Abstract
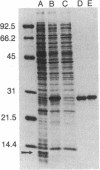
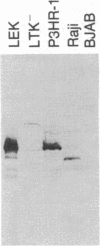
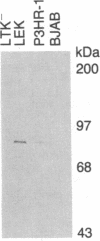
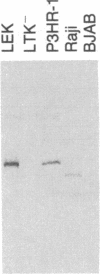
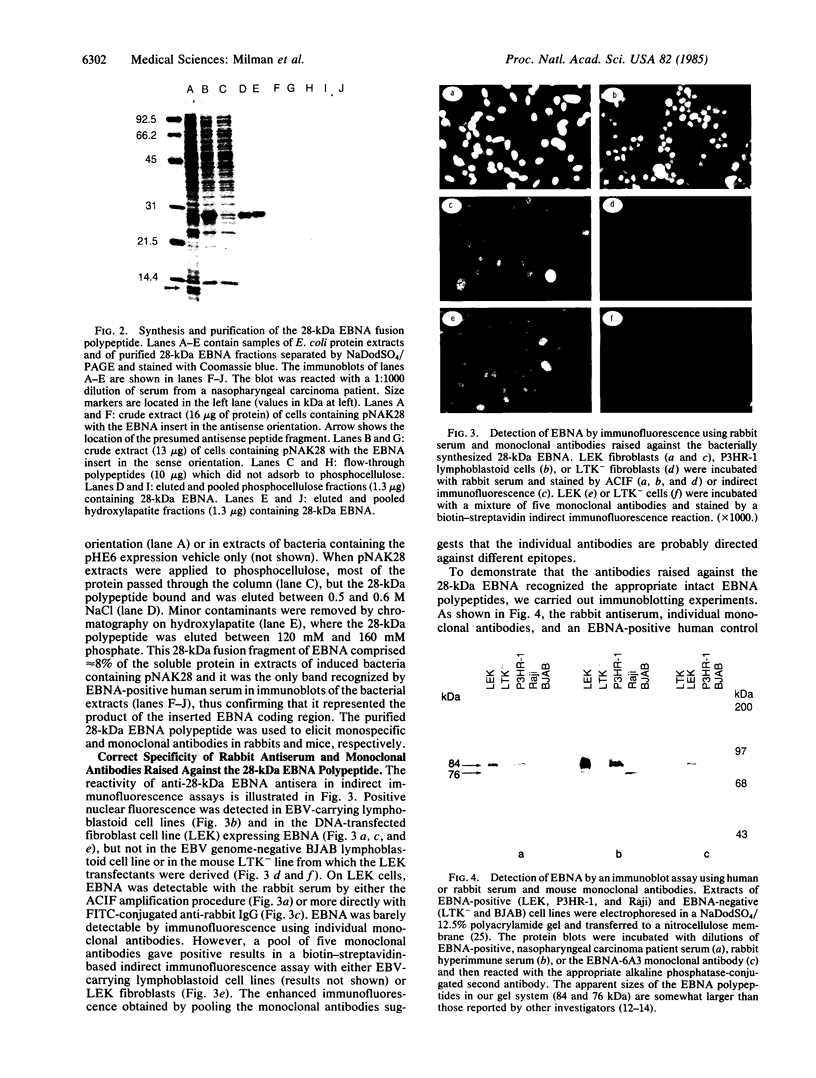
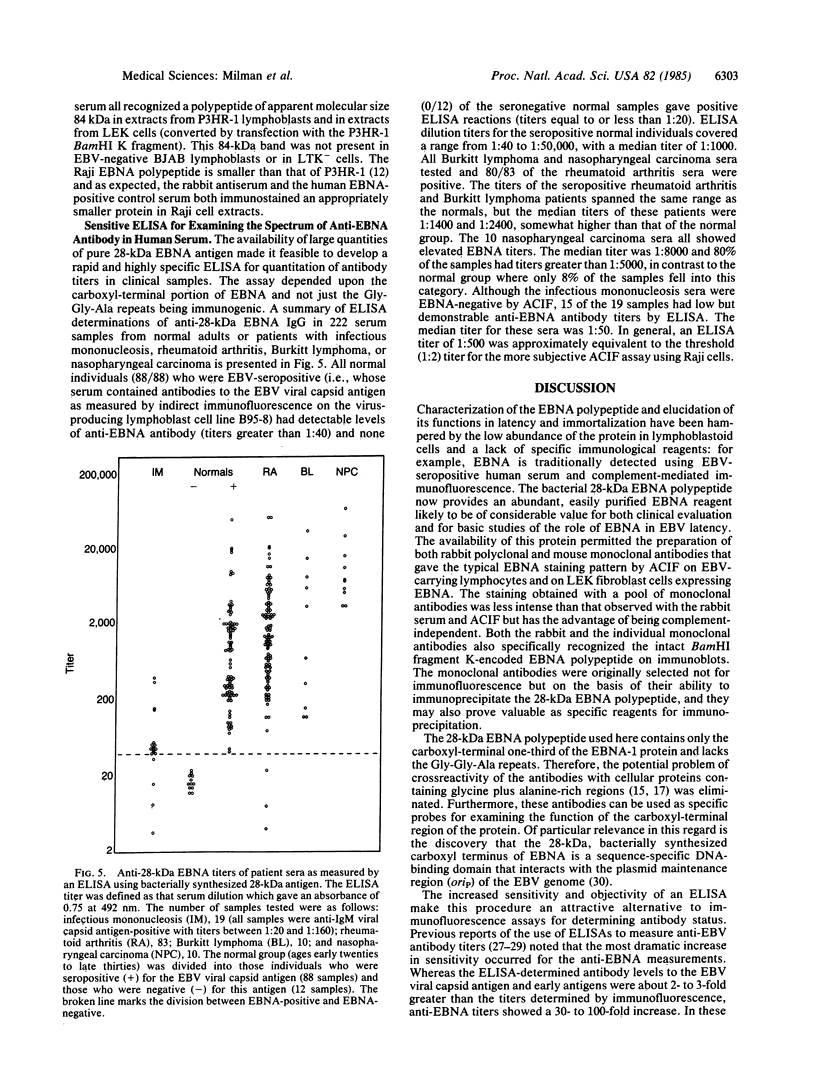
The carboxyl-terminal one-third of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) encoded by the BamHI restriction fragment K was synthesized in Escherichia coli by use of a high-expression plasmid. The resultant 28-kDa EBNA fusion polypeptide, comprising 5-10% of the total soluble bacterial protein, was purified to apparent homogeneity by phosphocellulose and hydroxylapatite column chromatography. Both rabbit monospecific antibodies and mouse monoclonal antibodies against 28-kDa EBNA gave nuclear immunofluorescence staining on Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected lymphoblastoid cell lines and recognized the appropriate intact EBNA polypeptide bands on immunoblots. An ELISA with the purified 28-kDa EBNA as antigen was used to quantitate anti-EBNA antibody in human serum samples. The ELISA method was approximately 100-fold more sensitive than the classical anticomplement immunofluorescence assay. Anti-EBNA antibody was detected in sera from 100% of normal individuals who were seropositive for the viral capsid antigen, and low anti-EBNA titers were detected in serum from most patients with acute infectious mononucleosis. The assay gave the expected pattern of titers in sera from patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Burkitt lymphoma, or nasopharyngeal carcinoma, thus confirming the validity of this purified reagent for assessing EBNA antibody status. Approximately 10% of normal individuals and rheumatoid arthritis patients had anti-EBNA titers as high as those seen in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. In these high-titer individuals, greater than 1% of the total IgG are antibodies that recognize 28-kDa EBNA, which indicates that the carboxyl-terminal domain of EBNA is highly immunogenic.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillner J., Sternås L., Kallin B., Alexander H., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Jörnvall H., Klein G., Lerner R. Antibodies against a synthetic peptide identify the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4652–4656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D. K., Robert M. F., Shedd D., Summers W. P., Robinson J. E., Wolak J., Stefano J. E., Miller G. Identification of Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen polypeptide in mouse and monkey cells after gene transfer with a cloned 2.9-kilobase-pair subfragment of the genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):43–47. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan E. A., Summers W. P., Dowling S., Shedd D., Gradoville L., Miller G. Two Epstein-Barr viral nuclear neoantigens distinguished by gene transfer, serology, and chromosome binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7650–7653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Henderson A., Kieff E. Repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA is related to cell DNA sequences interspersed on human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5916–5920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat sequence in Epstein-Barr virus DNA is transcribed in latent and productive infections. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):311–320. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.311-320.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Ho J. H., Henle G., Chau J. C., Kwan H. C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: significance of changes in Epstein-Barr virus-related antibody patterns following therapy. Int J Cancer. 1977 Nov 15;20(5):663–672. