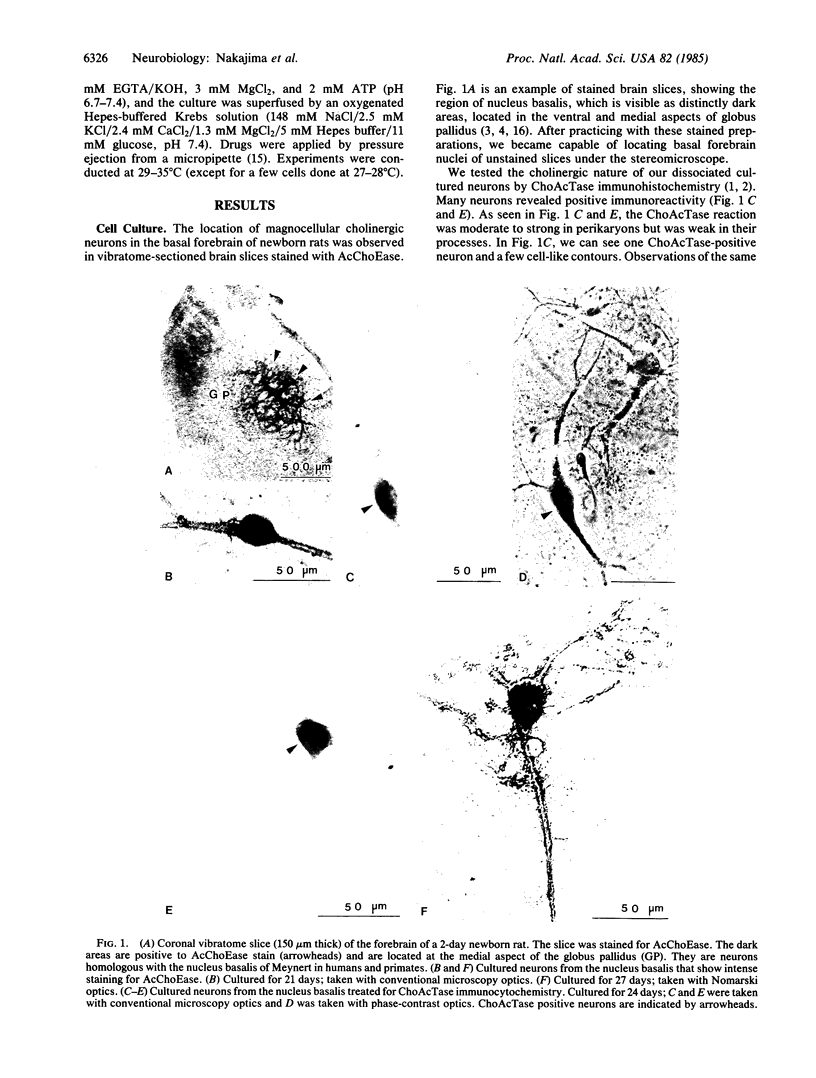
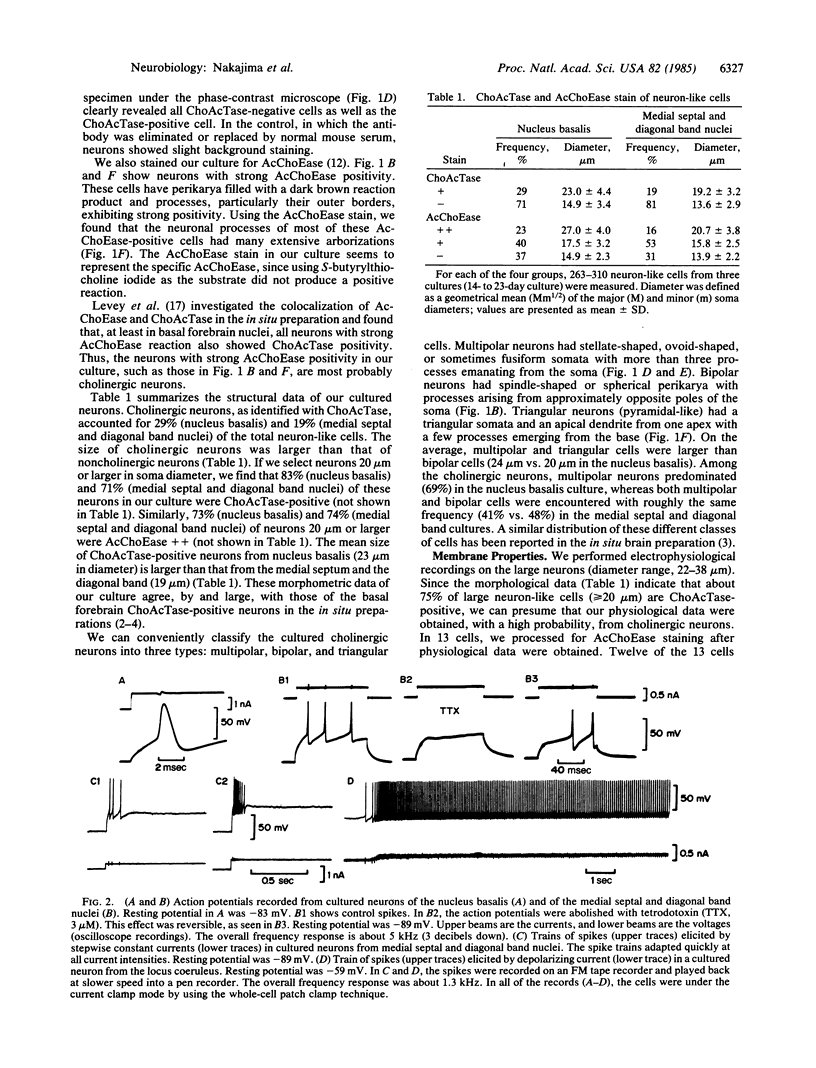
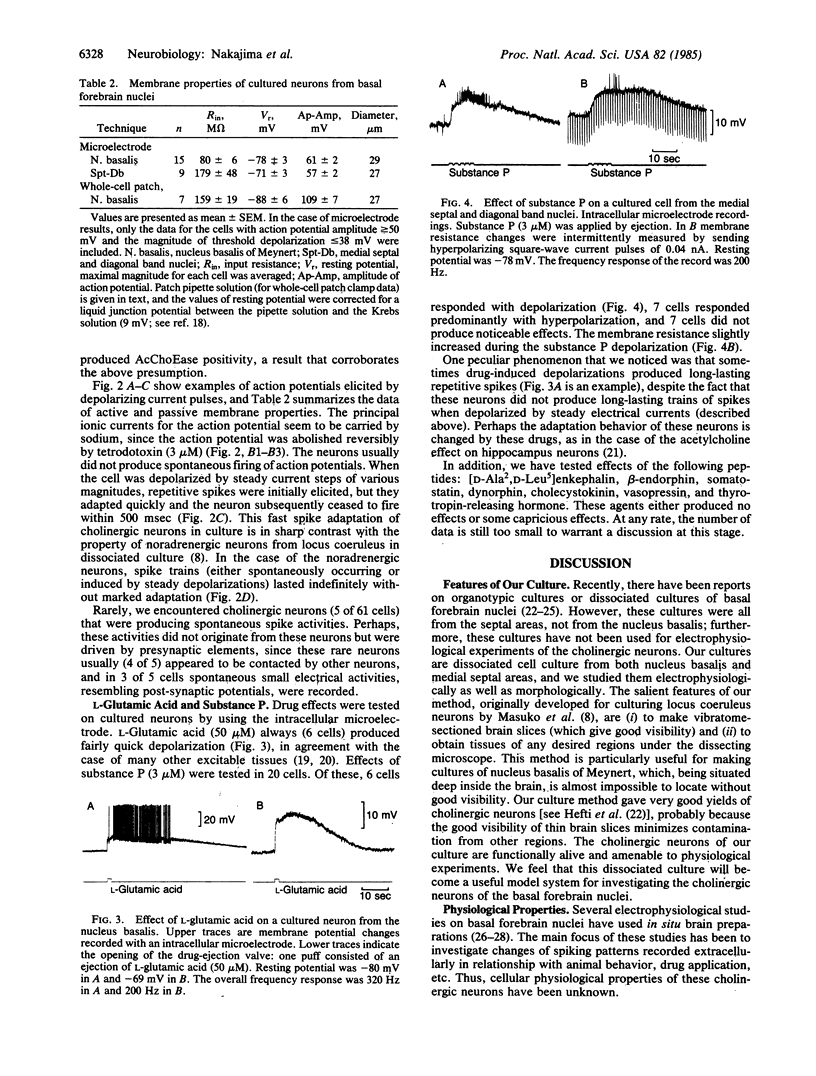
Abstract
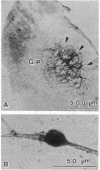
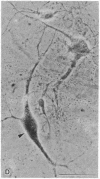
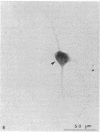
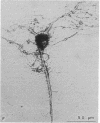
Degeneration of cholinergic neurons from the basal forebrain nuclei is suspected to be the cause of Alzheimer disease. We have developed dissociated cultures of cholinergic neurons from these nuclei (the nucleus basalis of Meynert, the medial septal nucleus, and the diagonal band nuclei). Brain slices of the forebrains were made by a vibratome, and the basal forebrain nuclei were dissected out, dissociated, and cultured. Choline acetyltransferase immunocytochemistry and acetylcholinesterase cytochemistry revealed large cholinergic cells (average diameter, 20-25 micron) in these cultures. About 75% of large neurons (20 micron or larger in diameter) were cholinergic. Electrophysiological experiments were performed on these large neurons. The neurons usually did not show spontaneous firing, but steady depolarizations produced trains of action potentials, which adapted quickly. The neurons responded with depolarization to the application of L-glutamic acid. Substance P produced depolarization (sometimes hyperpolarization), and during the depolarization membrane resistance was increased.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Brown D. A., Jones S. W. Substance P inhibits the M-current in bullfrog sympathetic neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):330–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akasu T., Nishimura T., Koketsu K. Substance P inhibits the action potentials in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Oct 31;41(1-2):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90240-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURTIS D. R., PHILLIS J. W., WATKINS J. C. The chemical excitation of spinal neurones by certain acidic amino acids. J Physiol. 1960 Mar;150:656–682. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W., Fischbach G. D. GABA conductance of chick spinal cord and dorsal root ganglion neurons in cell culture. J Neurophysiol. 1981 Apr;45(4):605–620. doi: 10.1152/jn.1981.45.4.605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Nicoll R. A. Characterization of a slow cholinergic post-synaptic potential recorded in vitro from rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:173–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Price D. L., DeLong M. R. Alzheimer's disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1184–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.6338589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demain A. L. New route to antibiotic creation. