Abstract
The myosin motor of the malaria parasite’s invasion machinery moves over actin fibers while it is making critical contacts with the myosin-tail interacting protein (MTIP). Previously, in a “compact” Plasmodium falciparum MTIP•MyoA complex, MTIP domains 2 (D2) and 3 (D3) make contacts with the MyoA helix, and the central helix is kinked, but in an “extended” Plasmodium knowlesi MTIP•MyoA complex only D3 interacts with the MyoA helix, and the central helix is fully extended. Here we report the crystal structure of the compact P. knowlesi MTIP•MyoA complex. It appears that, depending on the pH, P. knowlesi MTIP can adopt either the compact or the extended conformation to interact with MyoA. Only at pH values above ~7.0, can key hydrogen bonds can be formed by the imidazole group of MyoA His810 with an aspartate carboxylate from the hinge of MTIP and a lysine amino group of MyoA simultaneously.
Keywords: Malaria, Invasion, Glideosome, MTIP, X-ray structure
1. Introduction
The machinery used by malaria parasites for the invasion of host cells is currently the subject of intense investigations (for recent reviews see [1,2]), which reflects the crucial importance of this machinery in understanding the biology of the parasite. Such studies can at the same time yield possible starting points for the design of molecules which interfere with the invasion process and which might be developed into novel anti-malarials [3–7]. Key proteins such as TRAP, aldolase, actin, myosin A, MTIP, GAP40, GAP45, GAP50 and others have been identified as crucial components of the invasion machinery, also called the glideosome. We have previously been successful in determining crystal structures of several proteins of this system. These include (i) Plasmodium falciparum aldolase in complex with the TRAP tail [8]; (ii) the soluble domain of GAP50 from P. falciparum [7]; (iii) ligand-free Plasmodium knowlesi MTIP (PknoMTIP) and the complex of PknoMTIP with the MyoA tail peptide (PknoMTIP•MyoA) [9]; (iv) P. falciparum MTIP in complex with the MyoA tail peptide (PfalMTIP•MyoA) [10]; and (v) the structure of the C-terminal domain of PfalMTIP in complex with a nanobody (Khamrui et al., accompanying paper). Here we focus on MTIP from P. knowlesi. MTIP interacts with the C-terminal helix of myosin A and with GAP45. In doing so, MTIP performs a crucial role in the chain of proteins leading from TRAP interacting with a human cell surface protein to the inner membrane complex of the malaria parasite.
MTIP is a three-domain protein where the first domain (D1) is involved in interactions with GAP45 as observed in the closely related Apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii [11]. The second domain (D2) interacts with the MyoA tail helix in the compact PfalMTIP•MyoA complex but not in the extended PknoMTIP•MyoA complex [9,10]. The third domain (D3) interacts with the MyoA tail in both reported PfalMTIP•MyoA and PknoMTIP•MyoA complexes [9,10]. The D3 domain undergoes substantial conformational changes when binding to the MyoA tail helix ([9,10]; Khamrui et al., accompanying paper).
The relative position and orientation of D2 and D3 in the PknoMTIP•MyoA complex appeared to be dramatically different from that in the PfalMTIP•MyoA complex. In the PknoMTIP•MyoA complex, MTIP is extended with domains D2 and D3 far apart, connected by an essentially straight central helix while only D3 interacts with the MyoA tail helix. In contrast, the conformation of MTIP in PfalMTIP•MyoA is compact with domains D2 and D3 much closer together, connected by a kinked central helix while both domains interact with the MyoA tail helix [9,10]. We previously suggested that both the pH and the length of the construct used could be a crucial factor in determining the conformation of MTIP in complex with the MyoA tail helix. Here we provide evidence that PknoMTIP can adopt an extended as well as a compact conformation when binding the MyoA tail helix, with a higher pH the crucial factor in making the compact PfalMTIP•MyoA complex possible.
