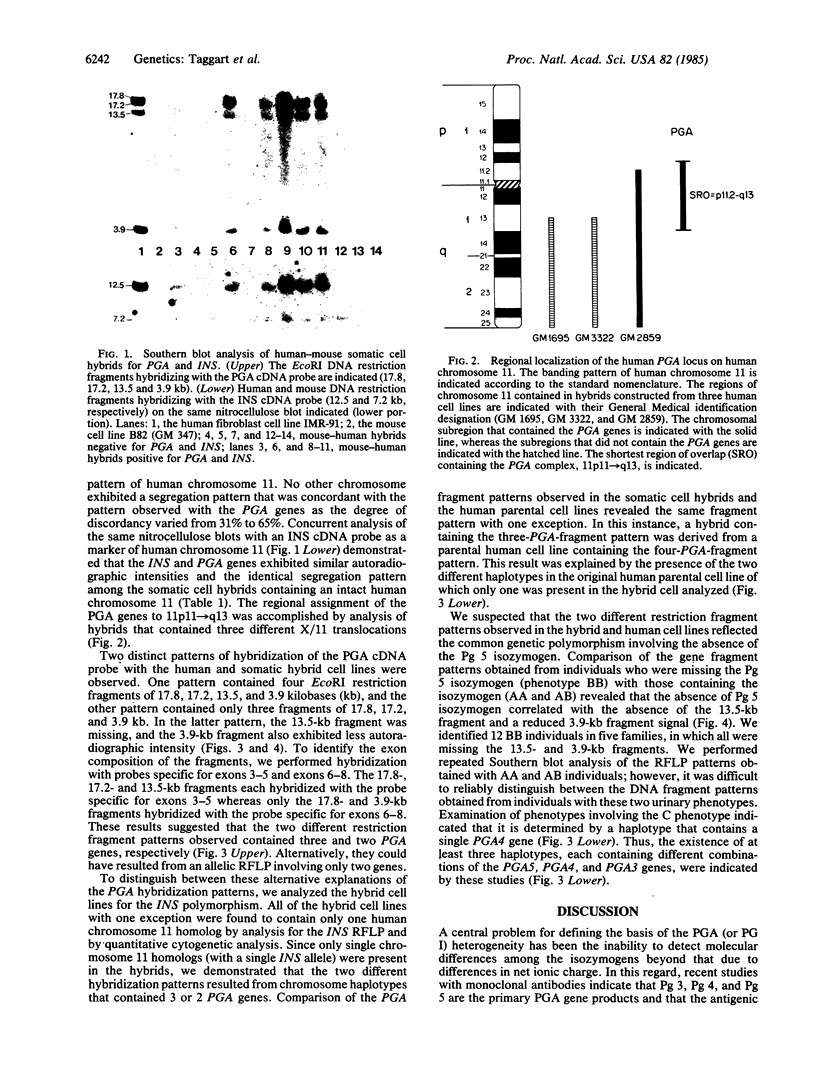
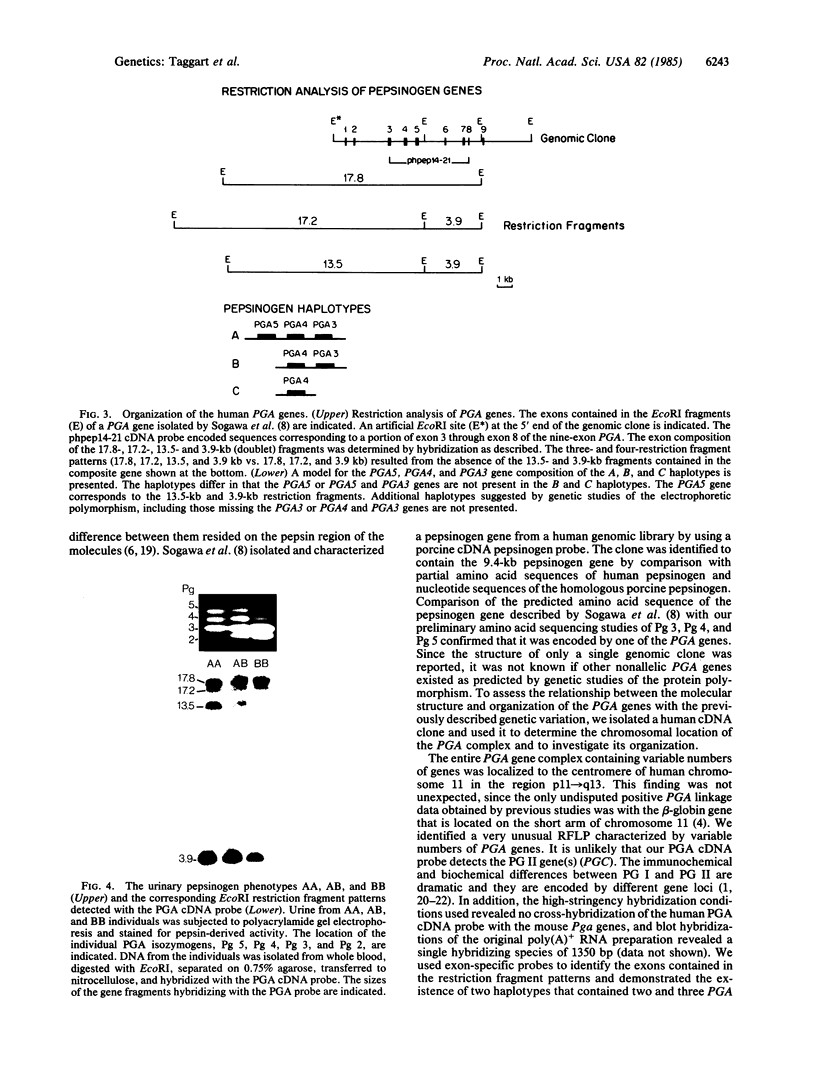
A panel of 26 mouse-human somatic cell hybrids containing different human chromosome complements was analyzed with a cloned human pepsinogen cDNA probe to determine the chromosomal location and the number of genes encoding these proteins. A complex containing variable numbers of pepsinogen genes was localized to the centromeric region of human chromosome 11 (p11----q13). Examination of somatic cell hybrids containing single copies of chromosome 11 and the corresponding human parental cell lines revealed a restriction fragment length polymorphism determined by pepsinogen haplotypes that contained two or three genes, respectively. Concurrent studies of DNA from individuals exhibiting the most common pepsinogen electrophoretic phenotypes with exon-specific probes demonstrated that the absence of one gene among the different restriction fragment patterns correlated with the absence of one specific isozymogen (Pg 5). Thus, our studies demonstrate that this genetic polymorphism involving intensity variation of individual pepsinogen isozymogens results from chromosome haplotypes that contain different numbers of genes. The regional localization of this polymorphic gene complex will facilitate detailed linkage analysis of human chromosome 11.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amara S. G., Jonas V., Rosenfeld M. G., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):240–244. doi: 10.1038/298240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Horita S., Karam J. H. A polymorphic locus near the human insulin gene is associated with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1984 Feb;33(2):176–183. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.2.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champion M. J., Brown J. A., Shows T. B. Assignment of cytoplasmic alpha-mannosidase (MANA) and confirmation of mitochondrial isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDHM) to the q11 leads to qter region of chromosome 15 in man. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):498–502. doi: 10.1159/000131007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis A., Hughes S., McConnell R. B. Gastric neoplasms and pepsinogen phenotypes. Br J Cancer. 1982 Aug;46(2):289–290. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foltmann B., Jensen A. L. Human progastricsin. Analysis of intermediates during activation into gastricsin and determination of the amino acid sequence of the propart. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov;128(1):63–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frants R. R., Pronk J. C., Pals G., Defize J., Westerveld B. D., Meuwissen S. G., Kreuning J., Eriksson A. W. Genetics of urinary pepsinogen: a new hypothesis. Hum Genet. 1984;65(4):385–390. doi: 10.1007/BF00291564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goossens M., Dozy A. M., Embury S. H., Zachariades Z., Hadjiminas M. G., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Kan Y. W. Triplicated alpha-globin loci in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):518–521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsnes L., Gedde-Dahl T., Jr Genetics of pepsinogen I. Ann Hum Genet. 1980 Jan;43(3):199–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1980.tb01554.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Grez M., Hauser H., Lindenmaier W., Schütz G. 5'-Terminal sequences of eucaryotic mRNA can be cloned with high efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2251–2266. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas T., Sparkes R. S., Hellkuhl B., Grzeschik K. H., Shapiro L. J. Expression of an X-linked gene from an inactive human X chromosome in mouse-human hybrid cells: further evidence for the noninactivation of the steroid sulfatase locus in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6759–6763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J., Brown J. A., Shows T. B. The insulin gene is located on the short arm of chromosome 11 in humans. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):267–270. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owerbach D., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J., Shows T. B. The insulin gene is located on chromosome 11 in humans. Nature. 1980 Jul 3;286(5768):82–84. doi: 10.1038/286082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Mermod J. J., Amara S. G., Swanson L. W., Sawchenko P. E., Rivier J., Vale W. W., Evans R. M. Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):129–135. doi: 10.1038/304129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I., Petersen G., Samloff I. M., McConnell R. B., Ellis A., Spence M. A., Rimoin D. L. Genetic heterogeneity of hyperpepsinogenemic I and normopepsinogenemic I duodenal ulcer disease. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Sep;91(3):372–377. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-3-372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter J. I., Sones J. Q., Samloff I. M., Richardson C. T., Gursky J. M., Walsh J. H., Rimoin D. L. Duodenal-ulcer disease associated with elevated serum pepsinogen I: an inherited autosomal dominant disorder. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 11;300(2):63–66. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901113000203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M., Liebman W. M., Glober G. A., Moore J. O., Indra D. Population studies of pepsinogen polymorphism. Am J Hum Genet. 1973 Mar;25(2):178–180. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M., Liebman W. M., Panitch N. M. Serum group I pepsinogens by radioimmunoassay in control subjects and patients with peptic ulcer. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jul;69(1):83–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M. Pepsinogens I and II: purification from gastric mucosa and radioimmunoassay in serum. Gastroenterology. 1982 Jan;82(1):26–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M., Townes P. L. Electrophoretic heterogeneity and relationships of pepsinogens in human urine, serum, and gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1970 Apr;58(4):462–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samloff I. M., Townes P. L. Pepsinogens: genetic polymorphism in man. Science. 1970 Apr 3;168(3927):144–145. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3927.144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pescador R., Urdea M. S. Use of unpurified synthetic deoxynucleotide primers for rapid dideoxynucleotide chain termination sequencing. DNA. 1984 Aug;3(4):339–343. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Mizukami Y., Ichihara Y., Takahashi K. Primary structure of human pepsinogen gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5306–5311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taggart R. T., Karn R. C., Merritt A. D., Yu P. L., Conneally P. M. Urinary pepsinogen isozymes: a highly polymorphic locus in man. Hum Genet. 1979 Nov;52(2):227–238. doi: 10.1007/BF00271578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]