Abstract
Understanding the survival of fecal indicator bacteria (FIB) and microbial source-tracking (MST) markers is critical to developing pathogen fate and transport models. Although pathogen survival in water microcosms and manure-amended soils is well documented, little is known about their survival in intact cow pats deposited on pastures. We conducted a study to determine decay rates of fecal indicator bacteria (Escherichia coli and enterococci) and bovine-associated MST markers (CowM3, Rum-2-bac, and GenBac) in 18 freshly deposited cattle feces from three farms in northern Georgia. Samples were randomly assigned to shaded or unshaded treatment in order to determine the effects of sunlight, moisture, and temperature on decay rates. A general linear model (GLM) framework was used to determine decay rates. Shading significantly decreased the decay rate of the E. coli population (P < 0.0001), with a rate of −0.176 day−1 for the shaded treatment and −0.297 day−1 for the unshaded treatment. Shading had no significant effect on decay rates of enterococci, CowM3, Rum-2-bac, and GenBac (P > 0.05). In addition, E. coli populations showed a significant growth rate (0.881 day−1) in the unshaded samples during the first 5 days after deposition. UV-B was the most important parameter explaining the decay rate of E. coli populations. A comparison of the decay behaviors among all markers indicated that enterococcus concentrations exhibit a better correlation with the MST markers than E. coli concentrations. Our results indicate that bovine-associated MST markers can survive in cow pats for at least 1 month after excretion, and although their decay dynamic differs from the decay dynamic of E. coli populations, they seem to be reliable markers to use in combination with enterococci to monitor fecal pollution from pasture lands.
INTRODUCTION
Elevated levels of fecal indicator bacteria (FIB) remain the most common cause of impairment in streams and rivers in the United States, with agriculture as the primary source of contamination (1). The federal Clean Water Act defines impaired surface waters as rivers, lakes, or streams that do not meet one or more water quality standards and therefore categorizes these water resources as too polluted for their intended uses. FIB are recommended for water monitoring because of their correlation with gastrointestinal illness (2–4), but they cannot indicate the origin of fecal pollution. This shortcoming is one of the challenges present when attempting to protect and remediate water sources that are impaired due to fecal contamination (5). Emerging library- and culture-independent microbial source-tracking (MST) methods that target host-associated markers and offer information about the sources of fecal contamination are now used widely by state and federal agencies monitoring water resources (6–9). Information can be used for total maximum daily load (TMDL) development and implementation of remediation practices.
Ideally, MST markers and FIB will have similar fates and transport behaviors governed by their concentrations in polluting matrices, extraintestinal survival, growth rates after excretion, and mobility in the environment (10, 11). Of these factors, survival of FIB and MST markers plays an integral role in determining their fate and transport in the environment, since survival can strongly influence prevalence in both fecal sources and water environments. The ability to estimate concentrations of bacteria in feces deposited on a given area of pasture over time will benefit management and mitigation of animal pollution of water, as well as zoonotic pathogen risk assessment (12).
Decay kinetics of FIB and MST markers in waters and manure-amended soils are well documented (13–17), but little is known about the survival of MST markers in bovine feces deposited on pastureland. Many previously published decay rates of FIB, pathogens, and MST markers from bovine feces focused primarily on studies of manure and slurries applied to soil (11, 13, 14). To the best of our knowledge, no study has investigated their decay patterns in naturally occurring fecal deposits. Procedures used in the manure, slurry, and water microcosm studies may enhance microbial inactivation, since fecal materials are subjected to elevated composting temperature, antagonistic microbiota, pH changes, and desiccation associated with soil mixing (12). Mixing of manure also increases aeration, which could decrease survival of the obligately anaerobic Bacteroidales cells, the most commonly used MST markers due to their abundance in feces and their superior host specificity. Studies on the survival of FIB and MST markers in freshly deposited cow pats are warranted, therefore, since fecal pollution occurs not only by runoff from applied manure but also from deposited feces.
Contradictory results for factors affecting the survival of FIB and MST markers in bovine manure or slurry and water microcosms have been reported. In water microcosms, sunlight has been reported to decrease the persistence of human-specific MST markers (15) and ruminant-associated markers (16, 17). In contrast, Sokolova et al. (18) reported no significant effect of light on the decay of FIB and MST markers. Temperature has also been shown to correlate strongly with inactivation of Bacteroidales spp. in water microcosms (19–23). Positive correlations between moisture and FIB concentrations have been documented in several studies (12, 24–27), but an overall negative relationship between moisture and Escherichia coli (14) has been reported.
In our study, the persistence of bovine-associated MST markers, culturable FIB, and their genomes in freshly deposited bovine feces was investigated. Factors that can affect their survival and persistence, such as UV, moisture, and temperature, were also studied under field conditions. With the objective of establishing relationships between each type of measurement under the same environmental conditions, we compared the decay behaviors of MST markers and FIB. The selected quantitative PCR (qPCR) markers used here were the general Bacteroidales marker GenBac (28); a cattle-associated marker, CowM3 (29); and a ruminant-specific marker, Rum-2-bac (30).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Manure collection and study site.
Twenty freshly excreted bovine fecal samples were collected from three farms in northern Georgia during the summer of 2012. One farm practices organic beef cattle farming, and the others are traditional beef-producing commercial farms, and the farms handle 20, 50, and >150 heads of cattle, respectively. Cow pats were collected as whole as possible, using 8-in.-diameter, 24-gauge round-end stove caps (Grainger Inc., Lake Forest, IL) and a 24-in. by 12-in. piece of sheet metal-gauge steel (Stanley Hardware, New Britain, CT). Following excretion, the round stove-cap end was placed carefully on the cow pat to avoid disturbing its original structure as much as possible. The metal sheet was slid under the pat, after which the stove cap containing the feces was flipped and covered with a clear plastic bag. Samples were immediately transported to the study site on ice and in the dark.