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Heller M., van Santen V., Kieff E. Simple repeat array in Epstein-Barr virus DNA encodes part of the Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1396–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.6304878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy K., Kieff E. One of two Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigens contains a glycine-alanine copolymer domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho H. C., Ng M. H., Kwan H. C. Factors affecting serum IgA antibody to Epstein-Barr viral capsid antigens in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 1978 Mar;37(3):356–362. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1978.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Witmer T. J., Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. Detection of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus antigens by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Infect Dis. 1982 Dec;146(6):734–740. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.6.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes E. N., August J. T. Characterization of plasma membrane proteins identified by monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):664–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Chase R. C., Pearson G. R. A sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) against the major EBV-associated antigens. I. Correlation between ELISA and immunofluorescence titers using purified antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 24;67(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Kreofsky T., Pearson G. R., Hennessy K., Kieff E. Identification and characterization of a cellular protein that cross-reacts with the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):833–838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.833-838.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Weiland L. H., Neel H. B., 3rd, Taylor W., Earle J., Mulroney S. E., Goepfert H., Lanier A., Talvot M. L., Pilch B. Application of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) serology to the diagnosis of North American nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 1983 Jan 15;51(2):260–268. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830115)51:2<260::aid-cncr2820510216>3.0.co;2-#. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert M. F., Shedd D., Weigel R. J., Fischer D. K., Miller G. Expression in COS-1 cells of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen from a complete gene and a deleted gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):822–831. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.822-831.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternås L., Luka J., Kallin B., Rosén A., Henle W., Henle G., Klein G. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of Epstein-Barr virus-induced antigens and antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Oct 14;63(2):171–185. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90422-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strnad B. C., Schuster T. C., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. Identification of an Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen by fluoroimmunoelectrophoresis and radioimmunoelectrophoresis. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):996–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.996-1004.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers W. P., Grogan E. A., Shedd D., Robert M., Liu C. R., Miller G. Stable expression in mouse cells of nuclear neoantigen after transfer of a 3.4-megadalton cloned fragment of Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman A. S., Haeusslein E., Milman G. Purification and characterization of herpes simplex virus (type 1) thymidine kinase produced in Escherichia coli by a high efficiency expression plasmid utilizing a lambda PL promoter and cI857 temperature-sensitive repressor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11571–11575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeng Y., Zhong J. M., Li L. Y., Wang P. Z., Tang H., Ma Y. R., Zhu J. S., Pan W. J., Liu Y. X., Wei Z. N. Follow-up studies on Epstein-Barr virus IgA/VCA antibody-positive persons in Zangwu County, China. Intervirology. 1983;20(4):190–194. doi: 10.1159/000149391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]