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):577–578. doi: 10.1038/314577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dichter M. A. Rat cortical neurons in cell culture: culture methods, cell morphology, electrophysiology, and synapse formation. Brain Res. 1978 Jun 30;149(2):279–293. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90476-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima Y., Hagiwara S. Currents carried by monovalent cations through calcium channels in mouse neoplastic B lymphocytes. J Physiol. 1985 Jan;358:255–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houser C. R., Crawford G. D., Barber R. P., Salvaterra P. M., Vaughn J. E. Organization and morphological characteristics of cholinergic neurons: an immunocytochemical study with a monoclonal antibody to choline acetyltransferase. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 25;266(1):97–119. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. J., ROOTS L. A "DIRECT-COLORING" THIOCHOLINE METHOD FOR CHOLINESTERASES. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Mar;12:219–221. doi: 10.1177/12.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama Y., North R. A., Williams J. T. The action of substance P on neurons of the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Nov 30;206(1163):191–208. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller F., Rimvall K., Waser P. G. Choline acetyltransferase in organotypic cultures of rat septum and hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Dec 11;42(3):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90274-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamour Y., Dutar P., Jobert A. Septo-hippocampal and other medial septum-diagonal band neurons: electrophysiological and pharmacological properties. Brain Res. 1984 Sep 10;309(2):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90588-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey A. I., Aoki M., Fitch F. W., Wainer B. H. The production of monoclonal antibodies reactive with bovine choline acetyltransferase. Brain Res. 1981 Aug 10;218(1-2):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91316-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levey A. I., Wainer B. H., Mufson E. J., Mesulam M. M. Co-localization of acetylcholinesterase and choline acetyltransferase in the rat cerebrum. Neuroscience. 1983 May;9(1):9–22. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesulam M. M., Mufson E. J., Wainer B. H., Levey A. I. Central cholinergic pathways in the rat: an overview based on an alternative nomenclature (Ch1-Ch6). Neuroscience. 