The study was conducted on a field site located at the U.S. EPA Ecosystems Research Division in Athens, GA. Three cow pats from each farm were randomly assigned to shaded or unshaded treatments, for a total of nine replicate pats per treatment. Cow pat weights ranged from 0.6 to 1.5 kg. Plot covers (2.4 m by 1.7 m) were constructed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) frames lined with clear acetate films (80% UV transmission; Grafix Plastics, Cleveland, OH) and were placed on top of each treatment set to protect the cow pats from natural rain events. The shaded treatment was created by placing a solid-color tarp (100% UV block) over the clear acetate film structure; the unshaded treatment was covered only by the clear acetate film. Two additional cow pats—one for each treatment—were fitted with a 12-bit smart temperature sensor connected to an onset Hobo U30 data logger (Onset Computer Inc., Bourne, MA). A UV sensor (Satlantic model OCR-504) measuring four different wavelengths (305, 325, 340, and 380 nm) was installed underneath both treatment plot covers and connected to a Stor-X data logger (Satlantic, Halifax, Canada). One additional UV sensor was installed away from the plot covers to monitor full sunlight.
Sample collection.
Fecal samples from each cow pat were collected on days 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 15, 22, 29, 43, and 57, between 9:00 and 10:00 a.m.; they were collected from both the outer crust and the moist interior of the cow pat to obtain representative samples of the entire cow pat. Three or four cores were obtained at various depths from each cow pat, using a sterile V-shaped spatula. Samples were transported to the laboratory within 5 min of collection, and the cores were homogenized in sterile 50-ml centrifuge tubes, with the aid of a sterile spatula. The moisture content (MC) of each homogenous fecal sample was determined gravimetrically by drying 2 to 5 g at 105°C for 24 h. All microbial counts were expressed per gram of dry weight.
Microbiological analysis.
Fecal material was suspended in a phosphate buffer solution at a 1:10 ratio. Prior to enumeration, all samples were dispersed by hand shaking and vortexing for 10 min; serial dilutions were performed with sterilized Nanopure water. The concentrations of E. coli and enterococci in cow pat samples were enumerated using a Colilert Quanti Tray system (Idexx Lab Inc., Westbrook, ME) according to the manufacturer's instructions and membrane filtration (U.S. EPA method 1600), respectively.
DNA extraction.
One hundred milligrams of each homogenized cow pat sample was transferred to powerBead tubes in triplicate (MoBio Laboratories, Carlsbad, CA) and stored at −80°C until extraction, which occurred within 2 weeks of sampling. DNA was extracted using a MoBio Power-Soil DNA isolation kit, with the following modifications to the manufacturer's instructions: (i) bead beating was conducted at 6.5 m s−1 for 45 s, using a Fastprep-24 instrument (MP Biomedicals, Solon, Ohio); and (ii) to make the final quantification of the marker more accurate, only half of the bead solution and C1 mixture (405 μl) was transferred after the first step, because it was difficult to accurately carry over all of the supernatant due to absorption by the dried fecal material.
Genomic and plasmid DNA preparation.
American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) bacterial strains were used to prepare qPCR standard curves for E. coli (ATCC 25922), enterococci (Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212), and GenBac (Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron ATCC 29741). Plasmid DNA standards were synthesized for CowM3 and Rum-2-bac assays by amplifying a segment of the hydrolase domain (HD) superfamily and 16S rRNA loci, respectively, using PCR (Table 1). The amplification product was ligated into a pCR 2.1-TOPO plasmid vector and transformed into One Shot Top10 chemically competent E. coli, using a Topo TA kit (Life Technologies, Grand Island, NY). Recombinant bacteria were enumerated on ImMedia ampicillin and kanamycin agar (Life Technologies), and colonies were selected randomly for overnight culture propagation in ImMedia broths (Life Technologies). Plasmids were extracted using a PureLink Quick plasmid miniprep kit (Life Technologies) and then linearized with BamHI-HF enzyme (New England BioLabs, Ipswich, MA). Linearized plasmid DNA was purified using a QIAquick PCR purification kit (Qiagen Inc., Valencia, CA) and quantified with a NanoDrop ND-1000 UV/Vis spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies).
TABLE 1.
Primers and probes used for qPCR assays
| Assay name | Primer or probe | Primer or probe sequence (5′–3′)a | Target organism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon | Forward primer | GGTTTCCGCAGCTGGG | Salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) testes | 56 |
| Reverse primer | CCGAGCCGTCCTGGTCTA | |||
| Probe | FAM-AGTCGCAGGCGGCCACCGT-TAMRA | |||
| Entero1 | Forward primer | AGAAATTCCAAACGAACTTG | Enterococcus | 57 |
| Reverse primer | CAGTGCTCTACCTCCATCATT | |||
| Probe | FAM-TGGTTCTCTCCGAAATAGCTTTAGGGCTA-TAMRA | |||
| EPA-EC 23S | Forward primer | GGTAGAGCACTGTTTTGGCA | E. coli | 58 |
| Reverse primer | TGTCTCCCGTGATAACTTTCTC | |||
| Probe | FAM-TCATCCCGACTTACCAACCCG-TAMRA | |||
| Genbac | Forward primer | GGGGTTCTGAGAGGAAGGT | Bacteroidales | 28 |
| Reverse primer | CCGTCATCCTTCACGCTACT | |||
| Probe | VIC-CAATATTCCTCACTGCTGCCTCCCGTA-Iowa Black | |||
| CowM3 | Forward primer | CCTCTAATGGAAAATGGATGGTATCT | Cattle-associated microbial population | 29 |
| Reverse primer | CCATACTTCGCCTGCTAATACCTT | |||
| Probe | FAM-TTATGCATTGAGCATCGAGGCC-TAMRA | |||
| Rum-2-bac | Forward primer | ACAGCCCGCGATTGATACTGGTAA | Ruminant-associated microbial population | 30 |
| Reverse primer | CAATCGGAGTTCTTCGTGAT | |||
| Probe | FAM-ATGAGGTGGATGGAATTCGTGGTGT- TAMRA |
FAM, 6-carboxyfluorescein; TAMRA, 6-carboxytetramethylrhodamine.
qPCR assays and quantification.