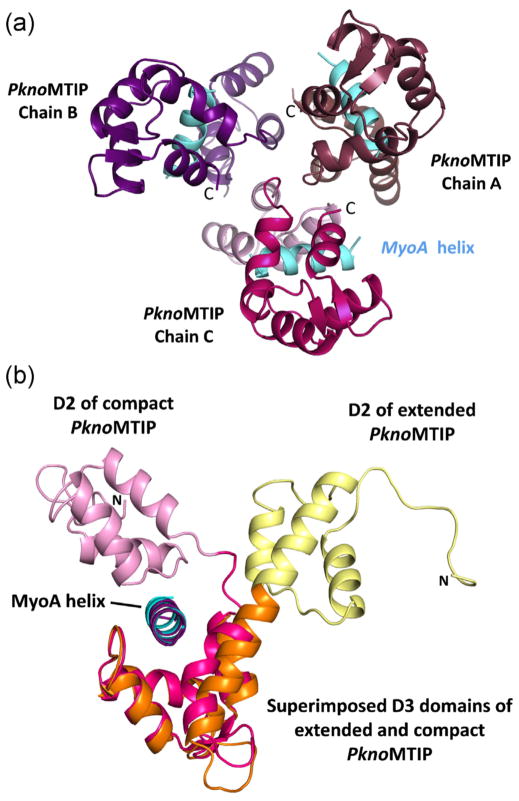
The protein preparation and structure determination of the new PknoMTIP•MyoA complex is described in Table 1, which also contains statistical parameters regarding X-ray diffraction data and model quality. Since full length MTIP resisted all crystallization attempts so far, all MTIP structures presented here and reported previously are from variants with the D1 domain deleted. The PknoMTIP variant described here contains residues K79 to C135 of D2, the hinge region V136-N141, and D3 residues M142-S205. The crystals of the PknoMTIP•MyoA complex obtained appeared to contain three copies of the PknoMTIP•MyoA complex in the asymmetric unit (Fig. 1A). The three complexes are similar in structure, with complexes A and B differing by an rmsd of 1.06 Å, complexes A and C by 0.87 Å, and complexes B and C by 0.63 Å. Since complex C has the lowest average B-factor, this complex will be used for further description and comparison. In the new PknoMTIP•MyoA structure each of the three PknoMTIP molecules surrounds the MyoA tail helix with both domains 2 and 3 engaging in contact with the MyoA helix. The solvent accessible surface area buried between PknoMTIP-D2 and MyoA is 728 Å2, and between PknoMTIP-D3 and MyoA 1451 Å2, as calculated by PISA [12].
Table 1.
Crystallographic data collection and refinement statistics.a
| Crystallization | JCSG+ #28 |
| Compound soak | 1 mM compoundb in 10% DMSO |
| Cryo-protection | 15% glycerol in JCSG+ #28 with A07 in DMSO |
| Space group | P21 21 21 |
| Unit cell (Å) | 82.560 83.403 84.316 |
| Mosaicity (degrees) | 0.67 |
| Total number of reflections | 196,472 |
| Unique reflections | 26,831 |
| Average redundancy | 7.3 (7.4) |
| Percent completeness | 99.8 (100) |
| Rmerge | 0.083 (0.845) |
| Average I/σ(I) | 23.5 (2.6) |
| Resolution (Å) | 2.3 (2.34–2.3) |
| Rwork & Rfree (%) | 22.58 & 27.94 |
| Rmsd bond lengths (Å) | 0.0085 |
| Rmsd bond angles (degrees) | 1.1838 |
| Ramachandran outliers | None |
PknoMTIP (residues 79–205) was expressed essentially as described previously [9]. The PknoMTIP•MyoA complex was obtained by mixing P. yoelii MyoA peptide (residues 803–817) at a 3:1 molar ratio with the protein at a concentration of 14 mg/mL in 20 mM HEPES buffer pH 7.5, 50 mM sodium chloride and 1 mM TCEP. Crystals were grown by sitting drop vapor equilibration using commercial screens and a Phoenix crystallization robot. The best diffracting crystals were obtained using JCSG+ screen condition #28 (0.1 M HEPES pH 7.0, 10% PEG6000) at room temperature. In addition, the crystals were soaked with a solution containing compound 2-(5-benzo[1,3]dioxol-5-yl-isoxazol-3-yl)-N-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-acetamide (LifeSciences) shown by SPR to bind weakly to PfalMTIP-D2-D3 (data not shown) to explore the possibility that the MyoA helix and the compound would bind simultaneously. (Eventually, no electron density corresponding to the compound was observed). The reservoir solution was supplemented with 10% glycerol, 1 mM compound and 10% DMSO. After flash freezing in 15% glycerol supplemented reservoir solution, data were collected at SSRL beamline 11-1 to 2.3 Å resolution, and processed by HKL2000 [13]. The structure was solved by the molecular replacement method using the program PHASER [14] and the PfalMTIP•MyoA complex [10] as a probe. The structure was refined by alternating REFMAC [15] refinement and manual corrections using Coot [16]. Coordinates and structure factors have been deposited at the Protein Data Bank with ID 4GGN.
Values in parentheses are those for the outermost resolution shell (2.34–2.3 Å).
A07 = 2-(5-benzo[1,3]dioxol-5-yl-isoxazol-3-yl)-N-pyridin-2-ylmethyl-acetamide.