1983 Dec;10(4):1185–1201. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoll R. A., Schenker C., Leeman S. E. Substance P as a transmitter candidate. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1980;3:227–268. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.03.030180.001303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L. M., MacDonald R. L. Substance P decreases a potassium conductance of spinal cord neurons in cell culture. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 15;214(2):416–423. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)91205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Lague P. H., Potter D. D., Furshpan E. J. Studies on rat sympathetic neurons developing in cell culture. I. Growth characteristics and electrophysiological properties. Dev Biol. 1978 Dec;67(2):384–403. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90208-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojika K., Appel S. H. Neurotrophic effects of hippocampal extracts on medial septal nucleus in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2567–2571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Takahashi T. Putative peptide neurotransmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1977;17:425–439. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.17.040177.002233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal M. Brain stem afferents to the rat medial septum. J Physiol. 1976 Oct;261(3):617–631. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shults C. W., Quirion R., Chronwall B., Chase T. N., O'Donohue T. L. A comparison of the anatomical distribution of substance P and substance P receptors in the rat central nervous system. Peptides. 1984 Nov-Dec;5(6):1097–1128. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(84)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R., Nakajima Y., Yamaguchi K. Substance P raises neuronal membrane excitability by reducing inward rectification. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):498–501. doi: 10.1038/315498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A., TAKEUCHI N. THE EFFECT ON CRAYFISH MUSCLE OF IONTOPHORETICALLY APPLIED GLUTAMATE. J Physiol. 1964 Mar;170:296–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D., Katzman R. Senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol. 1983 Nov;14(5):497–506. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto M., Steinbusch H. W., Jessell T. M. Differentiated properties of identified serotonin neurons in dissociated cultures of embryonic rat brain stem. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):142–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]