Primers and probes used in this study are shown in Table 1. Primers and probes were synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies (Coralville, IA) and rehydrated to concentrations of 500 μM and 100 μM, respectively, in nuclease-free water. qPCR assays were performed with a model 7500 HT Fast real-time sequence detector (Applied Biosystems). Reaction mixtures (20 μl) for all assays contained 1× TaqMan Fast universal PCR master mix with No AmpErase uracil-N-glycosylase (Life Technologies), 0.02 mg/ml bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Life Technologies), 1 μM (each) primers, 80 nM 6-carboxyfluorescein (FAM)- or VIC-labeled TaqMan probe, and 4 μl of either genomic DNA (fecal samples), 40 to 1 × 107 target sequence copies (CowM3 and Rum-2-Bac), or 5 to 4 × 104 target gene copies (E. coli, enterococci, and GenBac). All reactions were duplicated in MicroAmp Fast 96-well reaction plates covered with MicroAmp optical adhesive film (Life Technologies). Thermal conditions for all assays except CowM3 assays were 95°C for 20 s (initial denaturation), followed by 40 cycles of short denaturation at 95°C for 3 s and a combined annealing and primer extension phase at 60°C for 30 s. The initial and short denaturation durations for the CowM3 assay were 2 min and 5 s, respectively. Data were analyzed with Sequence Detector Software (SDS), set to start and end cycles of 3 and 15, respectively, and a threshold determination of 0.2 for the salmon and Entero1 assays; otherwise, the automatic baseline and threshold were used. Threshold cycle (CT) values were exported to Microsoft Excel for further statistical analysis. To prevent cross-contamination, dedicated equipment and separate laboratories were used for every step from DNA extraction to qPCR amplification. In addition, a minimum of two no-template controls and two DNA standards were included for each assay performed in a 96-well qPCR plate.
Inhibition.
To monitor qPCR inhibition from the fecal matrix, salmon DNA (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) was used as an exogenous internal positive control (IPC). Four microliters of DNA extracted from each sample was added to a qPCR mix consisting of salmon primers and probe, BSA, and 0.05 ng/μl salmon DNA. Extracted DNA from a pure culture of Enterococcus faecalis was included as a positive control for every 96-well qPCR. Mean uninhibited salmon CT values were obtained by adding salmon DNA to duplicate control samples containing extracted DNA from pure Enterococcus faecalis cultures. Reactions were deemed inhibited if the salmon CT value was 1 unit higher than the average salmon CT observed for the positive controls. All samples from cow pats collected at the commercial farms showed inhibition, so DNAs were diluted 5, 10, and 25 times with autoclaved Nanopure water and rechecked for inhibition. Twenty-five-fold dilution resulted in CT values close to the detection limits of our assays, so the 10-fold dilution was selected.
Statistical analysis.
Concentrations of FIB and MST markers were transformed by taking the natural logarithm (log). Decay rates and effects of environmental factors (e.g., UV-B) were estimated by appropriately parameterized linear models. To explore the effects of environmental factors, temperature and UV-B data were analyzed by temporal synchronization analysis (TSA) (31), where the sum or average of the independent variables is examined over a temporal window rather than relying on instantaneous values taken at the time of sampling. Cumulative UV-B data 5 days before sampling and temperature data a day prior to sampling were determined to be significant temporal windows that improved the model's ability to fit the data set. The general form of the linear model for the concentration of a given FIB or MST marker is as follows:
| (1) |
where Ci,t is the concentration in cow pat i at time t, βi,0 is the initial log concentration, β1 is the overall decay rate (i.e., effect due to time t), β2 is the difference in decay rate due to the environmental variable xi,t (i.e., the effect due to the interaction between xi,t and time t), and εi,t is a normally distributed error term with mean zero and variance σ2. We assume that errors are independent of each other. This general statistical model follows the decay model framework described by McCullough and Nelder (32).
This model has several notable features. Because multiple cow pats were used during the experiment, we included a separate βi,0 for each, allowing different initial concentrations; each FIB or MST marker was given a single decay rate (β1) and interaction parameter (β2), however. The parameter β2 represents the differential decay rate induced by the environmental factor xi,t. Statistical significance of the parameter β2 provides evidence that changes in the environmental factor xi,t induce changes in microbial decay. Thus, our hypothesis tests of environmental factors were conducted by testing for significance of the appropriate interaction term. The logarithmic transformation of the concentrations Ci,t and corresponding linear model also follow the assumption of exponential decay of the microorganisms.
For FIB experiencing an initial regrowth phase, a piecewise linear regression was used. The general form of the piecewise regression, where we assumed regrowth up until a time (t) of 5 days, was as follows:
| (2) |
| (3) |
In this case, β1 represents the initial exponential growth rate of microorganism i, which occurs through time 5 (with time being in days), and β2 represents the exponential decay experienced after time 5. To detect environmental effects for microbes experiencing regrowth, we appropriately combined the model in equation 1 with the model in equations 2 and 3.
Finally, a pairwise correlation was performed to access the relationship among FIB and MST markers, using STaTa-12 (StataCorp LP, College Station, TX). All other statistical analyses were performed with the publicly available R software (33). For each test, the acceptable level of significance (α) was 0.05.
RESULTS
There were no significant differences in decay rates of FIB and MST markers among collection sites (P > 0.05), so comparisons of results are not shown. After comparing treatments (shading versus no shading), results showed that treatment affected only the decay rates of E. coli populations, that is, E. coli had separate decay rates for shaded and unshaded samples (Table 2). Decay rates for all others were determined using combined shaded and unshaded data. FIB and MST markers were monitored for 49 and 57 days, respectively.
TABLE 2.
Growth and decay rates of FIB and MST markers in cow pats (n = 18)a
| Organism or genetic marker | Treatment | Growth rate (β1) | Decay rate (β2) | T90 (days)b | T99 (days)b | Model r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia coli | Unshaded | 0.881* | −0.297* | 7.75 | 15.51 | 0.82d |
| Shaded | 0.0544 | −0.176 | 13.08 | 26.16 | 0.82d | |
| EPA-EC23S | ND | −0.0621 | 37.08 | 74.15 | 0.80 | |
| Enterococcusc | NA | −0.163 | 14.13 | 28.25 | 0.76 | |
| Entero1c | NA | −0.0434 | 53.06 | 106.12 | 0.61 | |
| CowM3c | NA | −0.126 | 18.27 | 36.54 | 0.69 | |
| Rum-2-bacc | NA | −0.111 | 20.74 | 41.48 | 0.74 | |
| GenBacc | NA | −0.128 | 17.99 | 35.97 | 0.74 |
Log concentrations were modeled within the general linear model framework. Asterisks indicate statistical significance between the shaded and unshaded treatments (P < 0.05). ND, not determined; NA, not available.
Derived from decay rate (β2).
Since shading had no effect on decay rates, decay rates are not presented as a function of treatment.
The model includes shaded and unshaded treatments, since it was a significant term.