Fig. 1.
The structure of P. knowlesi MTIP•MyoA. (A) The three compact PknoMTIP•MyoA complexes in the asymmetric unit. The MyoA helices are depicted in sky blue. The D2 domain for each subunit is in lighter shade compared to the corresponding D3 domain. (B) Superposition of the D3 from the new compact PknoMTIP•MyoA complex (chain C, PknoMTIP-D2 is in pink, PknoMTIP-D3 in magenta and the MoyA helix in sky blue) onto the extended conformation in the PknoMTIP•MyoA complex (D2 is in yellow, D3 is in orange and MyoA helix is in deep purple) [9]. Residues D140-L204 from domain D3 were used to superpose the PknoMTIP-D3 domains. (For interpretation of the references to color in figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of the article.)
The conformation of MTIP in the new PknoMTIP•MyoA complex differs considerably from that seen in the previous PknoMTIP•MyoA crystal structure (Fig. 1B). While both structures contain three chains per asymmetric unit, previously the three subunits adopted three distinctly different conformations, all with an extended connecting helix, despite the fact that subunits A and B contained no MyoA, and subunit C did [9]. In contrast, in the current structure, the three MTIP molecules are all essentially the same, with the connecting helix kinked, resulting, in each instance, in a compact PknoMTIP conformation. Clearly, PknoMTIP is able to adopt two very different conformations even when in complex with the MyoA tail helix.
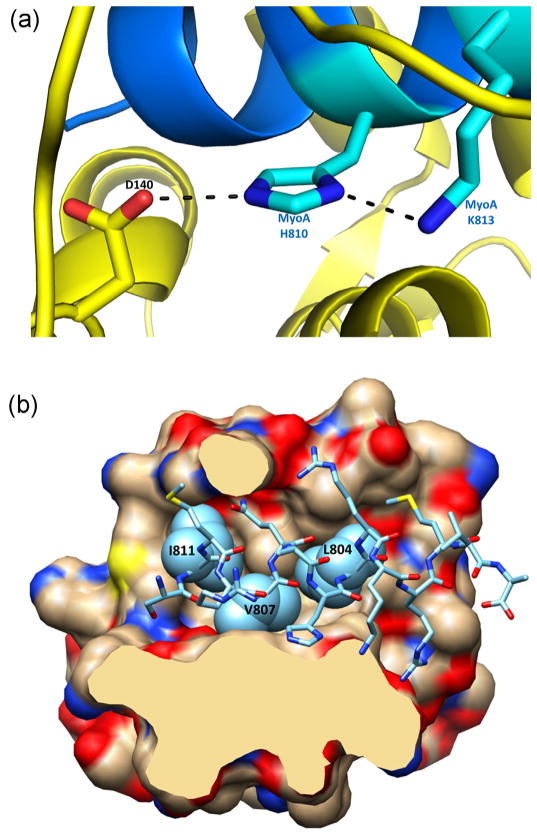
The interactions between MTIP and MyoA consists of a mainly hydrophilic interface between MyoA and PknoMTIP-D2 (Fig. 2A), an interface with D3 which is a combination of hydrophobic and hydrophilic interactions (Fig. 2B), and one PknoMTIP•MyoA interaction between MyoA-R806 and PknoMTIP-D140 from the central hinge region. In the D2•MyoA interface, the carbonyl O of A106 is interacting with the guanidinium group of R806. In this interface, the Cβ, Cγ and Cδ atoms of MyoA-K813 engage in hydrophobic interactions with the peptide units of PknoMTIP-L105 and PknoMTIP-G104. In the PknoMTIP-D3•MyoA interface, the side chains of three aliphatic residues of MyoA, L804, V807 and I811 are buried in hydrophobic pockets of D3 formed by residues L145, M148, F149, I168, L169, W172, L176, A184, L185, F199, C200 and I203 (Fig. 2B). The imidazole ring of MyoA-H810 plays a critical role as will be discussed below. Its Nδ1 is forming a 2.9 Å hydrogen bond with the side chain amino group of MyoA-K813, and its Nε2 is engaged in a hydrogen bond of equal length with the carboxylate of PknoMTIP-D140 of the hinge region (Fig. 2A).
Fig. 2.
Interactions of P. knowlesi MTIP with MyoA. (A) Key contacts of MyoA-H810 with MyoA-K813 and PknoMTIP-D140. At lower pH values, when the His810 imidazole moiety becomes protonated, these interactions cannot be maintained, leading to an extended conformation of MTIP at lower pH values. See also discussion in the text. (B) Hydrophobic contacts between the compact conformation of PknoMTIP and the MyoA tail helix. Cross-section of the MTIP-MyoA interface showing how the aliphatic side chains of MyoA L804, V807 and I811 (light blue spheres) reside in hydrophobic pockets of D3 of PknoMTIP. (For interpretation of the references to color in figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of the article.)
When comparing the compact and the extended PknoMTIP conformations, it appears that MTIP-D2 rotates considerably (117°, based on the superposition of α6-loop-α7 of D3 from subunits C in both crystal structures) with respect to MTIP-D3. Residues V136-N141 in the central part of the connecting helix adopt very different conformations in these two complexes (Fig. 1B). The conformations of MTIP-D2 in the two complexes are very similar with an rmsd of 0.45 Å. The MTIP-D3 domains in the two structures differ more, however, and superimpose with an rmsd of 1.06 Å as explained further in the accompanying paper (Khamrui et al., accompanying paper). It appears therefore that, upon forming a complex with MyoA, PknoMTIP-D3 adopts a conformation with a wide groove to accommodate the MyoA helix. Another change is a major bending of the connecting helix, turning residues V136-N141 into a non-helical conformation, thereby allowing D2, which remains essentially unaltered, to contact the MyoA helix from “above”.
The conformation of P. falciparum MTIP in the previously reported PfalMTIP•MyoA complex appeared to be compact with a kinked connecting helix and both PfalMTIP-D2 and PfalMTIP-D3 interacting with the MyoA tail helix [10]. The rmsd of MTIP in the PknoMTIP•MyoA and PfalMTIP•MyoA complexes after superposition is 1.06 Å for 121 amino acids with a sequence identity of 80%, with the individual domains D2 and D3 differing by 0.30 and 0.32 Å, respectively. The buried solvent accessible surface areas of D3 in the PfalMTIP•MyoA and PknoMTIP•MyoA complexes with the MyoA helix are remarkably similar with 2139 and 2063 Å2, of which 1478 and 1451 Å2 buried in the interface between MTIP-D3 and the MyoA helix, respectively. The side chains of PknoMTIP and PfalMTIP contacting MyoA are identical in the two complexes, except for the C-terminal S204 which is a glutamine in PfalMTIP.
Previously it was suggested [10] that two factors might play a role determining whether the MTIP•MyoA complex adopts an extended or a compact conformation. One putative factor was a lower pH in the crystals with the extended PknoMTIP•MyoA structure, and a second potential factor the slightly longer version, starting 20 residues closer to the N-terminus of the full length protein, of P. falciparum MTIP used for the PfalMTIP•MyoA studies compared to the PknoMTIP variant used for the PknoMTIP•MyoA structure. In the current compact PknoMTIP structure we used precisely the same variant of PknoMTIP as in the previous study which yielded the extended structures [9]. Hence, the length difference between the P. falciparum and P. knowlesi MTIP variants used is not the cause of the difference between compact and extended conformations.
The current compact structure was solved from crystals grown out of a solution with pH 7.0, while the previous structure yielding the extended PknoMTIP conformation was obtained from crystals grown at pH 5.3. The key interface residue which differs in protonation state at these pH values is MyoA-H810. In the compact PknoMTIP conformation (Fig. 2A), the imidazole of this residue interacts with the Nε of MyoA-K813 and with an Oδ of PknoMTIP-D140. The latter interaction requires a proton on one imidazole nitrogen, but, in order to form a hydrogen bond with the Nε of MyoA-K813, the second ring nitrogen of MyoA-H810 needs to be unprotonated. At the pH 7.0 in the current PknoMTIP•MyoA structure, the imidazole is uncharged thereby allowing favorable interactions with the negatively charged Asp carboxylate oxygen and the positively charged Lys side chain nitrogen to take place simultaneously (Fig. 2A). But at the lower pH 5.3 of the crystals used for the previous PknoMTIP•MyoA structure determination, the imidazole ring of MyoA-H810 is charged and repulsion with the Lys side chain nitrogen prevents the tight interactions in the compact MTIP•MyoA complex, resulting in an extended MTIP conformation.