FIB.
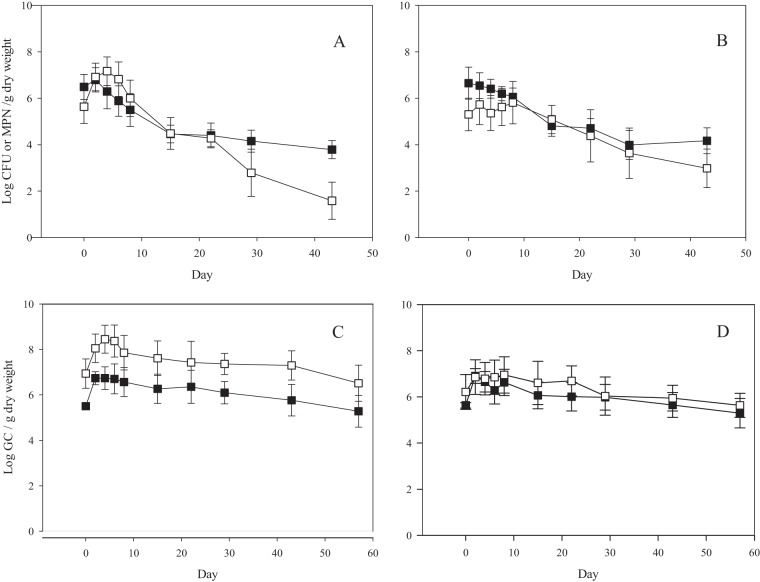
The initial average concentrations (arithmetic means) of culturable enterococci and genome copies (Entero1) were 1.74 × 107 CFU g−1 dry weight (coefficient of variation [CV] = 1.40) and 4.25 × 105 gene copies (GC) g−1 dry weight (CV = 0.56), respectively. A slight increase in culturable enterococcus concentrations was observed during the first 2 days after deposition in 33% of shaded and 66% of unshaded samples. Likewise, enterococcal genomic concentrations also showed an increase of 1.25 log for the first 2 days after deposition, followed by a slow decline until day 57. The slight increase in enterococcus concentration was not significantly different from the starting concentration (Fig. 1). Since regrowth was not significant, a first-order decay model was used. There were no statistically significant differences between the decay rate coefficients of shaded and unshaded treatments for culturable and genomic enterococci.
FIG 1.
Decay curves for FIB as a function of treatment (n = 18). Levels of culturable E. coli (□) and enterococci (■) in unshaded (A) and shaded (B) plots and of their corresponding qPCR markers in unshaded (C) and shaded (D) plots are shown. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
Culturable E. coli and its genomic marker (EPA-EC23S) had average initial concentrations of 2.20 × 106 most probable number (MPN) g−1dry weight (CV = 2.0) and 3.80 × 107 GC g−1 dry weight (CV = 2.2), respectively. The culturable E. coli concentration increased significantly from days 0 to 5 in unshaded cow pats (P < 0.05), but no significant increase was observed in shaded cow pats (P > 0.05) (Fig. 1 and Table 2). The genomic concentration of E. coli also increased for unshaded samples during the first 5 days, by 1.51 log, and for shaded samples during the first 2 days, by 1.11 log (Fig. 1).
MST markers.
The MST markers exhibited fairly consistent concentrations between replicate cow pats for each sampling point, with narrow confidence intervals (Fig. 2). CowM3 had an average initial concentration of 1.69 × 109 target sequence copies (TSC) g−1 dry weight (CV = 1.1), Rum-2-bac had an initial concentration of 3.36 × 1010 TSC g−1 dry weight (CV = 0.46), and GenBac had an initial concentration of 5.70 × 1010 TSC g−1 dry weight (CV = 0.42). There was no significant difference in decay rates between treatments for each marker or between markers (P > 0.05) (Table 2).
FIG 2.
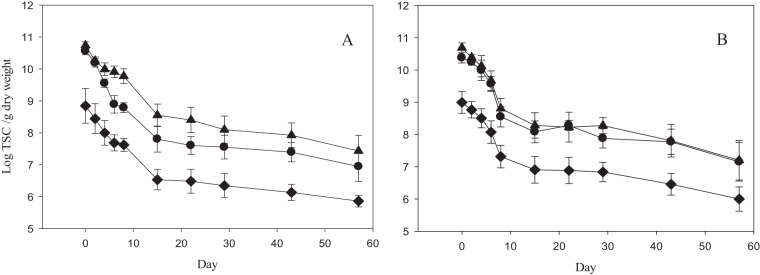
Decay curves for MST markers as a function of treatment (n = 18). Levels of CowM3 (◆), Rum-2-Bac (●), and GenBac (▲) in unshaded (A) and shaded (B) plots are shown. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals.
Correlation among FIB and MST markers.
A pairwise correlation analysis was performed to determine how significantly concentrations of FIB and MST markers correlated. Culturable E. coli and enterococci had a strong correlation coefficient of 0.68 (P < 0.001) relative to each other but slightly lower correlation coefficients (0.49 to 0.57) with their corresponding genomic markers (Table 3). In addition, culturable enterococci had higher correlation coefficients with each MST marker than did E. coli. The correlation coefficients among MST markers were >0.9 (Table 3); FIB genomic concentrations had only moderate correlations with MST markers (0.37 to 0.44).
TABLE 3.
r2 values based on pairwise correlations among FIB and MST markersa
| Organism or genetic marker |
r2 value |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterococcus | E. coli | Entero1 | CowM3 | Rum-2-bac | GenBac | EPA-EC23S | |
| Enterococcus | 1.0000 | ||||||
| E. coli | 0.6858 | 1.0000 | |||||
| Entero1 | 0.4944 | 0.4307 | 1.0000 | ||||
| CowM3 | 0.7859 | 0.6085 | 0.4297 | 1.0000 | |||
| Rum-2-bac | 0.7402 | 0.5453 | 0.395 | 0.9129 | 1.0000 | ||
| GenBac | 0.8156 | 0.5602 | 0.452 | 0.9032 | 0.9387 | 1.0000 | |
| EPA-EC23S | 0.3410 | 0.5661 | 0.6337 | 0.4429 | 0.3684 | 0.339 | 1.0000 |
P values are <0.001.
Environmental parameter effects on FIB and MST marker decay rates.
The average cow pat temperature 1 day prior to sampling was 31.4 ± 3.0°C for the unshaded treatment and 26.1 ± 1.8°C for the shaded one. Decay rate coefficients increased as temperature increased for CowM3 (P < 0.001) and Rum-2-bac (P < 0.05) (Table 4); temperature had no significant effect on E. coli and enterococci or their genomes. UV-B (305.9 nm) was below the detectable range for the shaded plot, and the cumulative 5-day average UV-B for the unshaded plot, measured prior to sampling, was 1.73 ± 0.41 μW cm−2. UV-B had a positive correlation only with the decay rate of culturable E. coli (P < 0.001) (Table 4), i.e., as UV-B increased, the E. coli concentration decreased. The percentages of moisture content of all fecal samples averaged 89% ± 1.2% on day 0 and decreased to 14% ± 3.0% and 19% ± 2.7% by day 57 for unshaded and shaded samples, respectively. The culturable E. coli population decayed faster, with a decrease in moisture content (P < 0.001), but the host-specific MST markers (CowM3 and Rum-2-bac) had a slower decay (P < 0.05) as moisture content decreased (Table 4). Moisture content had no effect on the enterococcal decay rate.
TABLE 4.
Regression coefficients for statistically significant environmental parameters
| Parameter | Organism or genetic marker | Regression coefficient | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | Escherichia coli | 0.0015 | 0.001 |
| Enterococcus | >0.05 | ||
| CowM3 | −0.0017 | 0.003 | |
| Rum-2-bac | −0.0014 | 0.005 | |
| GenBac | >0.05 | ||
| Temperature | Escherichia coli | >0.05 | |
| Enterococcus | >0.05 | ||
| CowM3 | −0.0027 | 0.001 | |
| Rum-2-bac | −0.0021 | 0.02 | |
| GenBac | −0.0012 | 0.04 | |
| UV-B | Escherichia coli | −0.075 | 0.001 |
| Enterococcus | >0.05 | ||
| CowM3 | >0.05 | ||
| Rum-2-bac | >0.05 | ||
| GenBac | >0.05 |
DISCUSSION
The aim of this study was to determine the persistence of FIB and bovine-associated MST markers in undisturbed cow pats. We characterized the decay rates of various FIB and molecular markers under a representative agricultural scenario where feces are surface deposited as cow pats and not incorporated into the soil. Our results show that E. coli concentrations were significantly higher (P < 0.05) than concentrations observed at 0 days in the unshaded treatments for the first 5 days after deposition. Regrowth of E. coli for up to 7 days has been well documented in the literature (14, 34–36). Meays et al. (37) observed E. coli increases on days 1 and 7 under 40% and 0% shading, respectively, which suggests that E. coli can replicate in the environment. Sinton et al. (12) reported that growth was determined primarily by manure water content and secondarily by temperature, while Muirhead and Littlejohn (34) concluded that temperature was the responsible factor. On day 5 of our study, we had only limited data and could not make statistical inferences from the effects of temperature, moisture, and UV on the growth rate of E. coli. It is possible that the observed growth of E. coli was affected by complex interactions of many variables, including photoreactivation, which was not determined herein (38, 39). Furthermore, microbes in freshly excreted feces are in the logarithmic growth phase, which may partly explain the frequently observed growth of fecal E. coli in fresh cow pats (12, 34, 35). In contrast to E. coli, enterococci did not exhibit the same regrowth dynamics during the first weeks of our study. This behavior is not unusual for enterococci. Using composited cow pats, Soupir et al. (35) observed no regrowth of enterococci during a summer sampling, the same period as in our study. In contrast, Sinton et al. (12) observed an increase in enterococcus concentration between the first and second sampling times during the summer season, but they did not find any statistical significance.
Exposure to sunlight significantly decreased survival of E. coli but not enterococci. After initial regrowth, E. coli populations decayed faster than enterococci in unshaded cow pats. Similar results were reported by Meays et al. (37), who indicated that shading was the only significant factor enhancing survival of E. coli from day 17 to day 45. In contrast, Van Kessel et al. (36) reported minimal differences in die-off rates between shaded and unshaded treatments; however, their shaded cow pats were placed under a tree, which would not have shielded them completely from sun or rain, resulting in a statistically insignificant die-off difference between both treatments. The most significant effect of shading, which is considered important to enhancing survival of FIB in cow pats, can be attributed to protection from UV (12, 15, 37). Furthermore, UV-B has been reported to have a more lethal effect on bacterial DNA inactivation than that of UV-A (15, 16, 40–45). In our study, a higher decay rate of the E. coli population was significantly associated with higher UV-B irradiance, but UV-B had no effect on enterococcal decay. Previous research suggested that enterococci may require a higher dose (i.e., intensity × residence time) of UV-B to achieve inactivation similar to that of E. coli (46). For instance, at a UV-B maximum of 21.3 μW cm−2, the time required for 99% decay or 2-log reduction (T99) values for pure cultures of E. coli and E. faecalis in sterile water were 45 min and 100 min, respectively (46). In other words, Enterococcus required an approximately 2.2-fold increase in the UV-B dose to attain E. coli's die-off rate. In our study, we calculated that a 1.8-fold increase in UV-B dose would be required for enterococci to exhibit a die-off rate similar to that of E. coli (Table 2). In considering the germicidal effect of UV light, previous studies reported that enterococci required an ∼1.5 times higher dose of UV-C for the same level of inactivation (99.9%) as that achieved in E. coli (39, 47). Furthermore, the authors of a review of UV disinfection of viruses, bacteria, and protozoa (48) calculated the microbial inactivation credit (MIC) for 1-, 2-, 3-, or 4-log inactivation for environmental E. coli and Streptococcus faecalis. For a 4-log inactivation, E. coli requires 18 mJ/cm2 and S. faecalis demands 30 mJ/cm2, a 1.6-fold increase in UV dose. The different responses to UV may be attributed to cell wall structures. A thick, uniform peptidoglycan layer forms 90% of the cell wall of enterococci, while E. coli has a multilayered cell wall structure with a relatively thin inner peptidoglycan layer (only 10% of the cell wall) and an outer membrane of lipopolysaccharide and proteins. It has been observed that the peptidoglycan layer is the most resistant membrane wall component (49, 50) for protection against UV-induced damage. Based on our study results, we conclude that the major factor responsible for the decay of E. coli populations is UV-B, with an estimated decay of 0.075 log per day for every unit increase in UV-B (Table 4).