2. Concluding remarks
The new crystal structure of the PknoMTIP•MyoA complex shows, in triplicate (Fig. 1A), that PknoMTIP is able to adopt a compact conformation where PknoMTIP-D2 and PknoMTIP-D3 surround the MyoA tail helix, different from the extended PknoMTIP conformations observed before. The four conformations of PknoMTIP now available indicate that PknoMTIP is a highly flexible protein able to adopt different extended conformations in the absence of the MyoA tail (i.e. subunits A and B of [9]), an extended conformation in complex with the MyoA tail (subunit C of [9]), and a compact conformation in complex with the MyoA tail (Fig. 1). In addition, the third domain can adopt different conformations in the absence and presence of the MyoA tail helix ([9]; Khamrui et al., accompanying paper). This spectrum of conformations indicates a considerable mobility of liganded and ligand-free MTIP in solution. The importance of this flexibility under physiological conditions still needs to be established with further investigations.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jonathan Kay for maintaining the computer environment at the Biomolecular Structure Center. We are particularly grateful to the staff at SSRL beamline 11-1 for their help and assistance during synchrotron data, to Jürgen Bosch for important contributions to earlier stages of the project, and to Erkang Fan and Christophe Verlinde for stimulating discussions. This project was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant AI48226 (to L.W.B.).
Abbreviations
- D2
domain 2 of MTIP
- D3
domain 3 of MTIP
- GAP
glideosome-associated protein
- MTIP
myosin-tail interacting protein
- PknoMTIP
Plasmodium knowlesi MTIP
- PfalMTIP
Plasmodium falciparum MTIP
- rmsd
root mean square deviation
- TRAP
thrombospondin-related anonymous protein
References
- 1.Montagna GN, Matuschewski K, Buscaglia CA. Plasmodium sporozoite motility: an update. Frontiers in Bioscience – Landmark. 2012;17:726–44. doi: 10.2741/3954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Besteiro S, Dubremetz JF, Lebrun M. The moving junction of apicomplexan parasites: a key structure for invasion. Cellular Microbiology. 2011;13:797–805. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2011.01597.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Carey KL, Westwood NJ, Mitchison TJ, Ward GE. A small-molecule approach to studying invasive mechanisms of Toxoplasma gondii. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2004;101:7433–8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0307769101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Heaslip AT, Leung JM, Carey KL, Catti F, Warshaw DM, Westwood NJ, et al. A small-molecule inhibitor of T. gondii motility induces the posttranslational modification of myosin light chain-1 and inhibits myosin motor activity. PLoS Pathogens. 2010:6. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kortagere S, Welsh WJ, Morrisey JM, Daly T, Ejigiri I, Sinnis P, et al. Structure-based design of novel small-molecule inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2010;50:840–9. doi: 10.1021/ci100039k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Thomas JC, Green JL, Howson RI, Simpson P, Moss DK, Martin SR, et al. Interaction and dynamics of the Plasmodium falciparum MTIP–MyoA complex, a key component of the invasion motor in the malaria parasite. Molecular BioSystems. 2010;6:494–8. doi: 10.1039/b922093c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bosch J, Paige MH, Vaidya AB, Bergman LW, Hol WG. Crystal structure of GAP50, the anchor of the invasion machinery in the inner membrane complex of Plasmodium falciparum. Journal of Structural Biology. 2012;178:61–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.02.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bosch J, Buscaglia CA, Krumm B, Ingason BP, Lucas R, Roach C, et al. Aldolase provides an unusual binding site for thrombospondin-related anonymous protein in the invasion machinery of the malaria parasite. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007;104:7015–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605301104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bosch J, Turley S, Daly TM, Bogh SM, Villasmil ML, Roach C, et al. Structure of the MTIP–MyoA complex, a key component of the malaria parasite invasion motor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2006;103:4852–7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510907103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bosch J, Turley S, Roach CM, Daly TM, Bergman LW, Hol WG. The closed MTIP-myosin A-tail complex from the malaria parasite invasion machinery. Journal of Molecular Biology. 2007;372:77–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.06.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Frenal K, Polonais V, Marq JB, Stratmann R, Limenitakis J, Soldati-Favre D. Functional dissection of the apicomplexan glideosome molecular architecture. Cell Host and Microbe. 2010;8:343–57. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2010.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Krissinel E, Henrick K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. Journal of Molecular Biology. 2007;372:774–97. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.05.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Otwinowski Z, Minor W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. In: Carter C, Sweet R, editors. Methods in enzymology. San Diego/London/Boston/New York/Sydney/Tokyo/Toronto: Academic Press; 1997. pp. 307–26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.McCoy AJ. Solving structures of protein complexes by molecular replacement with Phaser. Acta Crystallographica Section D – Biological Crystallography. 2007;63:32–41. doi: 10.1107/S0907444906045975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Murshudov GN, Vagin AA, Dodson EJ. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallographica Section D –Biological Crystallography. 1997;53:240–55. doi: 10.1107/S0907444996012255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Emsley P, Cowtan K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallographica Section D – Biological Crystallography. 2004;60:2126–32. doi: 10.1107/S0907444904019158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]