Moisture content (MC) had a minimal but significant effect on persistence of E. coli, with a coefficient of 0.0015 (Table 4). Reported results on the effect of moisture content on E. coli survival have been mixed. Some reports indicate that MC has a positive correlation with FIB concentration (12, 24–27); however, Wang et al. (14) reported a higher overall reduction in E. coli levels at 83% MC at 27°C, but no effect at 55% and 30% MC. Meays et al. (37) showed that the MC of fecal pats at sampling time was not correlated with the concentration of E. coli.
Another factor we addressed is the potential effect of temperature on persistence of host-specific and general Bacteroides sp. markers in cow pats. The influence of temperature on Bacteroidales inactivation has been reported elsewhere (18, 20–22), but no study has reported the coefficient associated with a decreased concentration. Our results indicate that for every unit increase in temperature, there was an ∼0.002-log decrease per day in the bovine-associated MST markers (CowM3 and Rum-2-bac) and a 0.0012-log decrease per day in the GenBac concentration (Table 4). This fractional decrease in marker concentration due to temperature is negligible compared to the overall decay rate, suggesting that temperature is not the dominant factor affecting the persistence of these markers in undisturbed cow pats.
FIB genomic markers exhibited lower decay rates than their culturable forms. One explanation is the ability of qPCR to detect DNAs from cells undergoing various metabolic stages, such as cultivable cells, viable but not culturable cells (VBNC), nonviable intact cells, and extracellular-free DNA (11). This was evident in our results for both EPA-EC23S and Entero1, which had a final concentration on day 57 that was not much different from the starting concentration.
Conversely, MST markers (CowM3, Rum-2-bac, and GenBac) persisted in cow pats, with similar decay rates: they did not grow in the environment, and shading had no effect. The effects of shading on bovine-associated MST markers have been reported in water microcosm studies (17, 18). Two ruminant-specific markers (CF 193 and BacR) were monitored in freshwater microcosms spiked with fresh cow feces and incubated under light and dark conditions. The authors reported no effect of light on decay rates of these markers. In another study (16), however, exposure to light resulted in faster decay of a cow-specific marker (BacCow-UCD), suggesting that under certain conditions (e.g., presence of oxygen), light could speed decay of these markers in the environment.
Our results indicate that quantification of MST markers was possible up to day 57, suggesting that these markers can persist in undisturbed cow pats long after deposition. To our knowledge, this is the first study to report decay constants of MST markers in this type of environmental matrix. Long persistence in dry cow pats (MC was down to about 15% by the end of our study) has implications for the impact of dry fecal material as a source of contamination to surface waters. These results suggest that pasturelands containing large amounts of dry cow pats may contribute high concentrations of both FIB and MST markers for extended periods after deposition during runoff-producing rain events. Therefore, in assessing contamination of surface waters in agricultural watersheds, pastures need to be taken into consideration as sources of contamination even when cattle are not actively grazing at the site. The persistence of bovine-associated MST markers in water microcosms or manure-amended soils (15–18, 51, 52) was lower than that reported here, suggesting that when fecal material reaches aquatic environments or is incorporated into the soil, MST markers do not persist as long as in intact cow pats. The shorter survival times (2 to 15 days) reported in these studies can be attributed to various physical and biological factors, including dissolved oxygen and predation, which have been implicated in shortening the persistence of strictly anaerobic Bacteroidales spp. (16, 19–22, 53–55). Balleste and Blanch (22) suggested that environmental Bacteroides strains may be more sensitive to dissolved oxygen than pure cultures of Bacteroidales spp. By sampling individual, undisturbed surface-deposited cow pats without prior mixing, our experimental design preserved a more intact atmospheric condition, which may have helped to protect environmental Bacteroidales cells against the toxic effect of oxygen and offered a more accurate estimation of their survival in agricultural settings. It is noteworthy that anoxic conditions may also enhance survival of enterococci in cow pats: for instance, Marti et al. (54) reported T90 values of ∼24 for E. coli and >43 days for enterococci under microaerophilic conditions at 20°C. Moreover, the persistence of enterococci was comparable to that of a universal Bacteroidales marker (AllBac) and two pig-specific Bacteroidales markers (Pig-1-bac and Pig-2-Bac) reported in the same study under the same conditions as the FIB, with T90s of >43 days. Because the decay of Bacteroidales markers could not be explained by any of the physical parameters tested herein, we suggest that more studies on the effect of UV-B on Bacteroidales markers in fecal matrices are warranted. Comparing MST markers and FIB decay behaviors revealed that MST markers seemed to persist at a rate similar to that of enterococci rather than that of E. coli populations. While the decay rate of E. coli populations was decreased by sunlight exposure, neither the MST markers nor enterococcal populations exhibited significant effects on their decay rates when exposed to sunlight. These results suggest that it is necessary to pay close attention to the type of indicator used to assess impairment of water resources in relation to the MST markers used to identify the potential sources of contamination. For instance, the difference in decay rates suggests that while a water body might not show impairment due to E. coli, bovine MST markers might still be present, indicating an impact by cattle, especially if dry fecal material is present in the area affecting the stream. The close relationship between enterococci and bovine MST markers could make them reliable markers to be used simultaneously to assess the water quality of surface waters in this type of scenario.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We are grateful to Rosalie Hendon for help with fecal sample analysis. We thank the Kennedy family at Covenant Valley Farm and the Nixon family at Cane Creek Farm, Inc., for allowing us access to their cattle.
Any opinions expressed in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official positions and policies of the U.S. EPA, and any mention of products or trade names does not constitute recommendation for use.
A.O., R.B., and B.S. are student services contractors for the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, National Exposure Research Laboratory. K.B. is an Oak Ridge Institute for Science and Education Postdoctoral Research Scientist at the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Office of Research and Development, National Exposure Research Laboratory.
Footnotes
Published ahead of print 18 October 2013
REFERENCES
- 1.USEPA 2009. National water quality inventory: report to Congress, 2004 reporting cycle. EPA/841/R-08/001 USEPA, Washington, DC [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cabelli VJ, Dufour AP, McCabe LJ. 1982. Swimming associated gastrointestinal illness and water quality. Am. J. Epidemiol. 115:606–616 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dufour AP. 1984. Health effects criteria for fresh recreational waters. EPA-600/601-684-004 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dufour AP, Ballantine P. 1986. Bacteriological ambient water quality criteria for marine and freshwater recreational waters. EPA 440/445-484-002 U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC [Google Scholar]
- 5.Savichtcheva O, Okabe S. 2006. Alternative indicators of fecal pollution: relations with pathogens and conventional indicators, current methodologies for direct pathogen monitoring and future application perspectives. Water Res. 40:2463–2476. 10.1016/j.watres.2006.04.040 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bernhard AE, Field KG. 2000. A PCR assay to discriminate human and ruminant feces on the basis of host differences in Bacteroides-Prevotella genes encoding 16S rRNA. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66:4571–4574. 10.1128/AEM.66.10.4571-4574.2000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bernhard AE, Goyard T, Simonich MT, Field KG. 2003. Application of a rapid method for identifying fecal pollution sources in a multi-use estuary. Water Res. 37:909–913. 10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00384-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Boehm AB, Fuhrman JA, Mrse RD, Grant SB. 2003. Tiered approach for identification of a human fecal pollution source at a recreational beach: case study at Avalon Bay, Catalina Island, California. Environ. Sci. Technol. 37:673–680. 10.1021/es025934x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dick LK, Bernhard AE, Brodeur TJ, Santo Domingo JW, Simpson JM, Walters SP, Field KG. 2005. Host distributions of uncultivated fecal Bacteroidales bacteria reveal genetic markers for fecal source identification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71:3184–3191. 10.1128/AEM.71.6.3184-3191.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jeanneau L, Solecki O, Wery N, Jarde E, Gourmelon M, Communal PY, Jadas-Hecart A, Caprais MP, Gruau G, Pourcher AM. 2012. Relative decay of fecal indicator bacteria and human-associated markers: a microcosm study simulating wastewater input into seawater and freshwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46:2375–2382. 10.1021/es203019y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rogers SW, Donnelly M, Peed L, Kelty CA, Mondal S, Zhong Z, Shanks OC. 2011. Decay of bacterial pathogens, fecal indicators, and real-time quantitative PCR genetic markers in manure-amended soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77:4839–4848. 10.1128/AEM.02427-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sinton LW, Braithwaite RR, Hall CH, Mackenzie ML. 2007. Survival of indicator and pathogenic bacteria in bovine feces on pasture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73:7917–7925. 10.1128/AEM.01620-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ellis JR, McCalla TR. 1978. Fate of pathogens in soils receiving animal wastes—a review. Trans. ASAE 21:309–313. 10.13031/2013.35294 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang LL, Mankin KR, Marchin GL. 2004. Survival of fecal bacteria in dairy cow manure. Trans. ASAE 47:1239–1246. 10.13031/2013.16574 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Green HC, Shanks OC, Sivaganesan M, Haugland RA, Field KG. 2011. Differential decay of human faecal Bacteroides in marine and freshwater. Environ. Microbiol. 13:3235–3249. 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02549.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bae S, Wuertz S. 2009. Rapid decay of host-specific fecal Bacteroidales cells in seawater as measured by quantitative PCR with propidium monoazide. Water Res. 43:4850–4859. 10.1016/j.watres.2009.06.053 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Walters SP, Field KG. 2009. Survival and persistence of human and ruminant-specific faecal Bacteroidales in freshwater microcosms. Environ. Microbiol. 11:1410–1421. 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01868.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sokolova E, Astrom J, Pettersson TJ, Bergstedt O, Hermansson M. 2012. Decay of Bacteroidales genetic markers in relation to traditional fecal indicators for water quality modeling of drinking water sources. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46:892–900. 10.1021/es2024498 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kreader CA. 1998. Persistence of PCR-detectable Bacteroides distasonis from human feces in river water. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64:4103–4105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Okabe S, Shimazu Y. 2007. Persistence of host-specific Bacteroides-Prevotella 16S rRNA genetic markers in environmental waters: effects of temperature and salinity. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 76:935–944. 10.1007/s00253-007-1048-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bell A, Layton AC, McKay L, Williams D, Gentry R, Sayler GS. 2009. Factors influencing the persistence of fecal Bacteroides in stream water. J. Environ. Qual. 38:1224–1232. 10.2134/jeq2008.0258 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Balleste E, Blanch AR. 2010. Persistence of Bacteroides species population in a river as measured by molecular and culture techniques. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76:7608–7616. 10.1128/AEM.00883-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Schulz CJ, Childers GW. 2011. Fecal Bacteroidales diversity and decay in response to variations in temperature and salinity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77:2563–2572. 10.1128/AEM.01473-10 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sjogren RE. 1994. Prolonged survival of an environmental Escherichia coli in laboratory soil microcosms. Water Air Soil Pollut. 75:389–403. 10.1007/BF00482948 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang G, Zhao T, Doyle MP. 1996. Fate of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 in bovine feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62:2567–2570 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Himathongkham S, Bahari S, Riemann H, Cliver D. 1999. Survival of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella typhimurium in cow manure and cow manure slurry. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 178:251–257. 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1999.tb08684.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Unc AA, Goss MJ. 2003. Impact of manure properties on the survival of manure Escherichia coli in soils, p 331–346 In Kelly H, Bryden J. (ed), Proceedings of 2nd Canadian Organic Residuals Recycling Conference, April 24-25, 2003. Penticton, British Columbia, Canada [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dick LK, Field KG. 2004. Rapid estimation of numbers of fecal Bacteroidetes by use of a quantitative PCR assay for 16S rRNA genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70:5695–5697. 10.1128/AEM.70.9.5695-5697.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shanks OC, Atikovic E, Blackwood AD, Lu J, Noble RT, Domingo JS, Seifring S, Sivaganesan M, Haugland RA. 2008. Quantitative PCR for detection and enumeration of genetic markers of bovine fecal pollution. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74:745–752. 10.1128/AEM.01843-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Mieszkin S, Yala JF, Joubrel R, Gourmelon M. 2010. Phylogenetic analysis of Bacteroidales 16S rRNA gene sequences from human and animal effluents and assessment of ruminant faecal pollution by real-time PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 108:974–984. 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04499.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cyterski M, Zhang S, White E, Molina M, Wolfe K, Parmar R, Zepp R. 2012. Temporal synchronization analysis for improving regression modeling of fecal indicator bacteria levels. Water Air Soil Pollut. 223:4841–4851. 10.1007/s11270-012-1240-3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.McCullough P, Nelder JA. 1989. Generalized linear models. Chapman and Hall, London, United Kingdom [Google Scholar]
- 33.R Development Core Team 2012. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria [Google Scholar]
- 34.Muirhead RW, Littlejohn RP. 2009. Die-off of Escherichia coli in intact and disrupted cowpats. Soil Use Manage. 25:389–394. 10.1111/j.1475-2743.2009.00239.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Soupir ML, Mostaghimi S, Lou J. 2008. Die-off of E. coli and enterococci in dairy cowpats. Trans. ASABE 51:1987–1996. 10.13031/2013.25403 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Van Kessel JS, Pachepsky YA, Shelton DR, Karns JS. 2007. Survival of Escherichia coli in cowpats in pasture and in laboratory conditions. J. Appl. Microbiol. 103:1122–1127. 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03347.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Meays CL, Broersma K, Nordin R, Mazumder A. 2005. Survival of Escherichia coli in beef cattle fecal pats under different levels of solar exposure. Rangeland Ecol. Manage. 58:279–283. 10.2111/1551-5028(2005)58[279:SOECIB]2.0.CO;2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Crane SR, Moore JA. 1986. Modeling enteric bacterial die-off: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 27:411–439. 10.1007/BF00649422 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Harris GD, Adams VD, Sorensen DL, Curtis MMSC. 1987. Ultraviolet inactivation of selected bacteria and viruses with photoreactivation of the bacteria. Water Res. 21:687. 10.1016/0043-1354(87)90080-7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Muela A, Garcia-Bringas JM, Seco C, Arana I, Barcina I. 2002. Participation of oxygen and role of exogenous and endogenous sensitizers in the photoinactivation of Escherichia coli by photosynthetically active radiation, UV-A and UV-B. Microb. Ecol. 44:354–364. 10.1007/s00248-002-1027-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bolton NF, Cromar NJ, Hallsworth P, Fallowfield HJ. 2010. A review of the factors affecting sunlight inactivation of micro-organisms in waste stabilisation ponds: preliminary results for enterococci. Water Sci. Technol. 61:885–890. 10.2166/wst.2010.958 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sassoubre LM, Nelson KL, Boehm AB. 2012. Mechanisms for photoinactivation of Enterococcus faecalis in seawater. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 78:7776–7785. 10.1128/AEM.02375-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Oscar JO. 2012. Contribution of UVB radiation to bacterial inactivation by natural sunlight. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 115:58–62. 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2012.06.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Muela A, García-Bringas JM, Arana I, Barcina I. 2000. The effect of simulated solar radiation on Escherichia coli: the relative roles of UV-B, UV-A, and photosynthetically active radiation. Microb. Ecol. 39:65–71. 10.1007/s002489900181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Fisher MB, Iriarte M, Nelson KL. 2012. Solar water disinfection (SODIS) of Escherichia coli, Enterococcus spp., and MS2 coliphage: effects of additives and alternative container materials. Water Res. 46:1745–1754. 10.1016/j.watres.2011.12.048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Deller S, Mascher F, Platzer S, Reinthaler FF, Marth E. 2006. Effect of solar radiation on survival of indicator bacteria in bathing waters. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 14:133–137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chang JCH, Ossoff SF, Lobe DC, Dorfman MH, Dumais CM, Quails RG, Johnson JD. 1985. UV inactivation of pathogenic and indicator microorganisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49:1361–1365 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hijnen WAM, Beerendonk EF, Medema GJ. 2006. Inactivation credit of UV radiation for viruses, bacteria and protozoan (oo)cysts in water: a review. Water Res. 40:3–22. 10.1016/j.watres.2005.10.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Arima H, Ibrahim HR, Kinoshita T, Kato A. 1997. Bactericidal action of lysozymes attached with various sizes of hydrophobic peptides to the C-terminal using genetic modification. FEBS Lett. 415:114–118. 10.1016/S0014-5793(97)01071-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Liu P, Duan W, Wang Q, Li X. 2010. The damage of outer membrane of Escherichia coli in the presence of TiO2 combined with UV light. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 78:171–176. 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.02.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tambalo DD, Fremaux B, Boa T, Yost CK. 2012. Persistence of host-associated Bacteroidales gene markers and their quantitative detection in an urban and agricultural mixed prairie watershed. Water Res. 46:2891–2904. 10.1016/j.watres.2012.02.048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Liang Z, He Z, Zhou X, Powell CA, Yang Y, Roberts MG, Stoffella PJ. 2012. High diversity and differential persistence of fecal Bacteroidales population spiked into freshwater microcosm. Water Res. 46:247–257. 10.1016/j.watres.2011.11.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Wang D, Silkie SS, Nelson KL, Wuertz S. 2010. Estimating true human and animal host source contribution in quantitative microbial source tracking using the Monte Carlo method. Water Res. 44:4760–4775. 10.1016/j.watres.2010.07.076 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Marti R, Mieszkin S, Solecki O, Pourcher AM, Hervio-Heath D, Gourmelon M. 2011. Effect of oxygen and temperature on the dynamic of the dominant bacterial population of pig manure and on the persistence of pig-associated genetic markers, assessed in river water microcosms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 111:1159–1175. 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05131.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Solecki O, Jeanneau L, Jardé E, Gourmelon M, Marin C, Pourcher AM. 2011. Persistence of microbial and chemical pig manure markers as compared to faecal indicator bacteria survival in freshwater and seawater microcosms. Water Res. 45:4623–4633. 10.1016/j.watres.2011.06.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Haugland RA, Siefring SC, Wymer LJ, Brenner KP, Dufour AP. 2005. Comparison of Enterococcus measurements in freshwater at two recreational beaches by quantitative polymerase chain reaction and membrane filter culture analysis. Water Res. 39:559–568. 10.1016/j.watres.2004.11.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ludwig W, Schleifer KH. 2000. How quantitative is quantitative PCR with respect to cell counts? Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 23:556–562. 10.1016/S0723-2020(00)80030-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chern EC, Siefring S, Paar J, Doolittle M, Haugland RA. 2011. Comparison of quantitative PCR assays for Escherichia coli targeting ribosomal RNA and single copy genes. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 52:298–306. 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2010.03001.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]